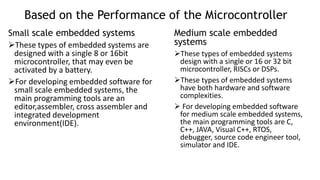
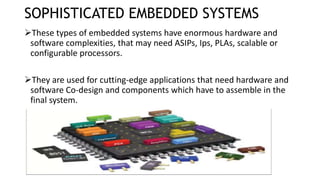
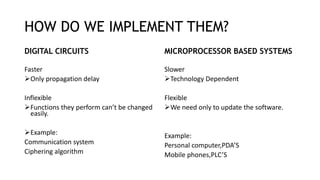
An embedded system is a combination of hardware and software specifically designed for a particular function, often found in devices like smartphones and medical equipment. They can be classified based on performance, such as real-time, standalone, networked, and mobile systems, and vary in complexity from small to sophisticated systems. Despite their advantages like efficiency and reliability, embedded systems face challenges such as scalability issues and difficulties in changing configurations.