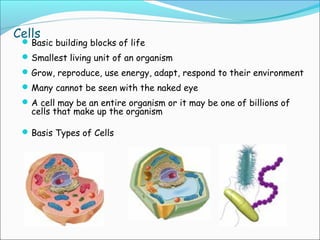
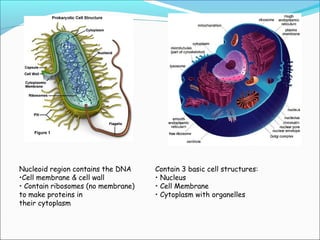
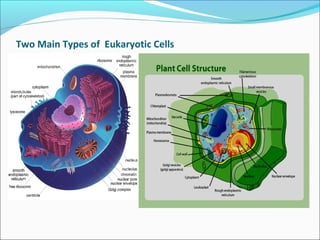
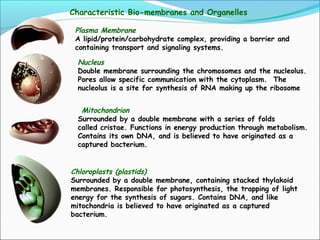
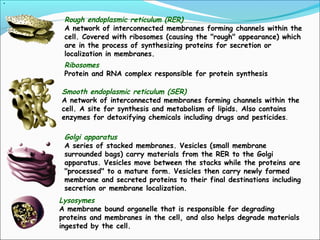
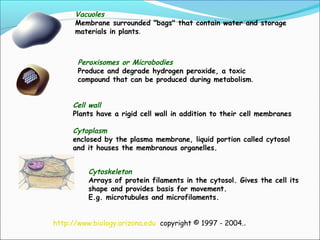
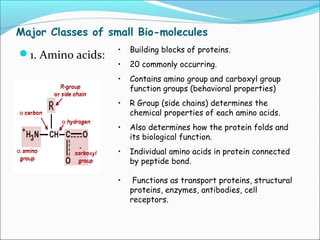
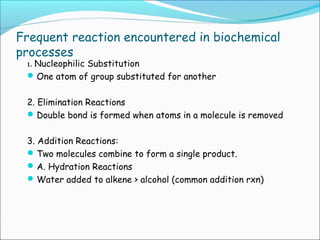
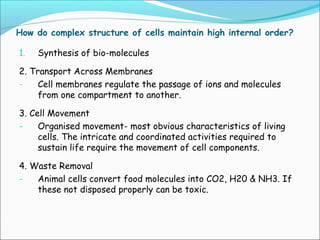
The document provides an introduction to biochemistry, emphasizing the principles of cell structure and function, including the different types of biomolecules and their roles in living organisms. It discusses the organization of cells, the significance of biochemical reactions, and the various components of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Key topics include the metabolism processes, the types of fundamental biochemical reactions, and how cells maintain internal order through energy management and molecular synthesis.