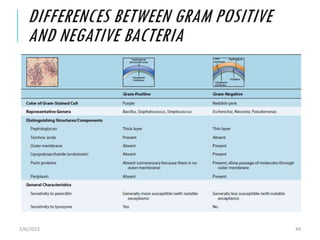
Bacteria have a simple cell structure compared to eukaryotic cells. They lack membrane-bound organelles and have three basic components - surface appendages, surface layers, and intracytoplasmic structures. Surface appendages include flagella for locomotion and fimbriae/pili for adhesion. The cell envelope varies between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, but both contain a cytoplasmic membrane, peptidoglycan layer, and nucleic DNA material. The bacterial cytoplasm contains ribosomes, plasmids, and the nucleoid where DNA is located. Bacteria reproduce through binary fission and have various shapes depending on their structure.









![SURFACE APPENDAGES
• 2 basic types of surface appendages:
1.FLAGELLA [organs of locomotion]
- thread-like appendages present on both Gram
positive and Gram negative bacteria
- their presence is useful for identification.
2.FIMBRIAE (PILI)
- found mostly on Gram negative bacteria and a few
Gram positives .e.g. Corynebacterium renale.
Some bacteria have both fimbriae and flagella. e.g.
E.coli which has numerous flagella and 2 types of
pili.
2/6/2023 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bacteriastructureandfunctionautosaved-230206013850-80c9a713/85/BACTERIA-STRUCTURE-AND-FUNCTION-Autosaved-pptx-10-320.jpg)








![FIMBRIAE (PILI)
• Fimbriae [pili] are slender, hair-like, proteinaceous
filaments on the surface of many Gram negative
bacteria
• Shorter, finer and more rigid than flagella, 4-8nm
long and 1-5nm thick
• Composed of protein subunits referred to as pilins
• Minor proteins termed adhesins are located on
the tips of the pili and are responsible for the
attachment properties.
2/6/2023 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bacteriastructureandfunctionautosaved-230206013850-80c9a713/85/BACTERIA-STRUCTURE-AND-FUNCTION-Autosaved-pptx-19-320.jpg)





























![CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE
• Plasma [cytoplasmic ]membrane: composed
primarily of lipids bilayer with interspersing proteins
• Protein to lipid ratio is usually 3:1
• Thickness about 4-5nm
• Lack sterols (except for Mycoplasma )
2/6/2023 51](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bacteriastructureandfunctionautosaved-230206013850-80c9a713/85/BACTERIA-STRUCTURE-AND-FUNCTION-Autosaved-pptx-51-320.jpg)










![BACTERIA STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION [Autosaved].pptx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bacteriastructureandfunctionautosaved-230206013850-80c9a713/85/BACTERIA-STRUCTURE-AND-FUNCTION-Autosaved-pptx-62-320.jpg)