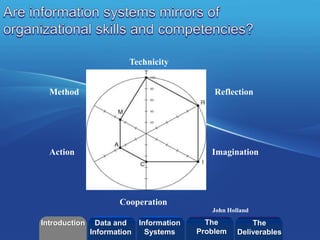
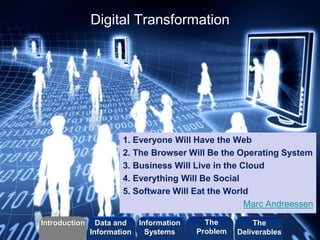
This document discusses a course on information systems. It covers several topics:
- The relationship between business IT and innovation and how to analyze applications in industry, commerce, and training.
- The course structure which explores context, methods/technologies, case studies, and evaluation metrics.
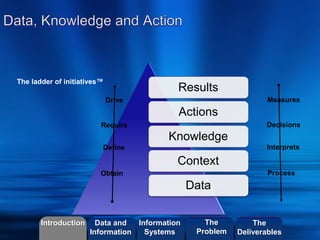
- Definitions of structured vs unstructured data and how organizations can compare and aggregate structured data.
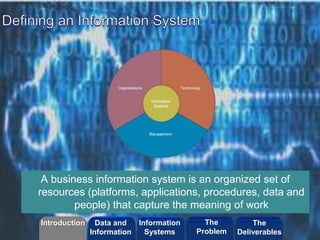
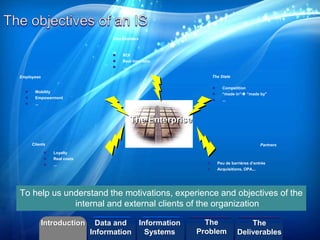
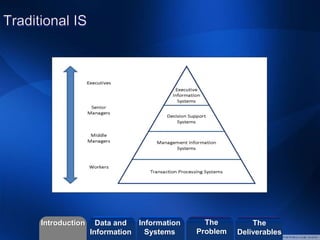
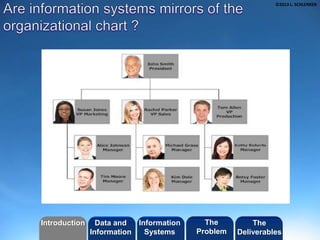
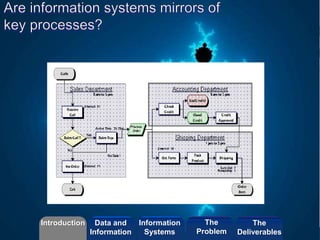
- The role of an information system as an organized set of resources that capture the meaning of work.