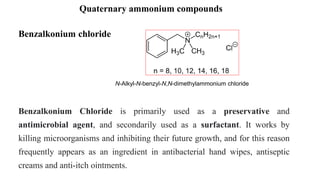
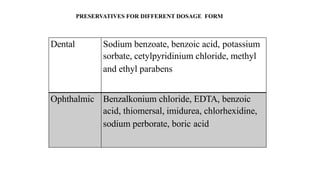
This document discusses preservatives used in pharmaceutical products. It defines preservatives as substances added to prevent microbial growth. Ideal preservatives are effective at low concentrations, nontoxic, compatible with other ingredients, and stable over the product's shelf life. Common preservatives discussed include parabens, benzoic acid derivatives, alcohols, phenols, and quaternary ammonium compounds. The document also covers preservative classification, mechanisms of action, analysis, side effects, and uses in different dosage forms like oral, dermal, ophthalmic, and more.