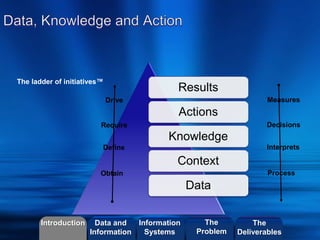
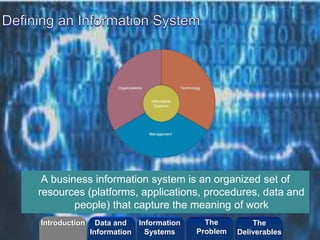
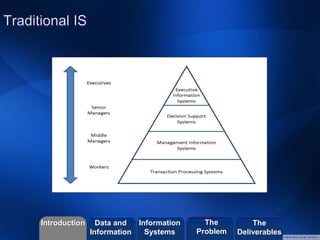
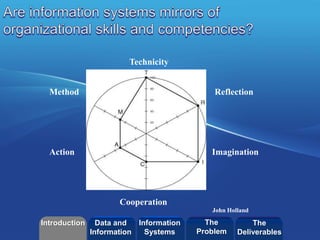
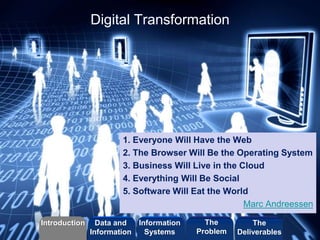
The document discusses how enterprise technologies can be used to improve apprenticeship programs. It covers topics like business processes, social networks, web services, search capabilities, mobile apps, self-tracking ("Quantified Self"), and digital transformation. Students will create a short video case study using Videoscribe on how information technology is used in a company. The goal is to help students understand the relationship between business and innovation using current industry applications and case studies.