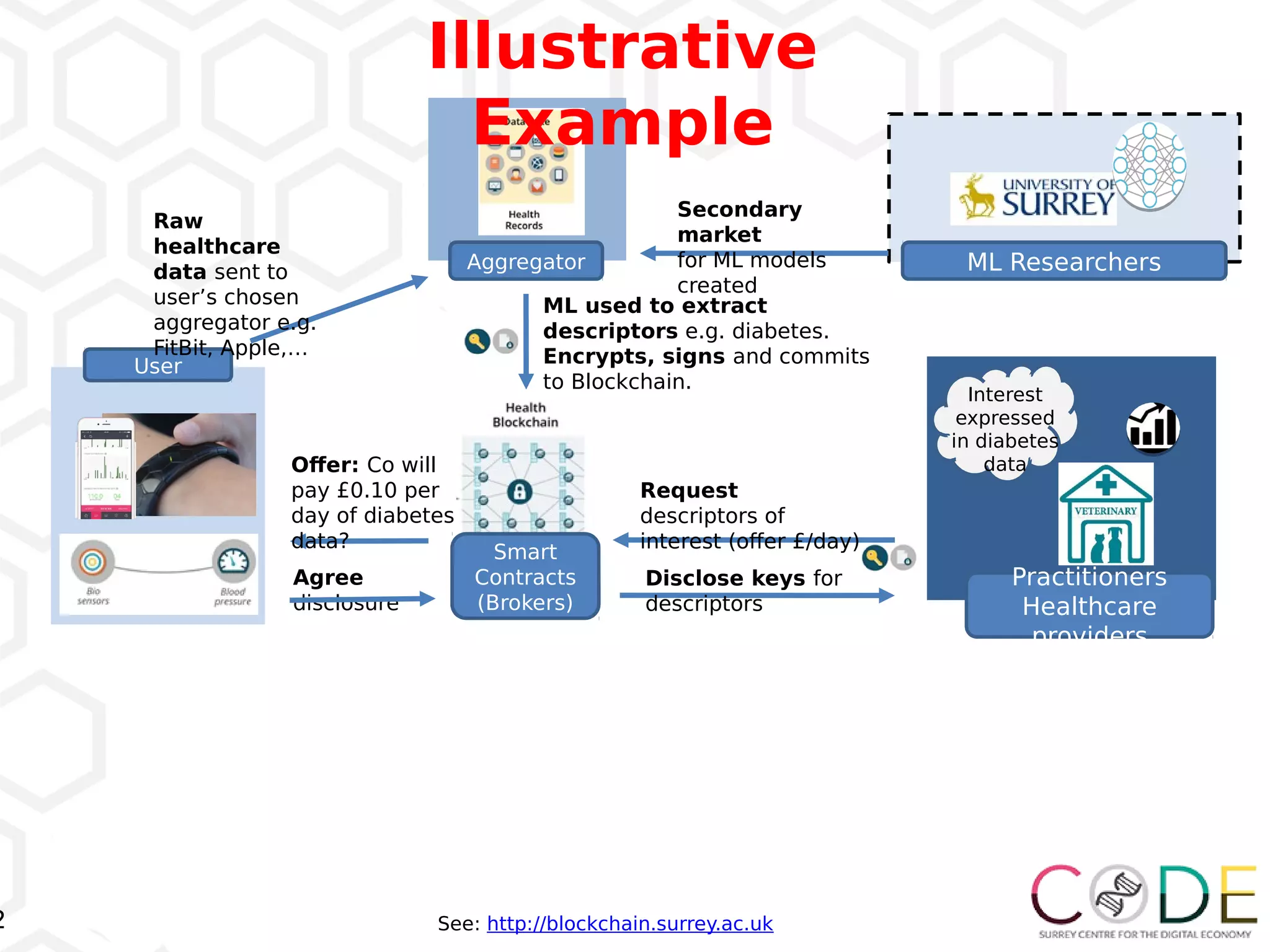
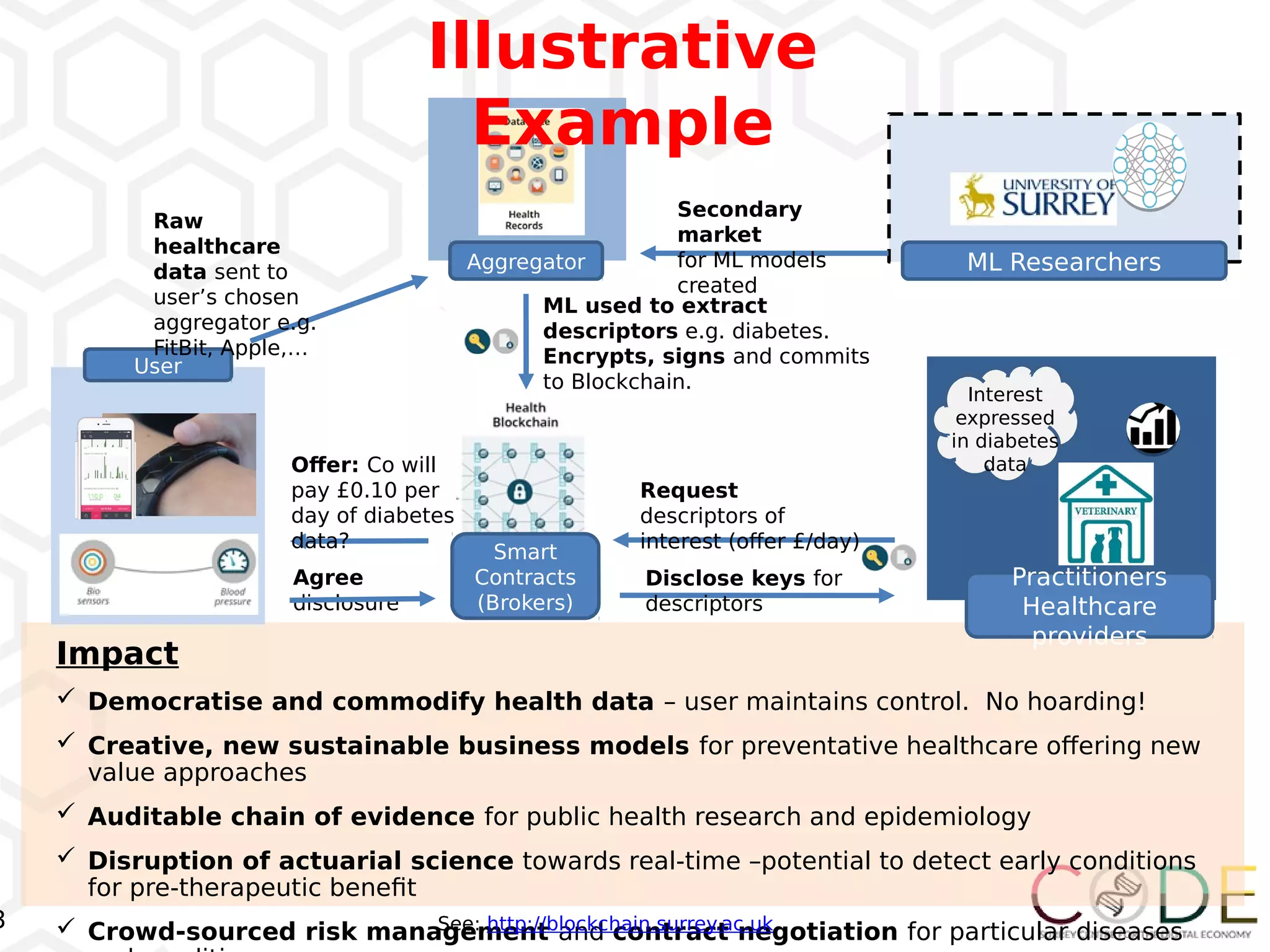
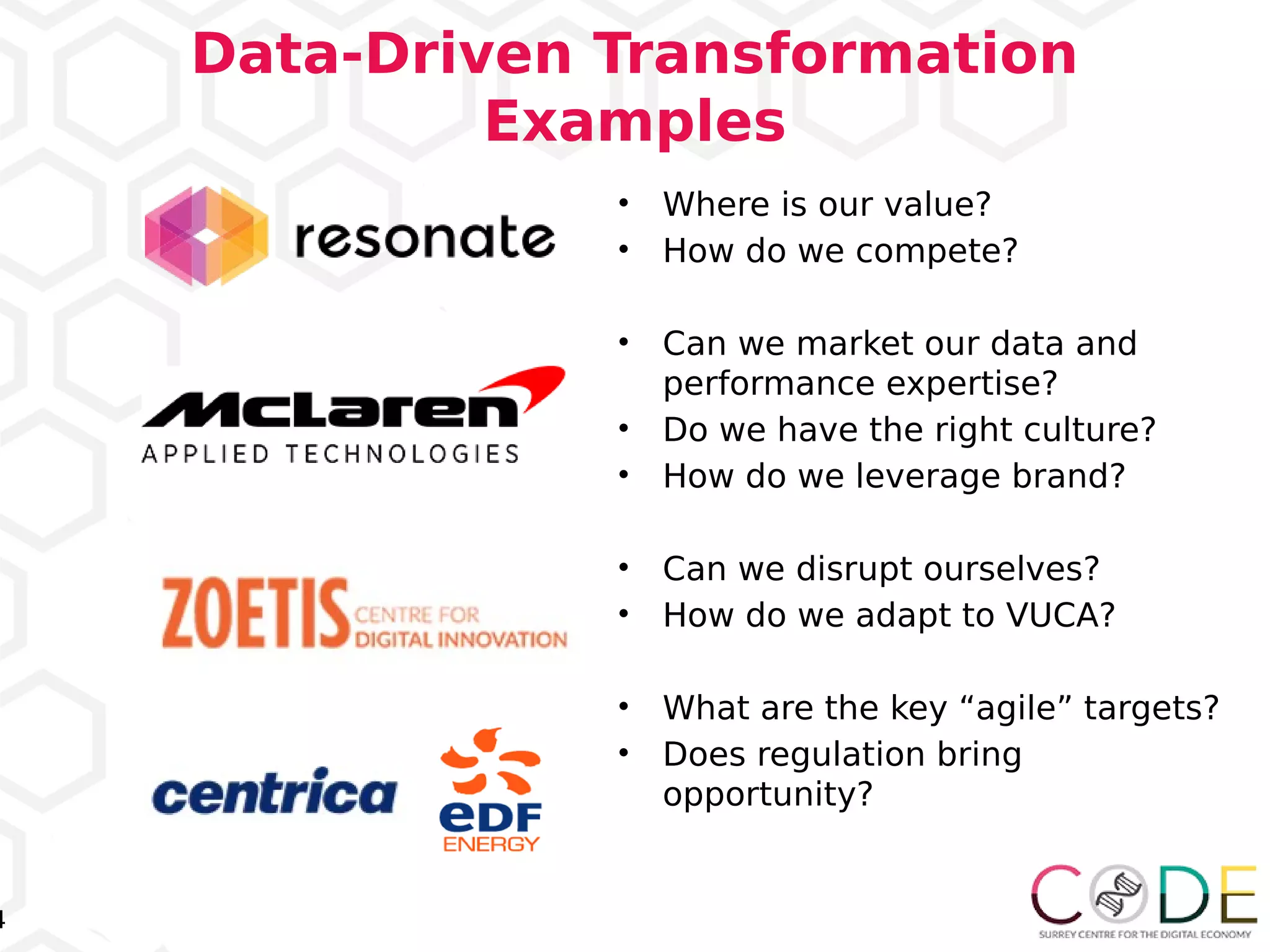
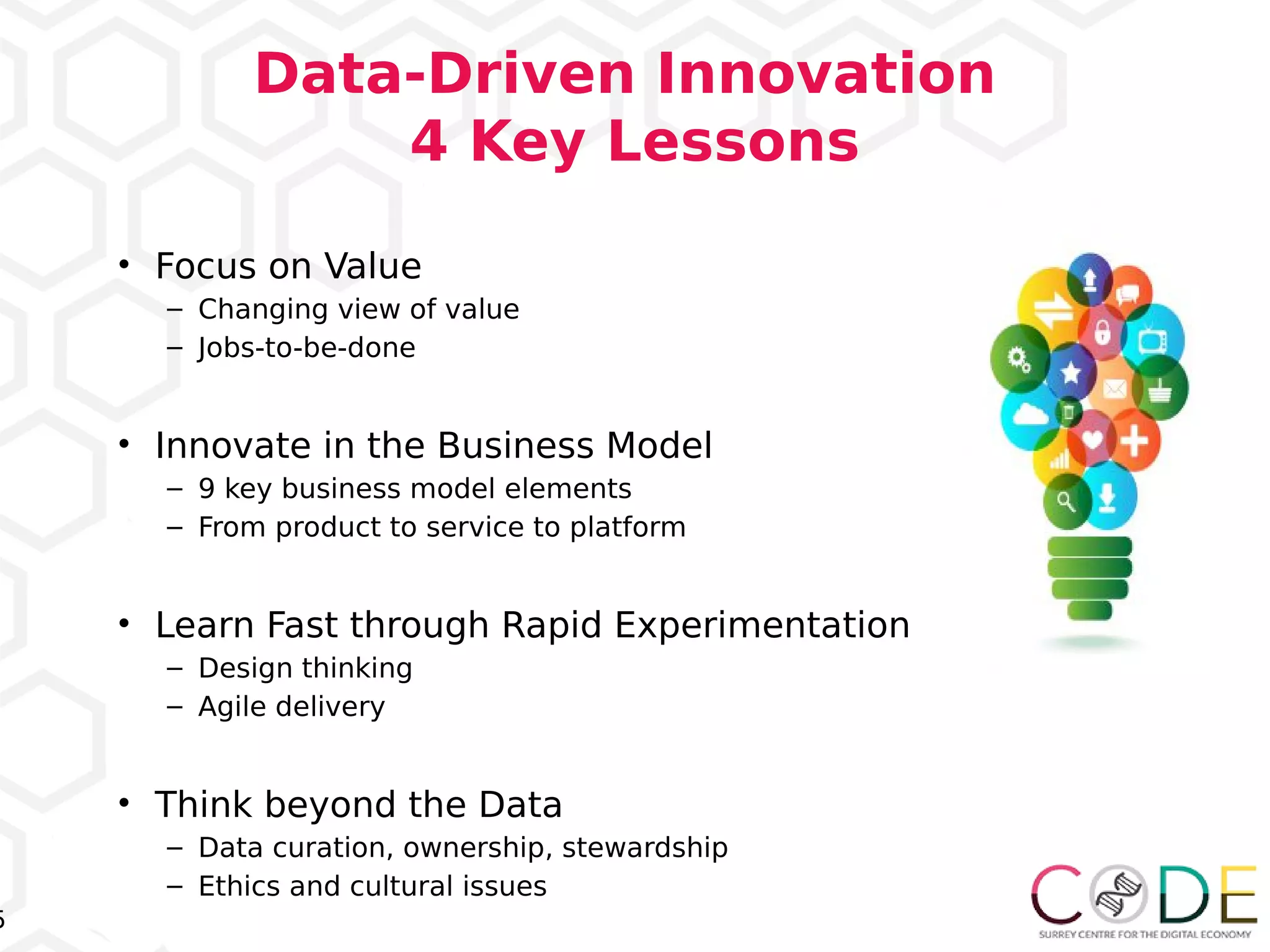
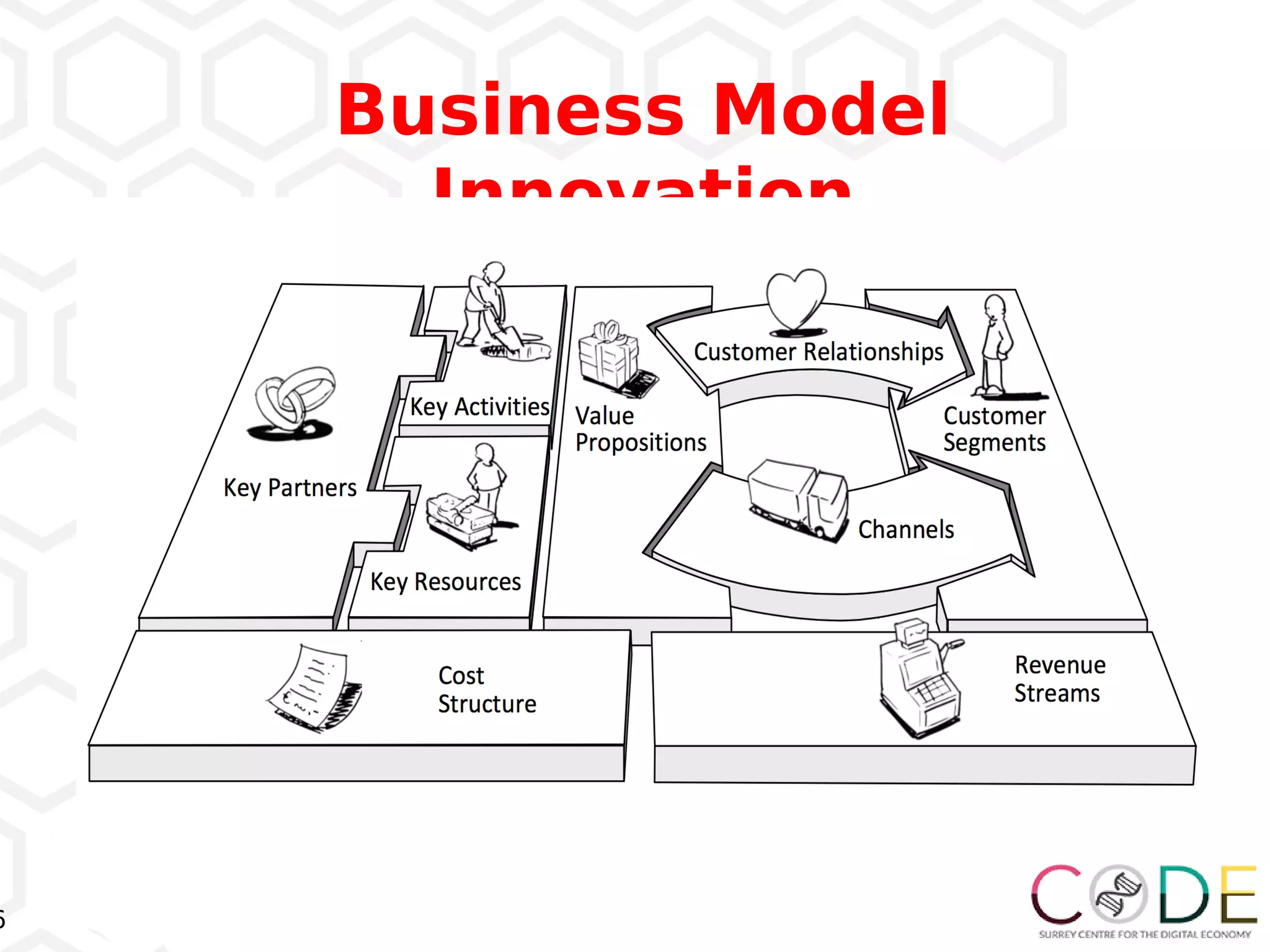
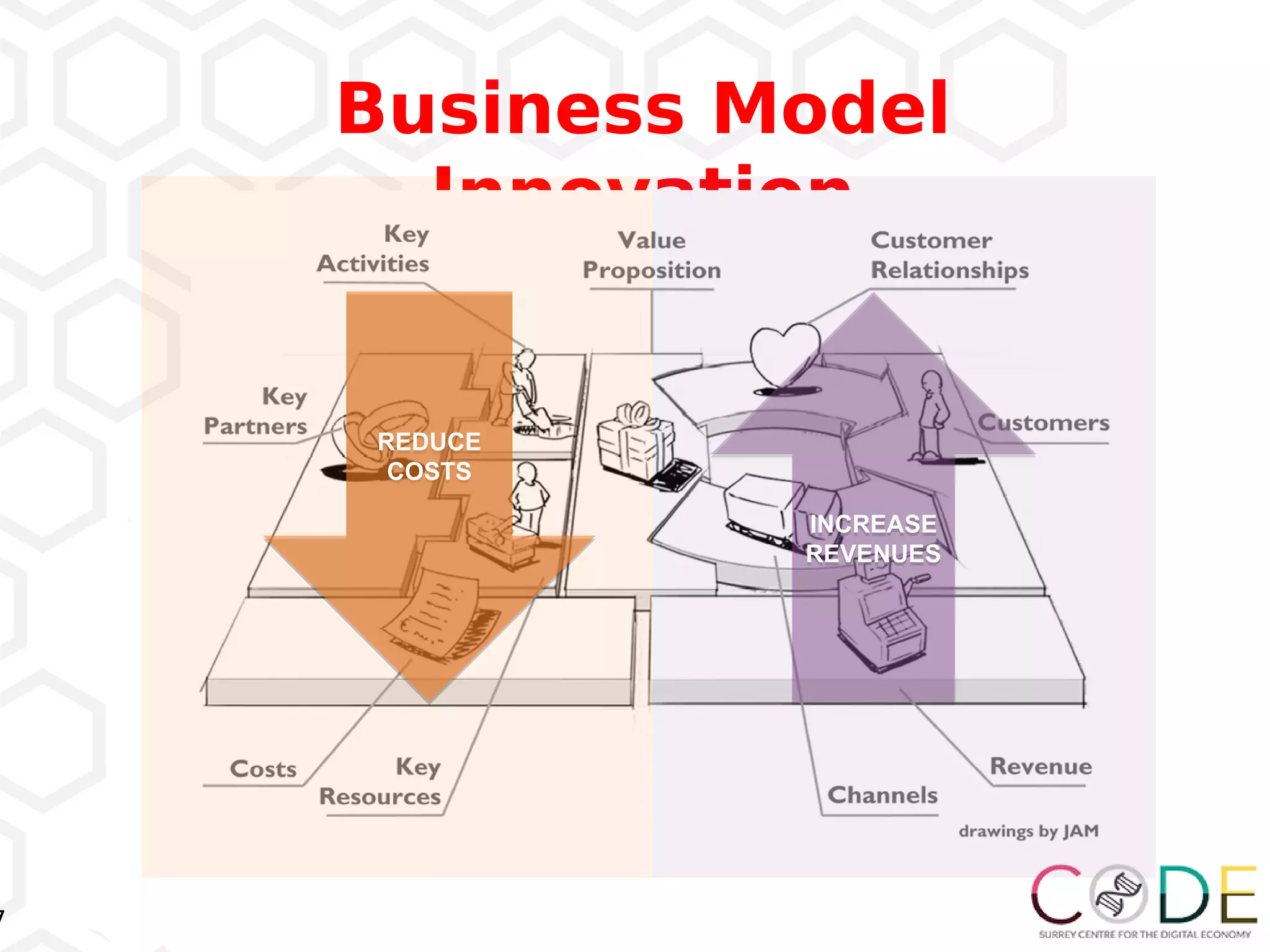
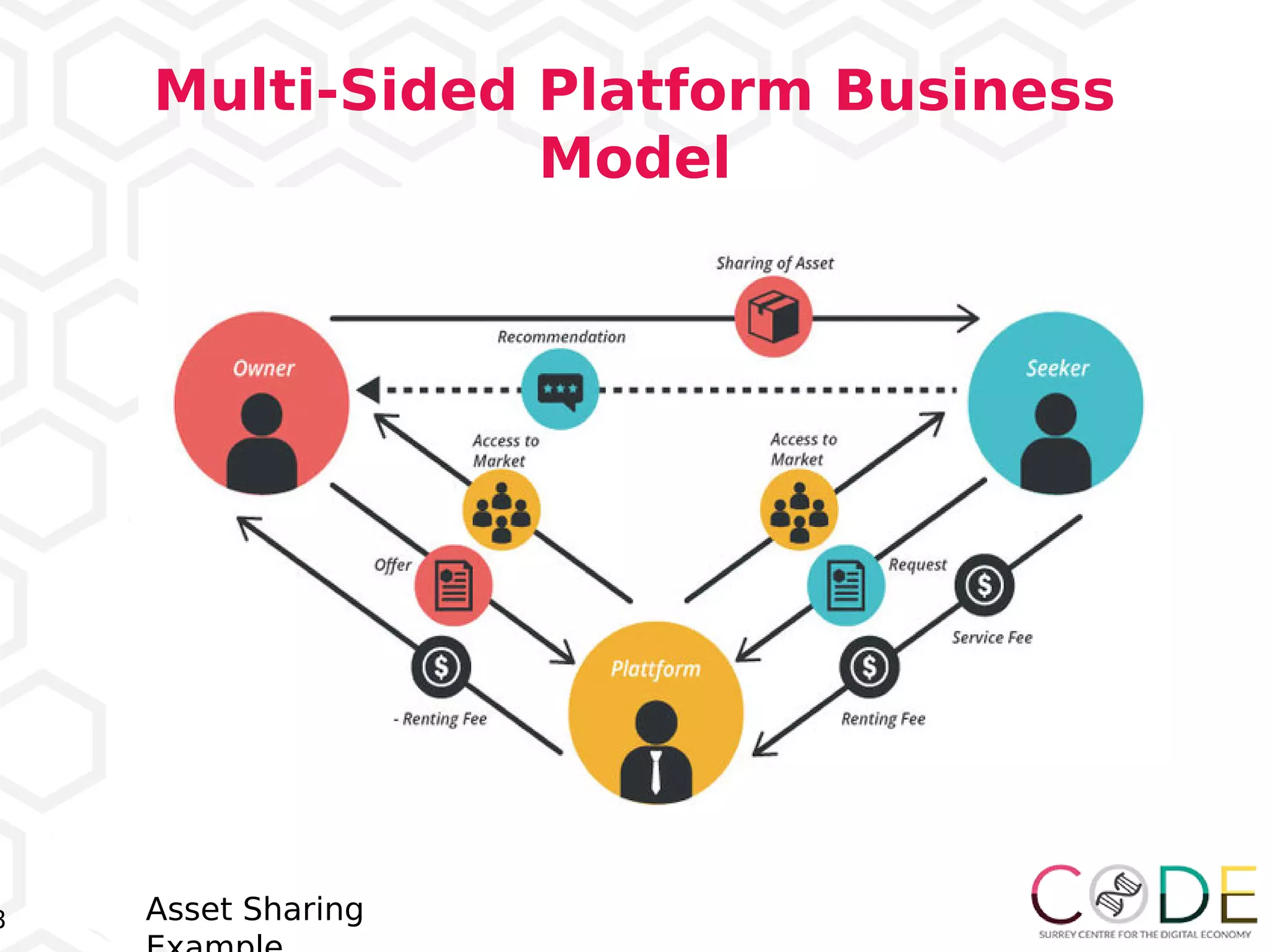
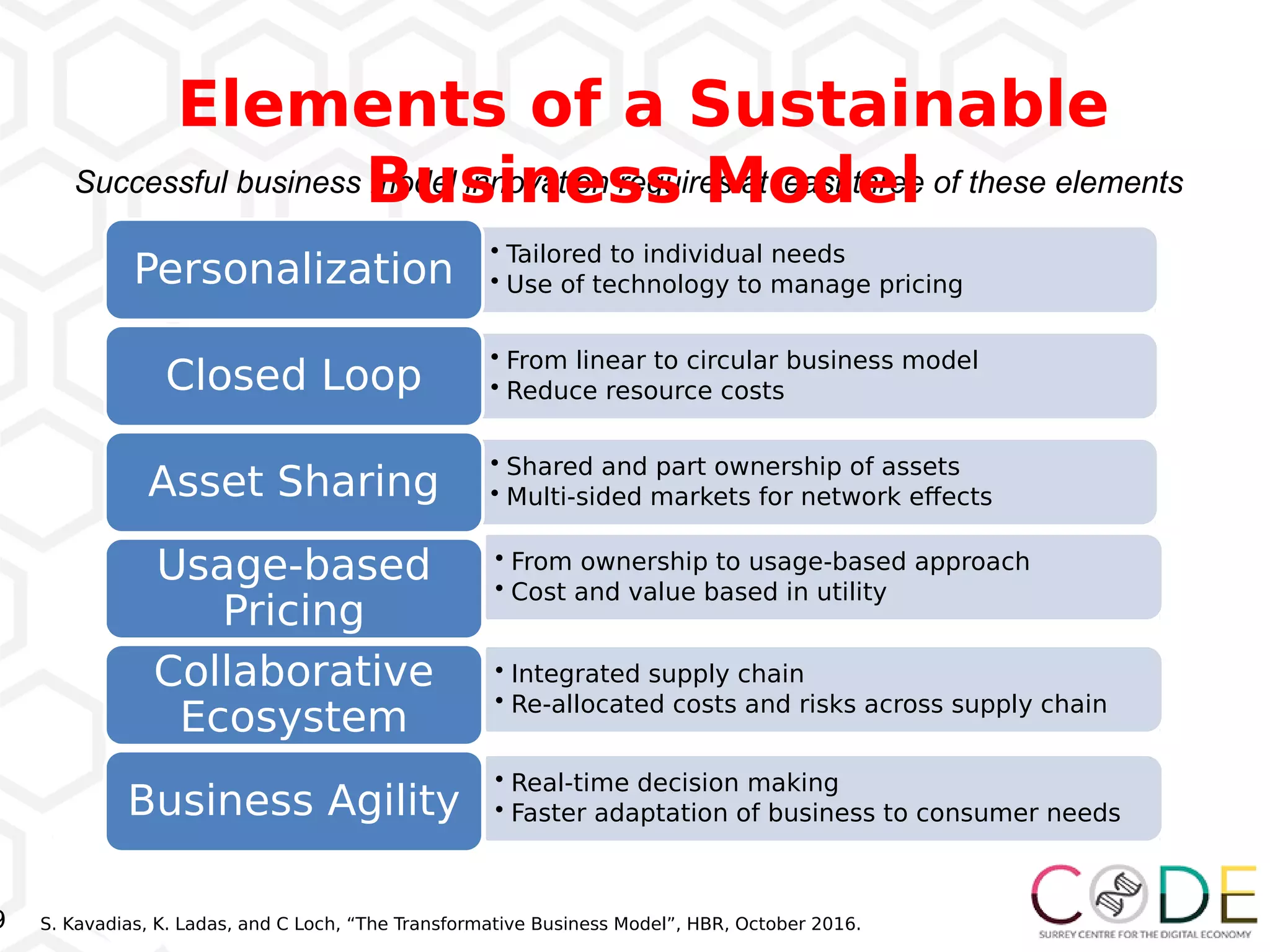
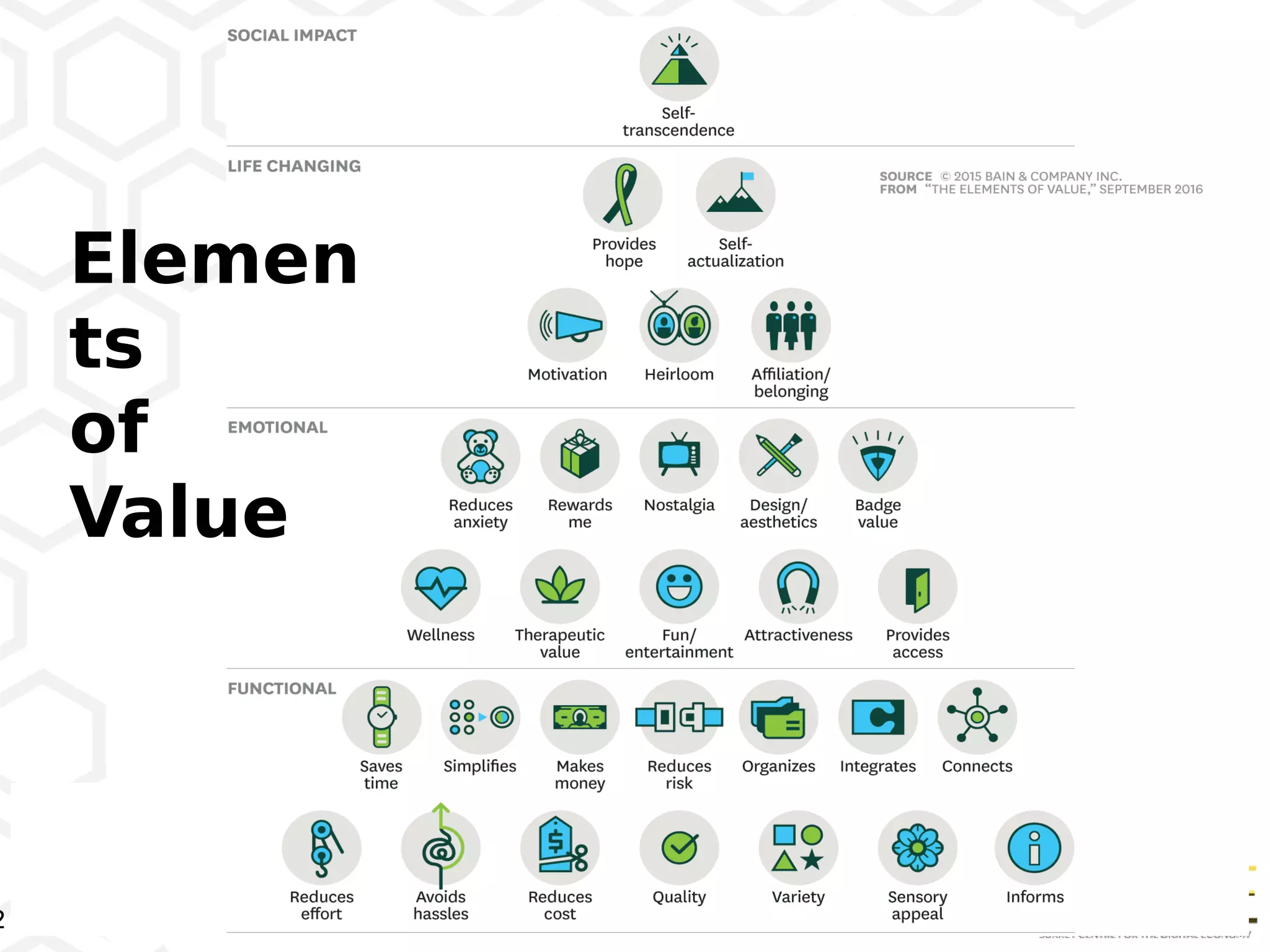
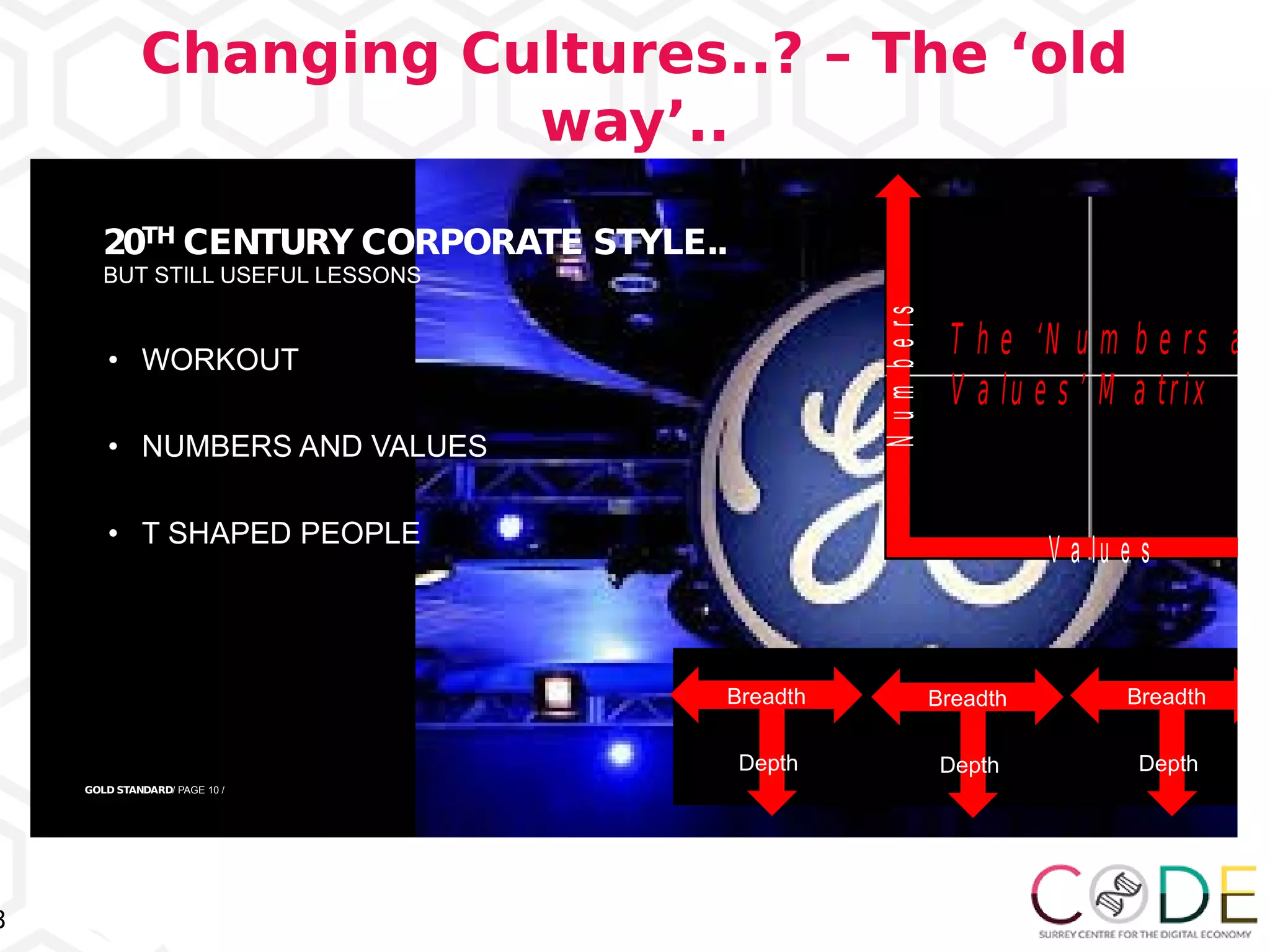
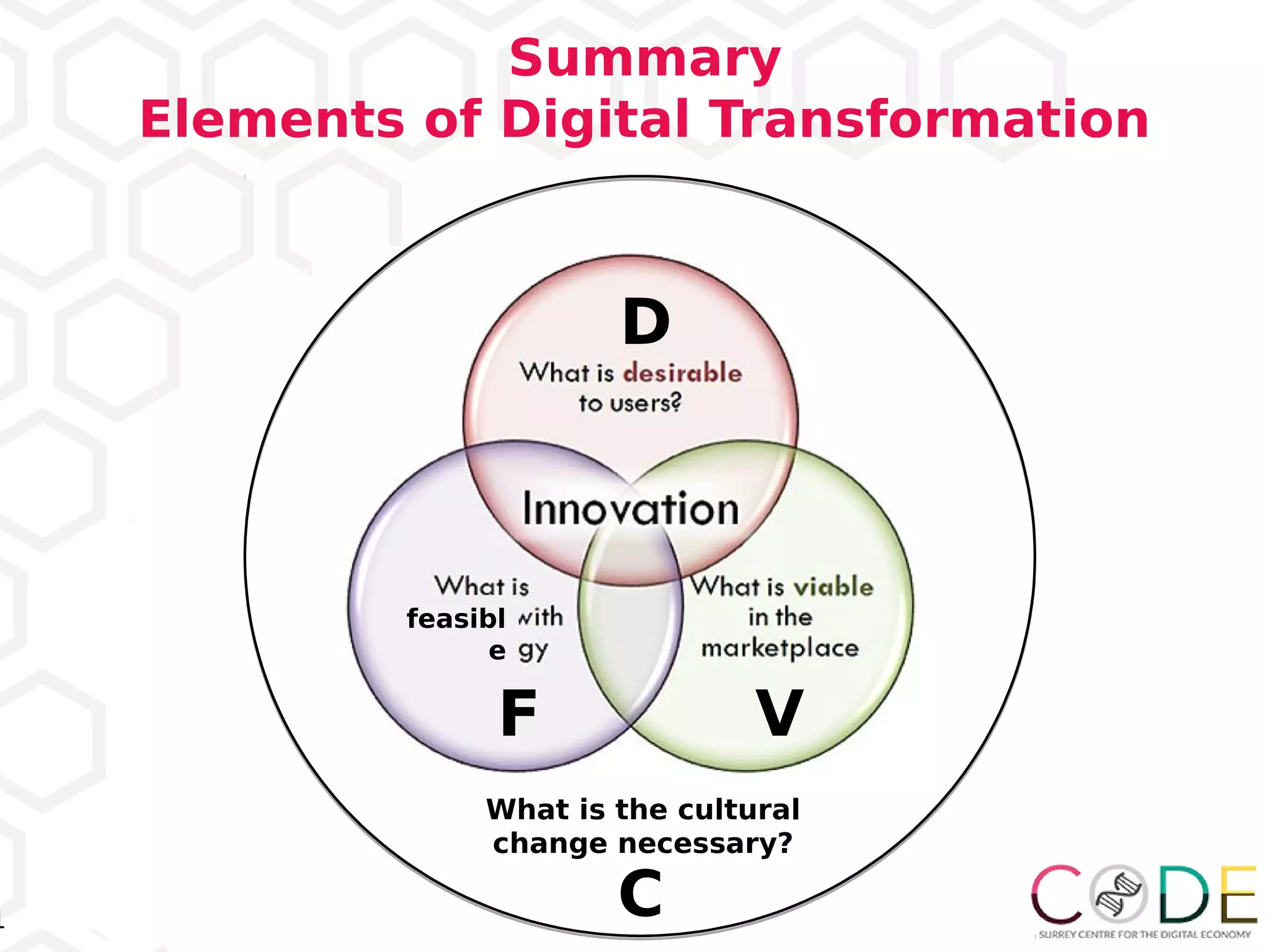
The document discusses key elements of digital transformation including:
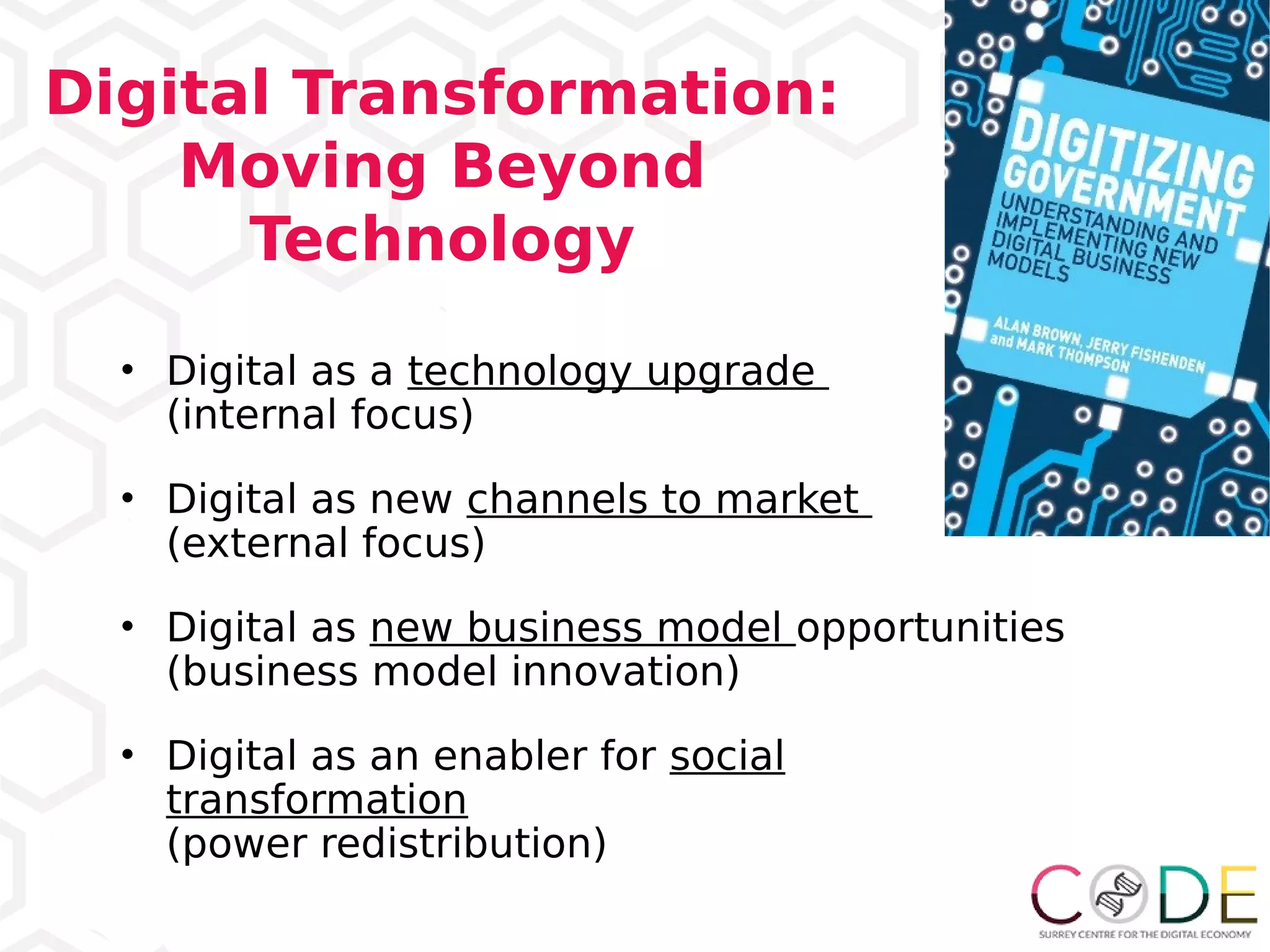
1) Seeing digital transformation as more than just technology upgrades but also new business models and opportunities for social change.
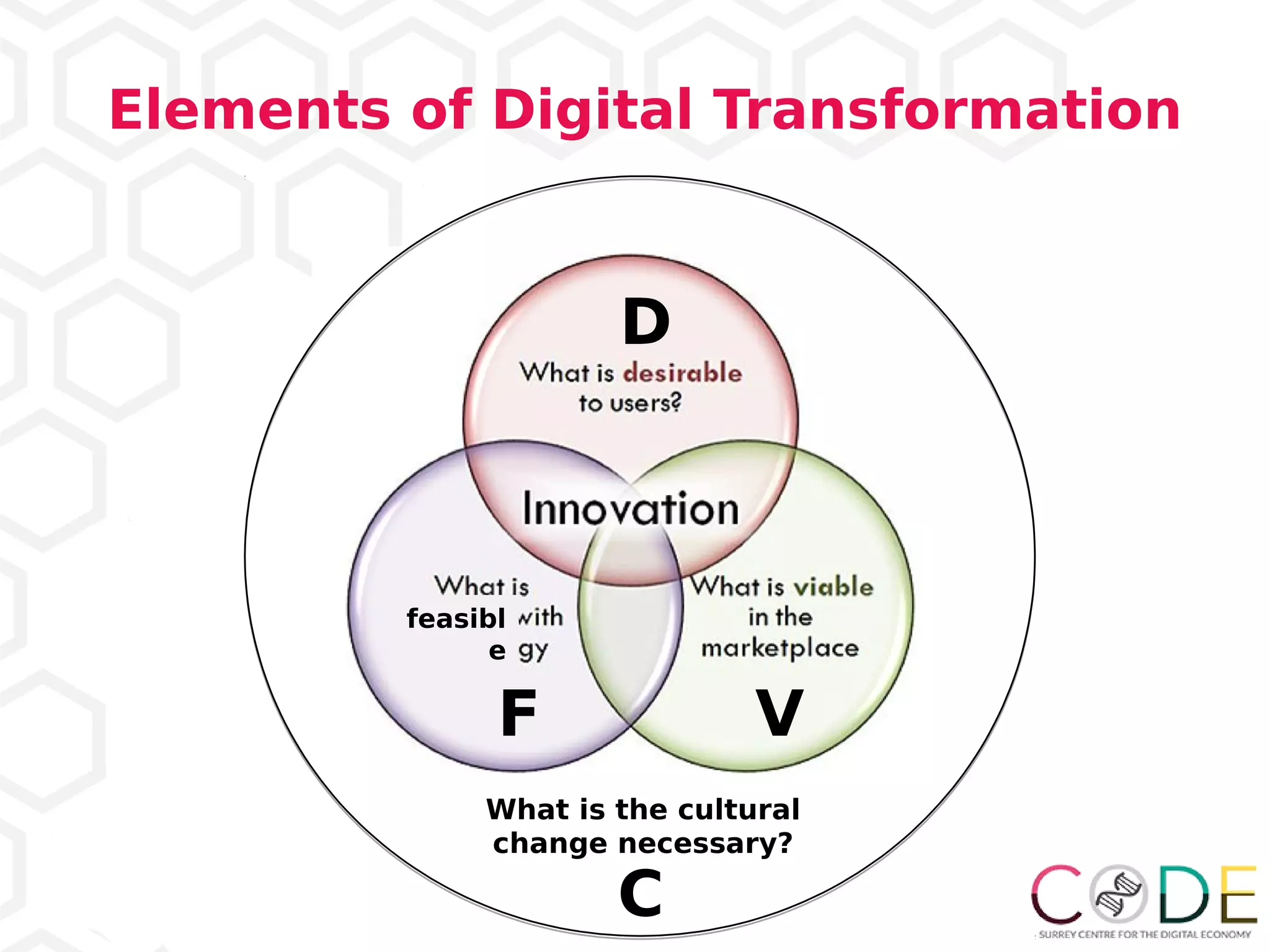
2) Cultural change is necessary to successfully implement digital transformation.
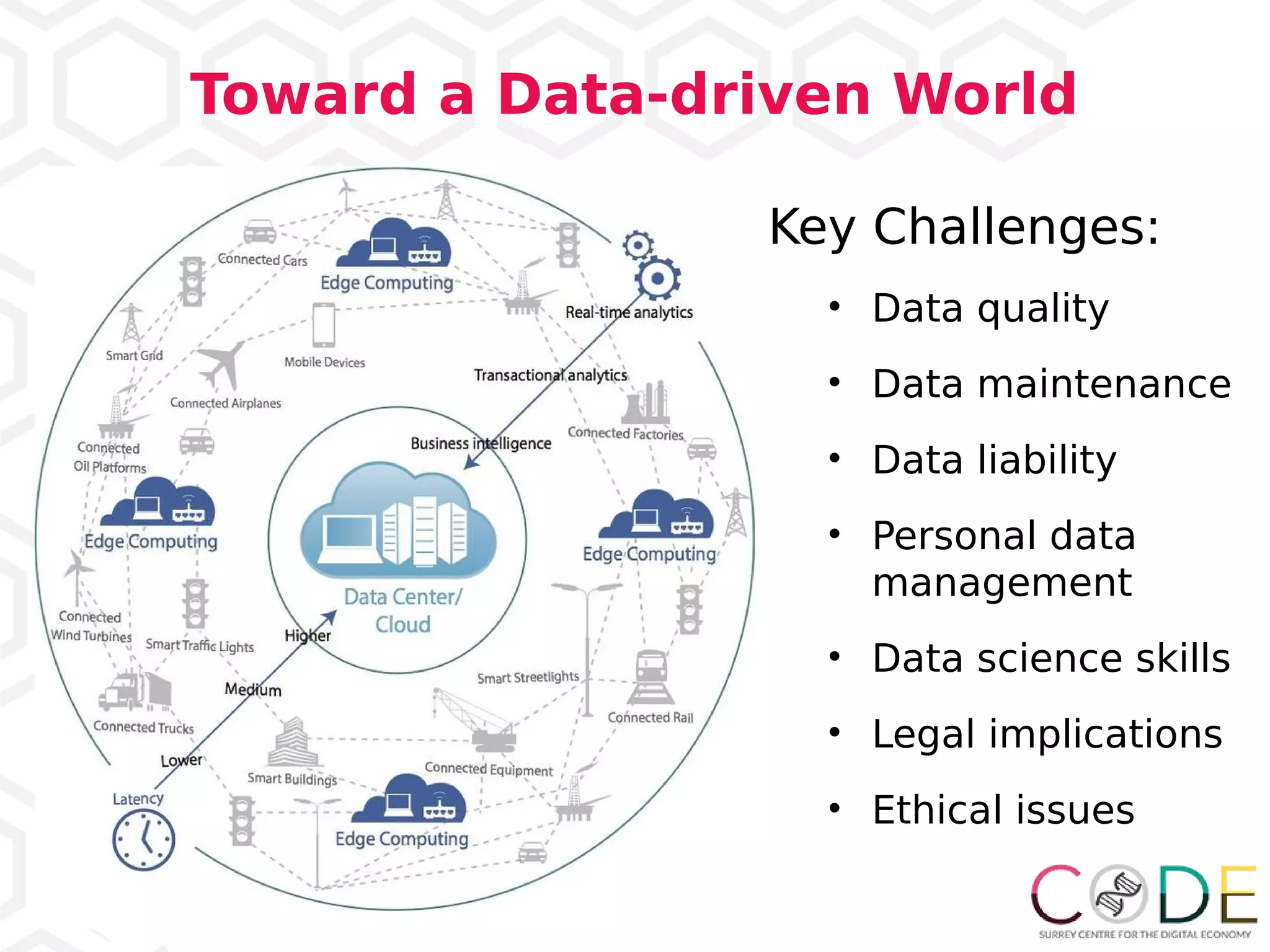
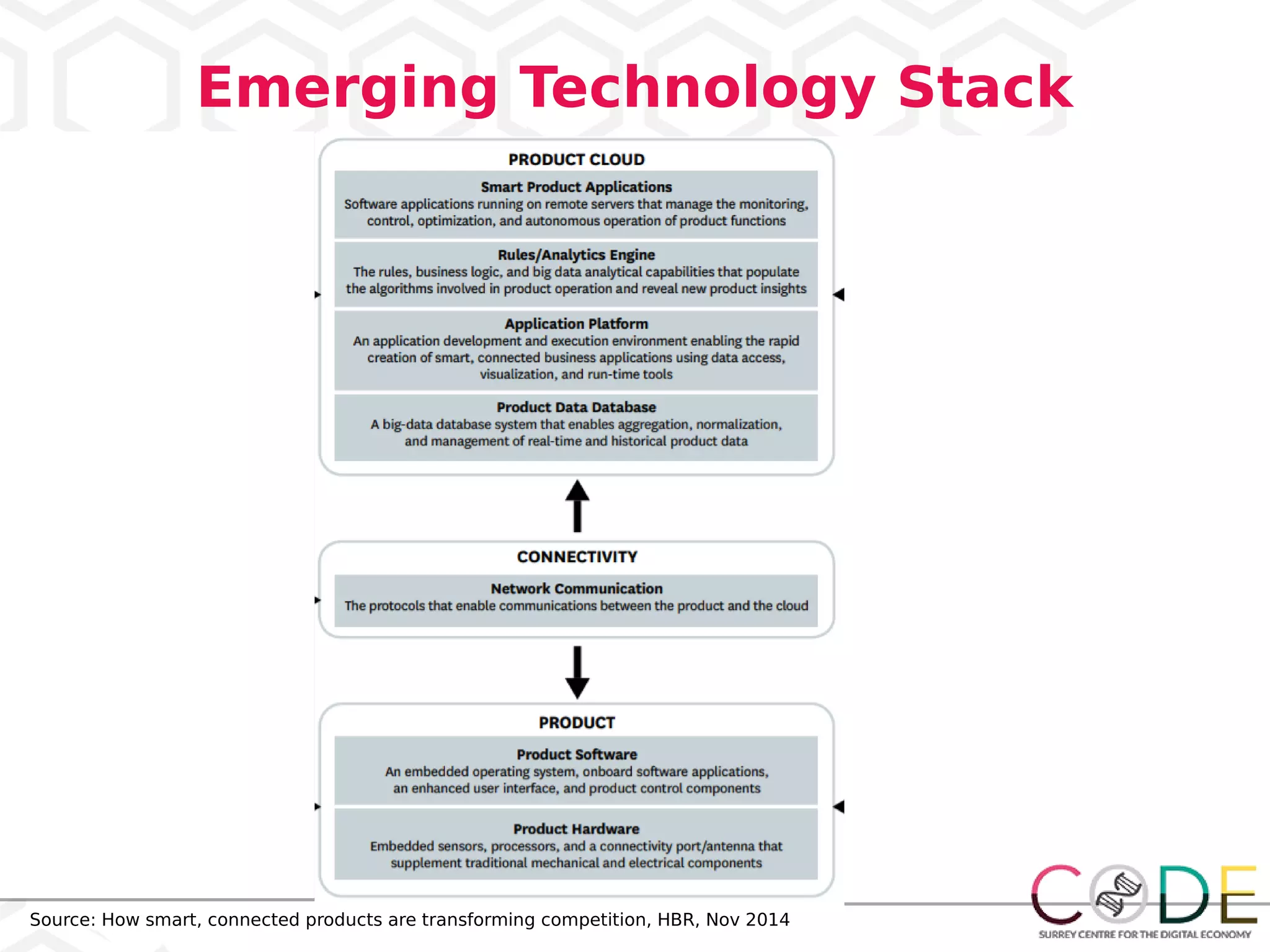
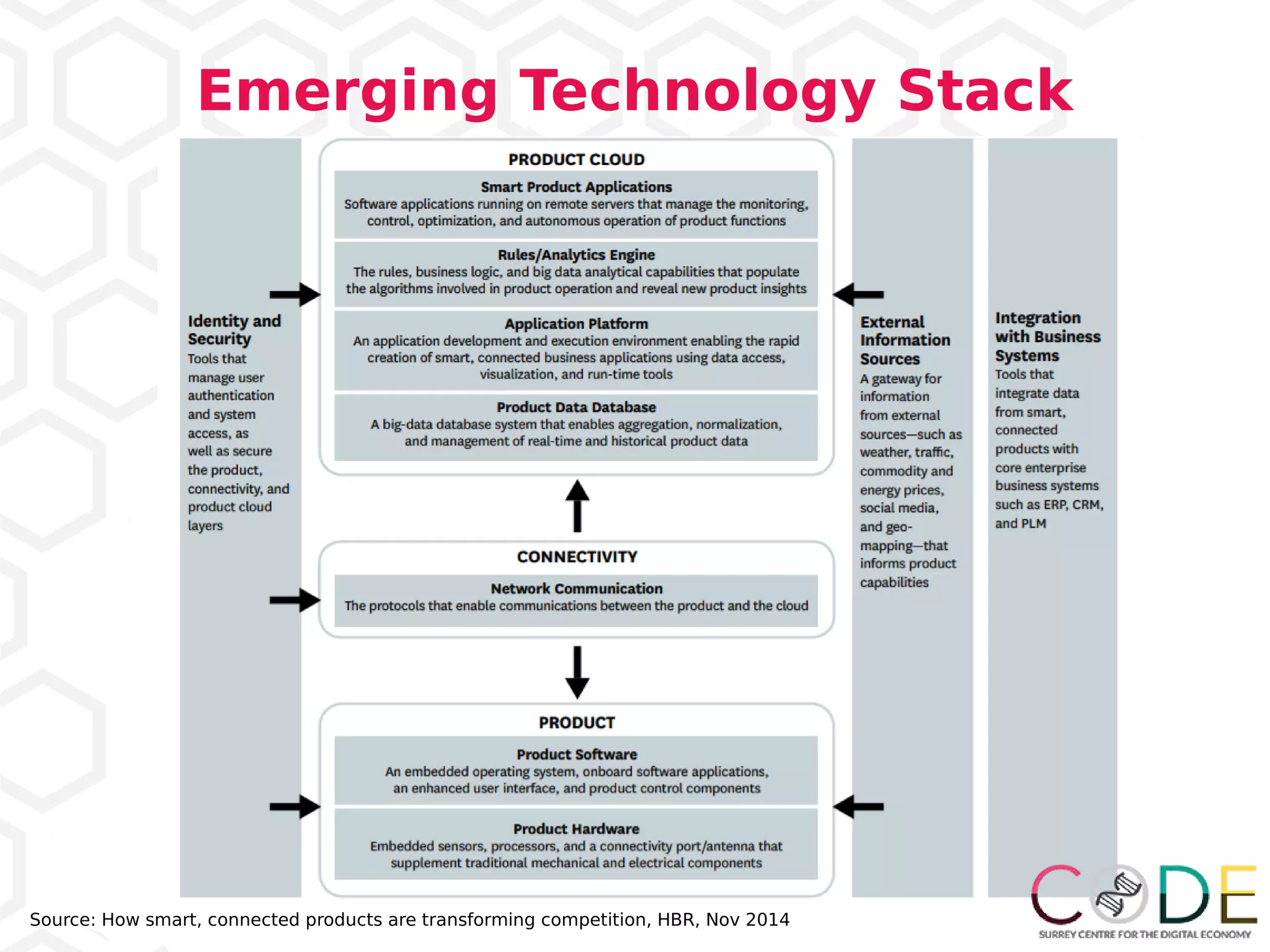
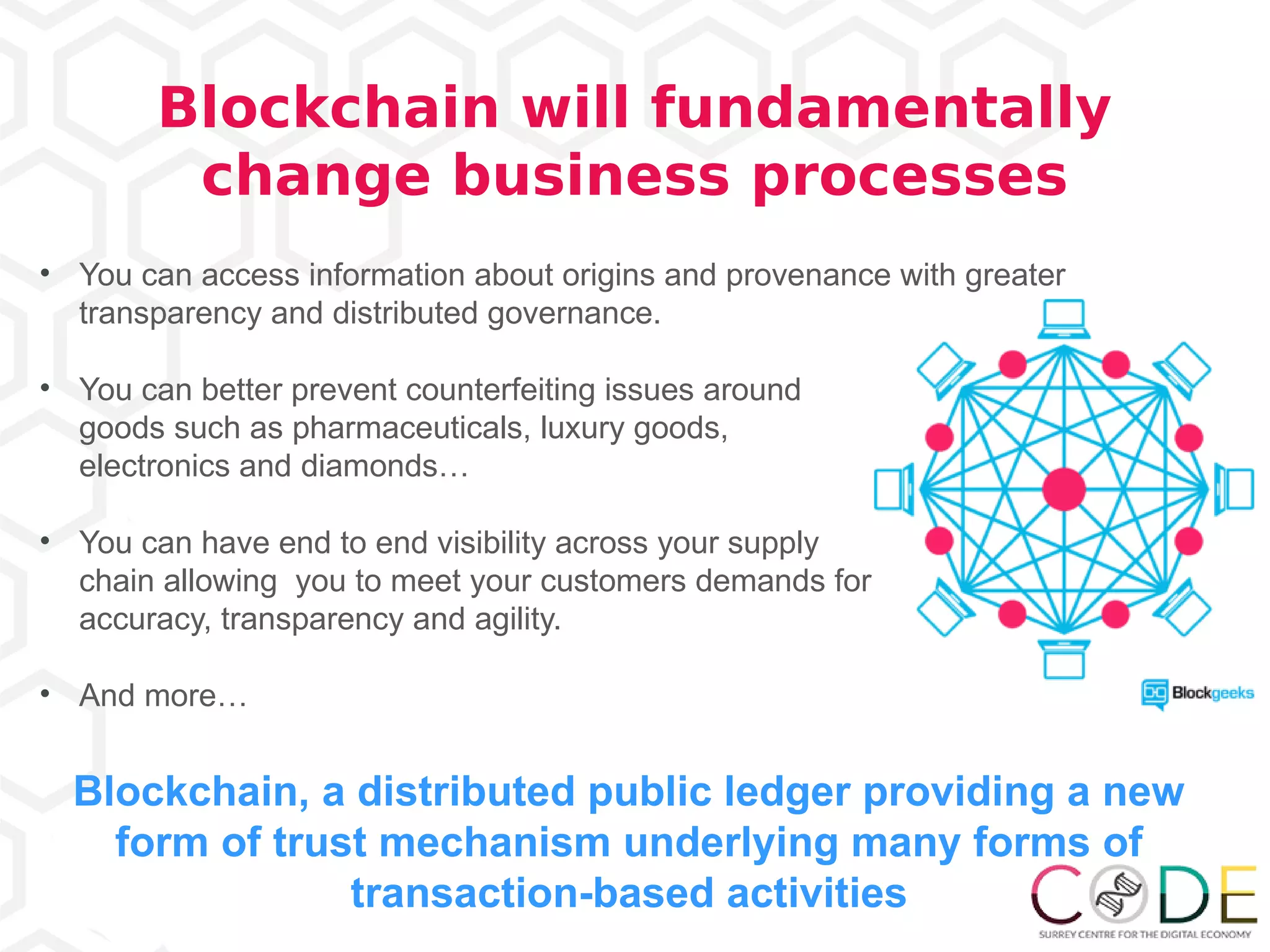
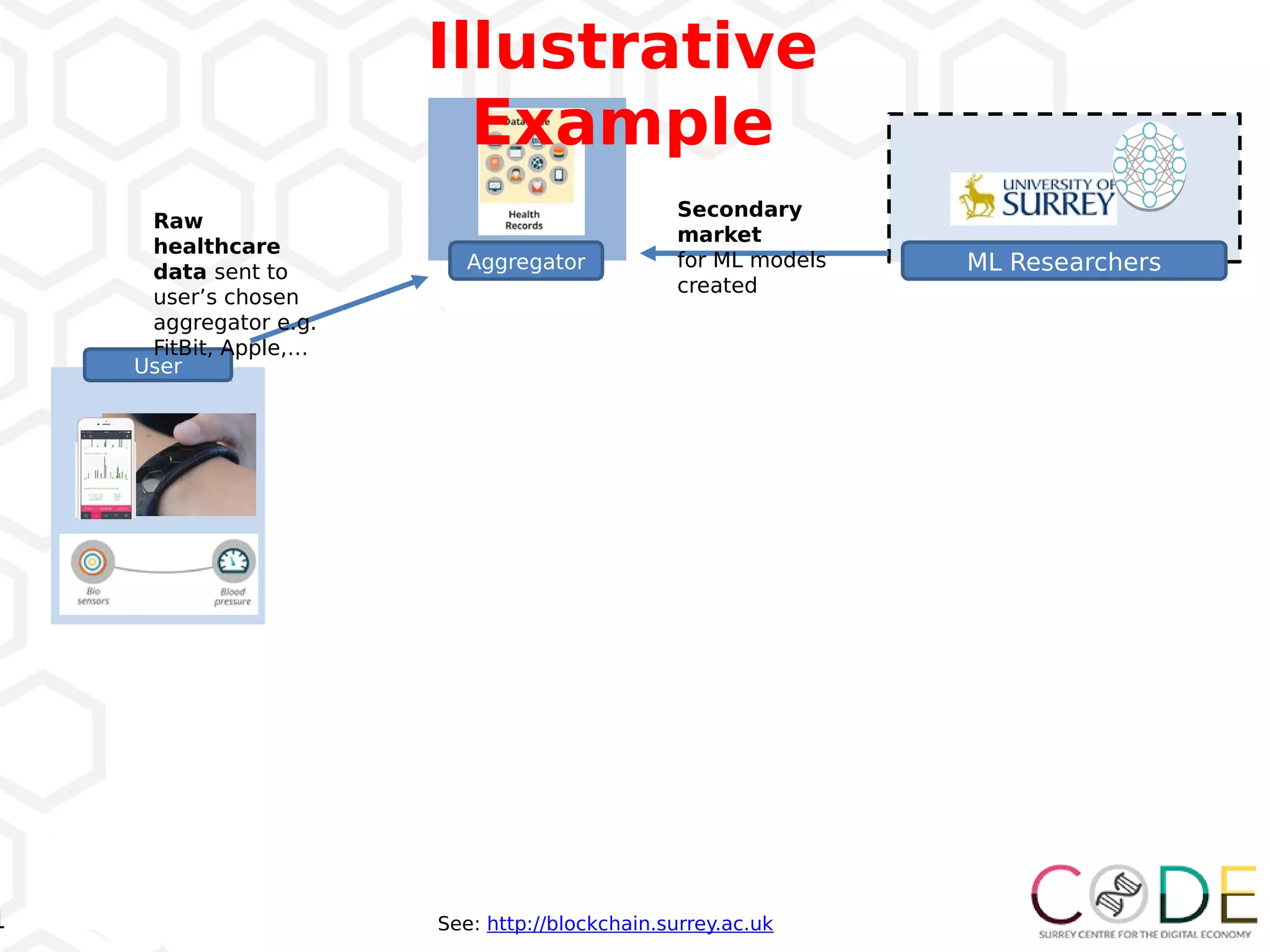
3) Emerging technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the internet of things are changing business processes.