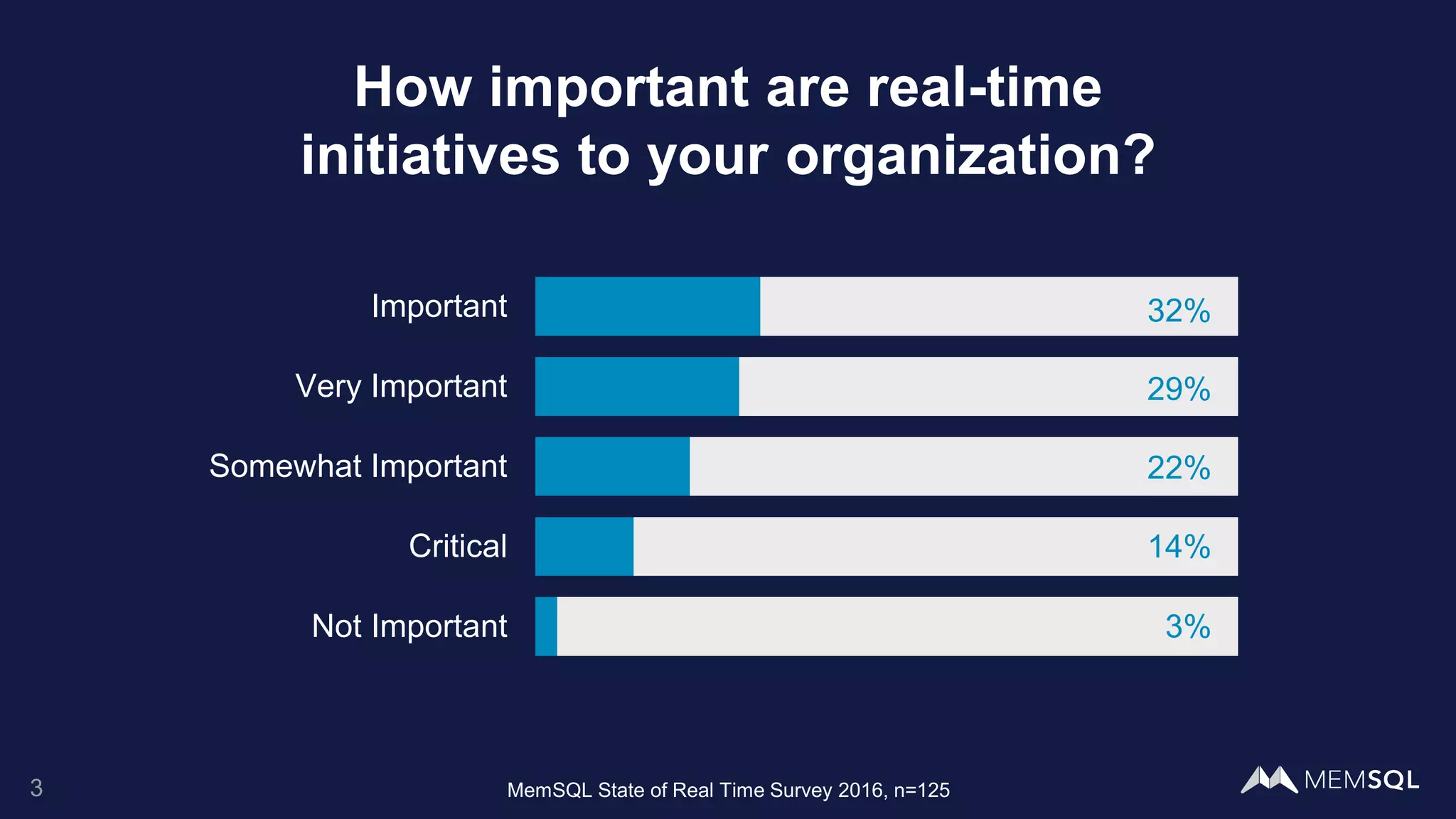
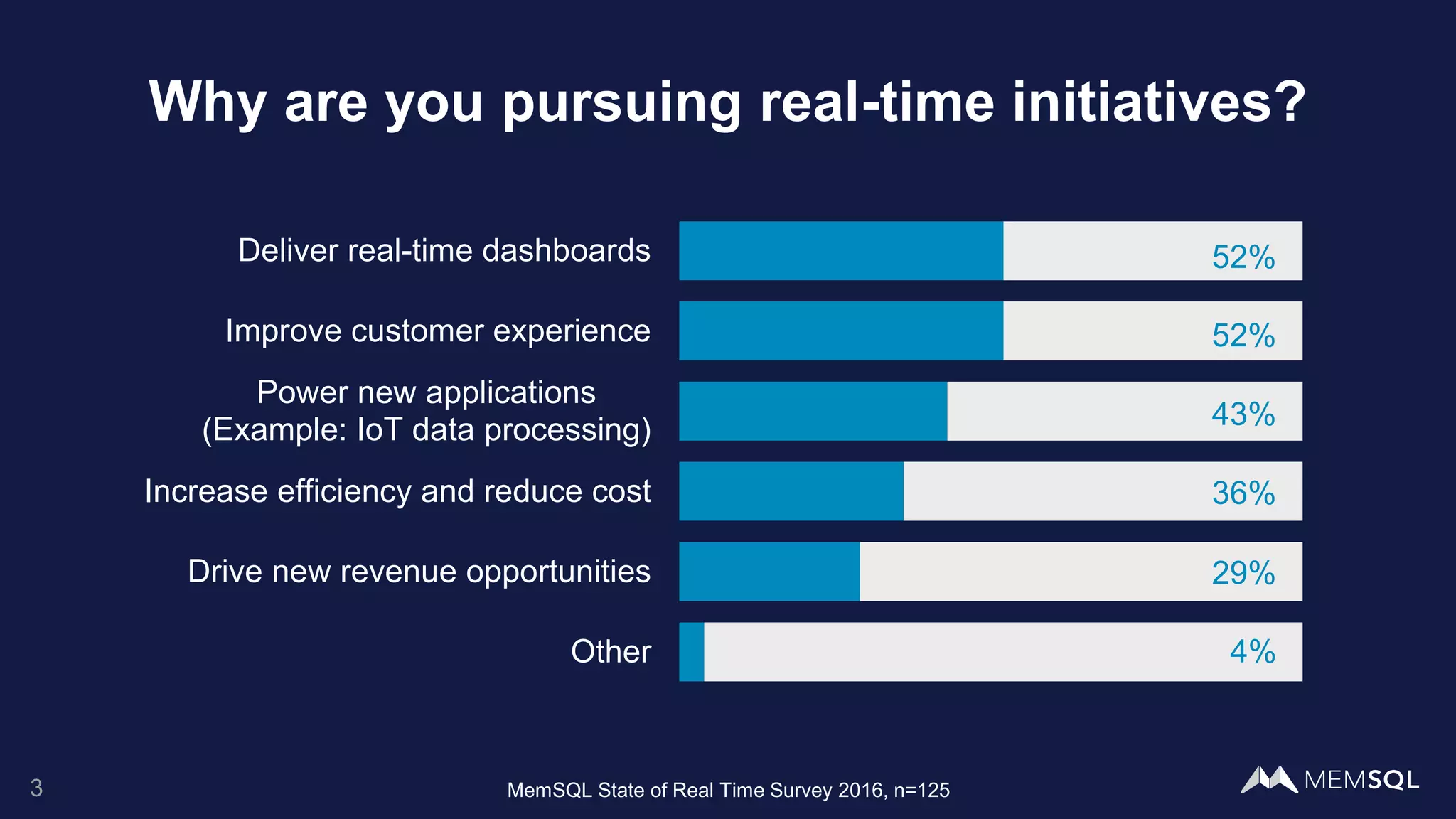
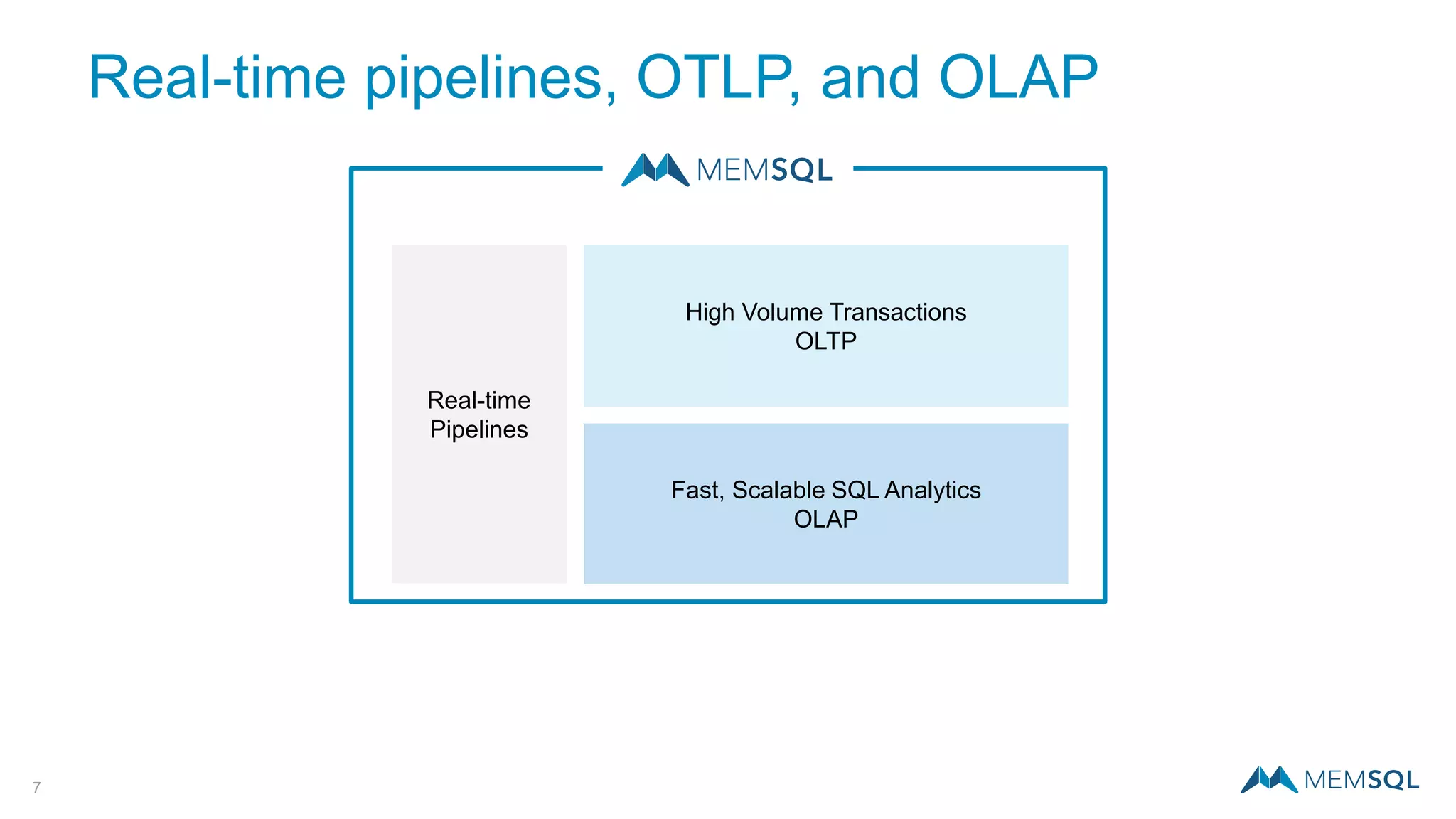
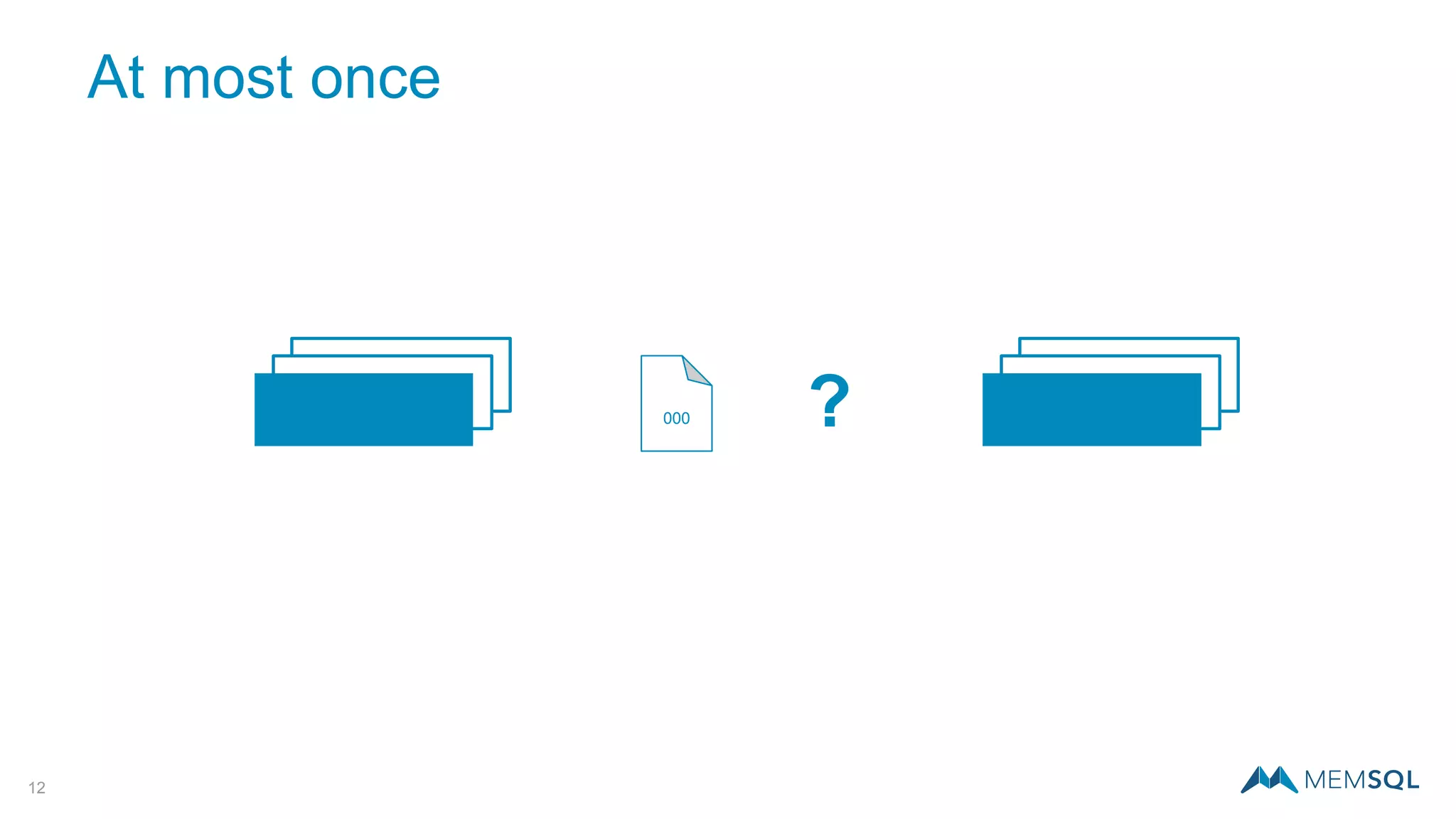
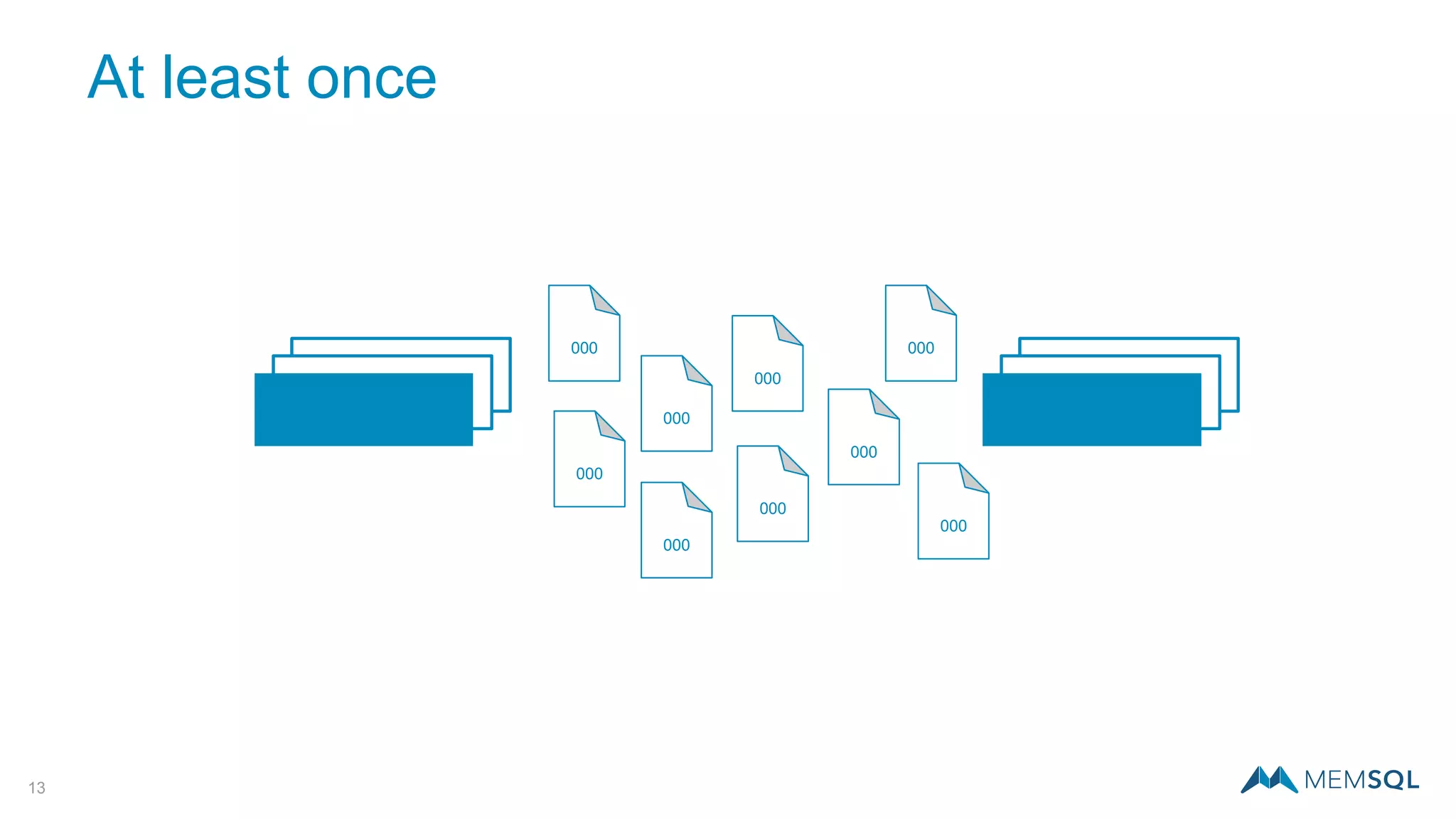
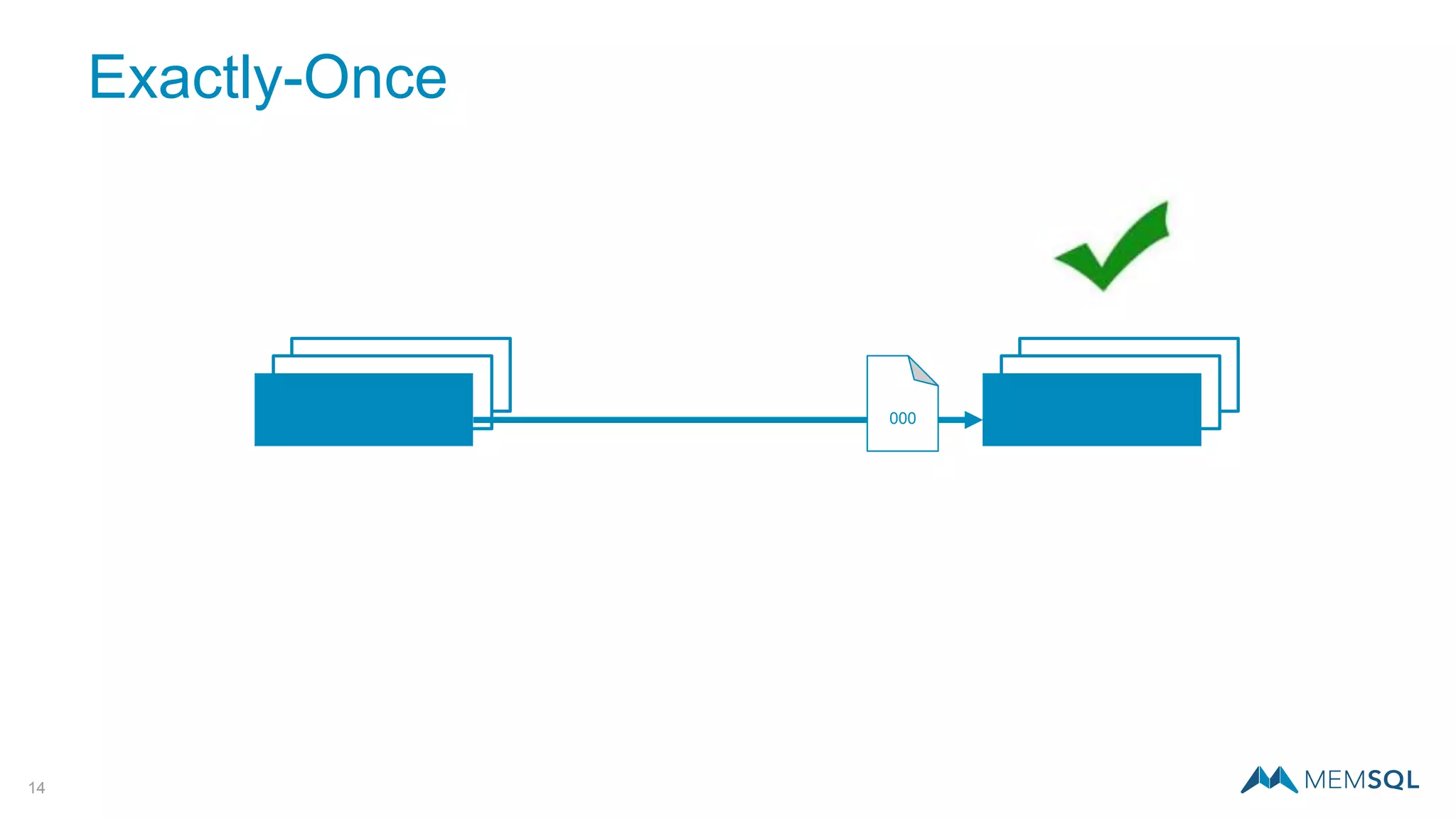
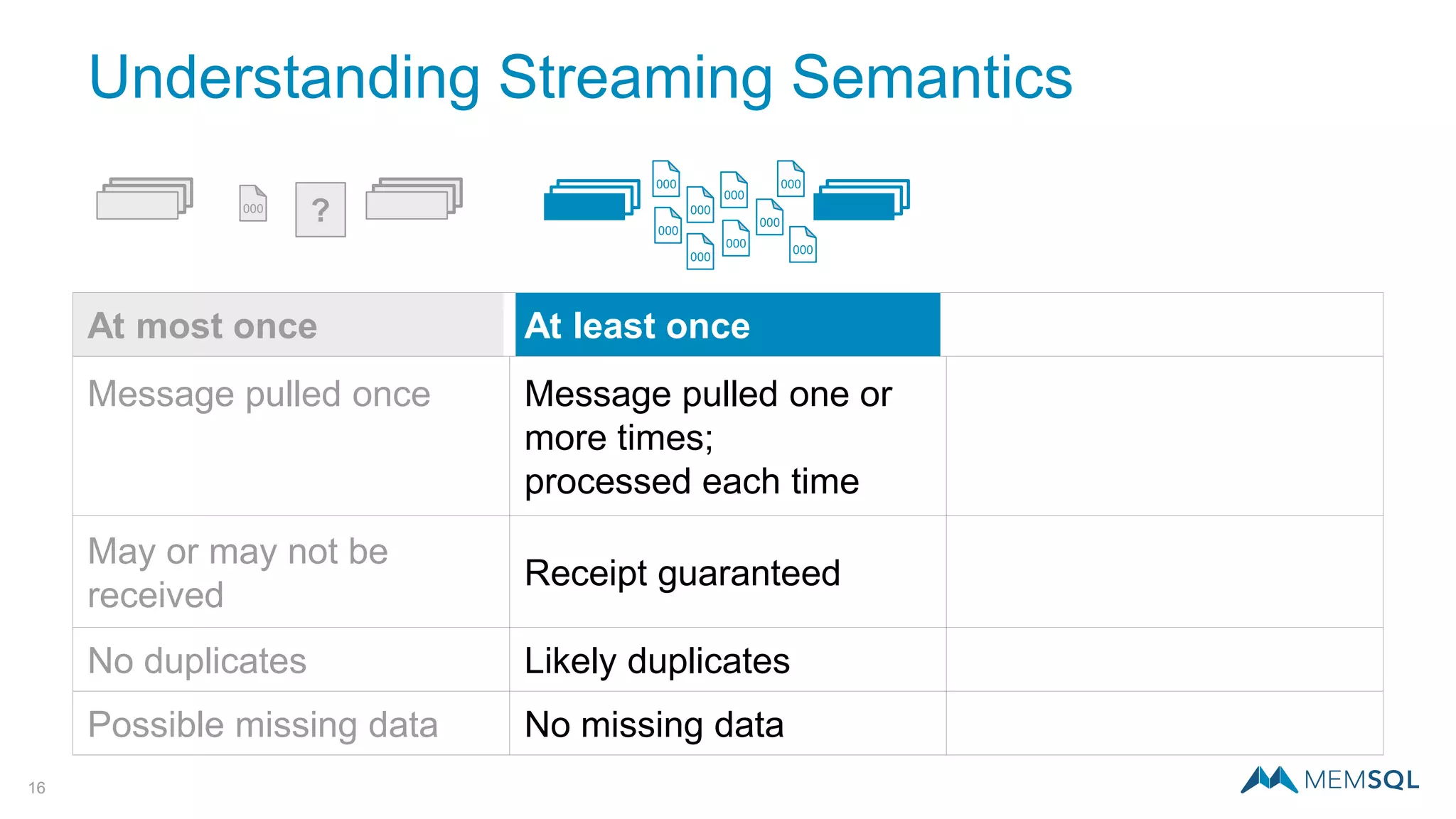
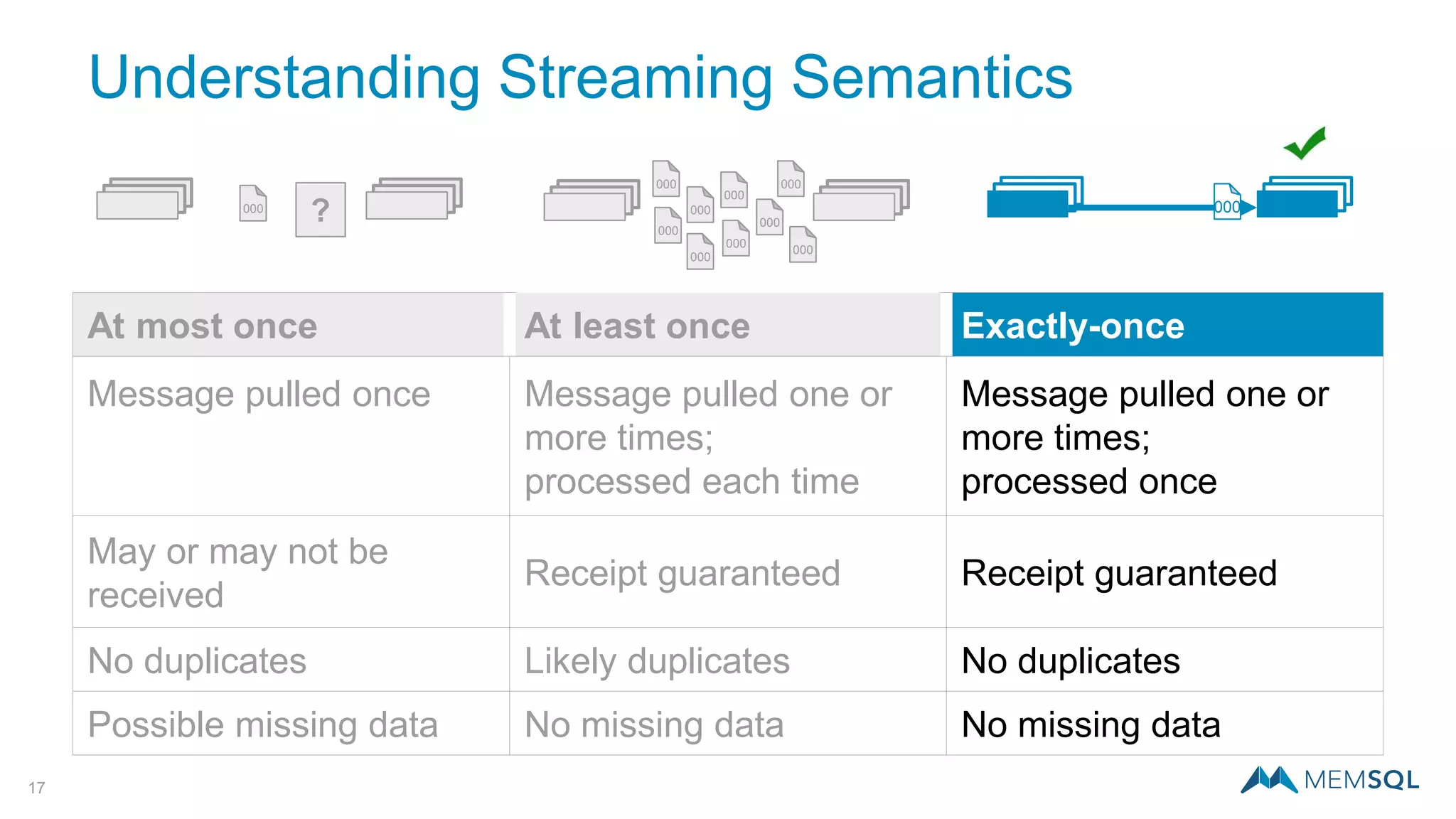
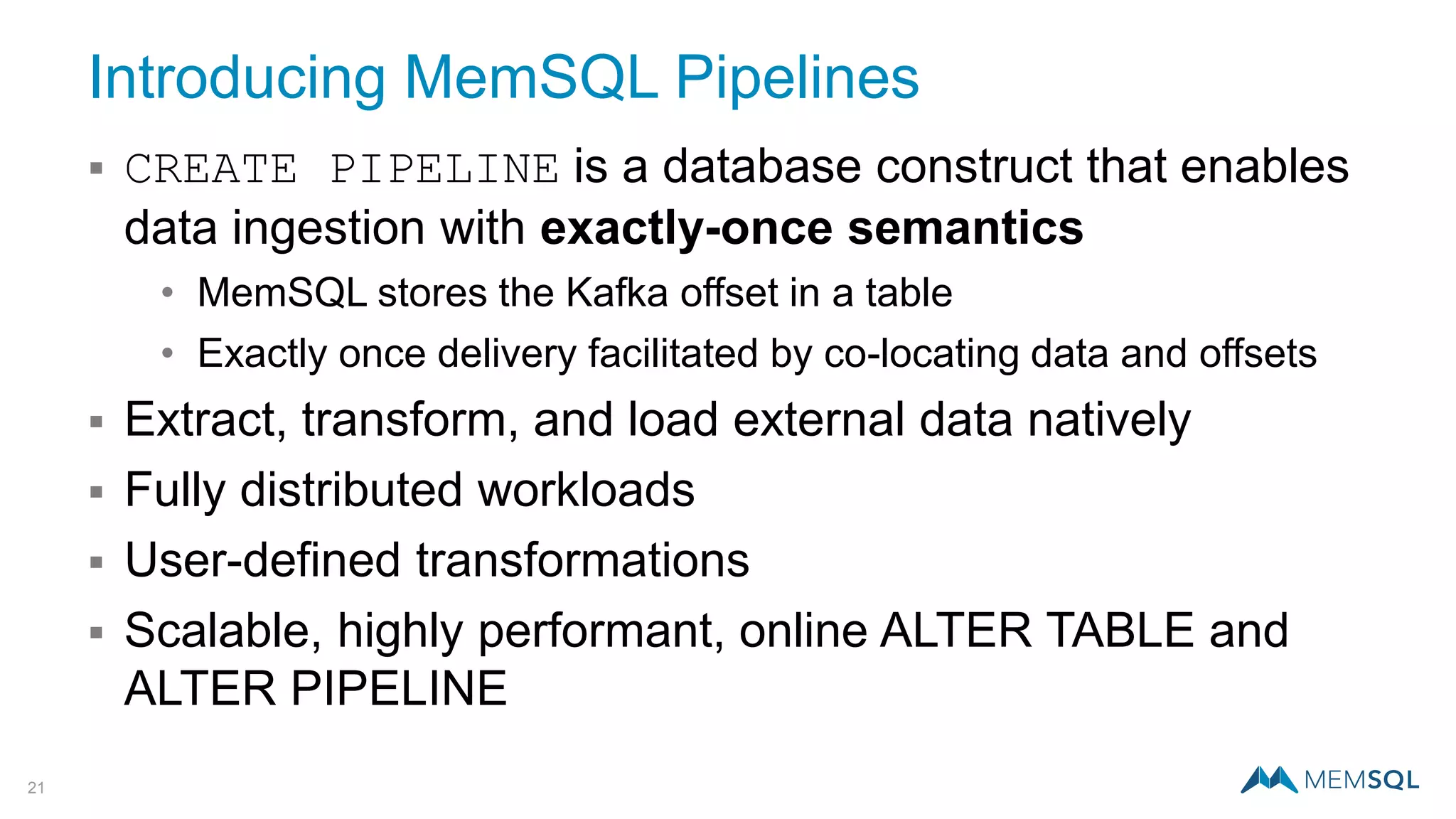
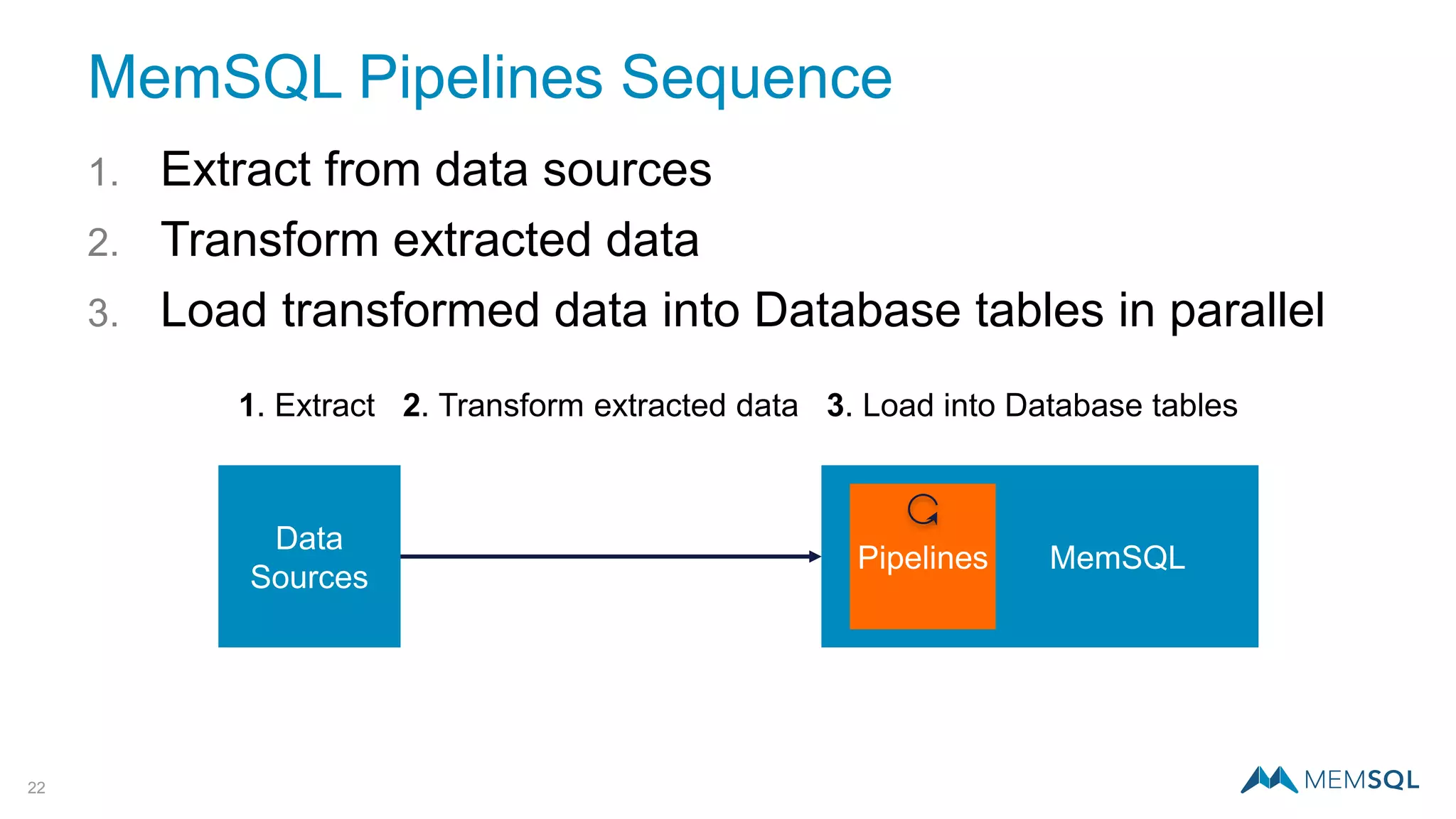
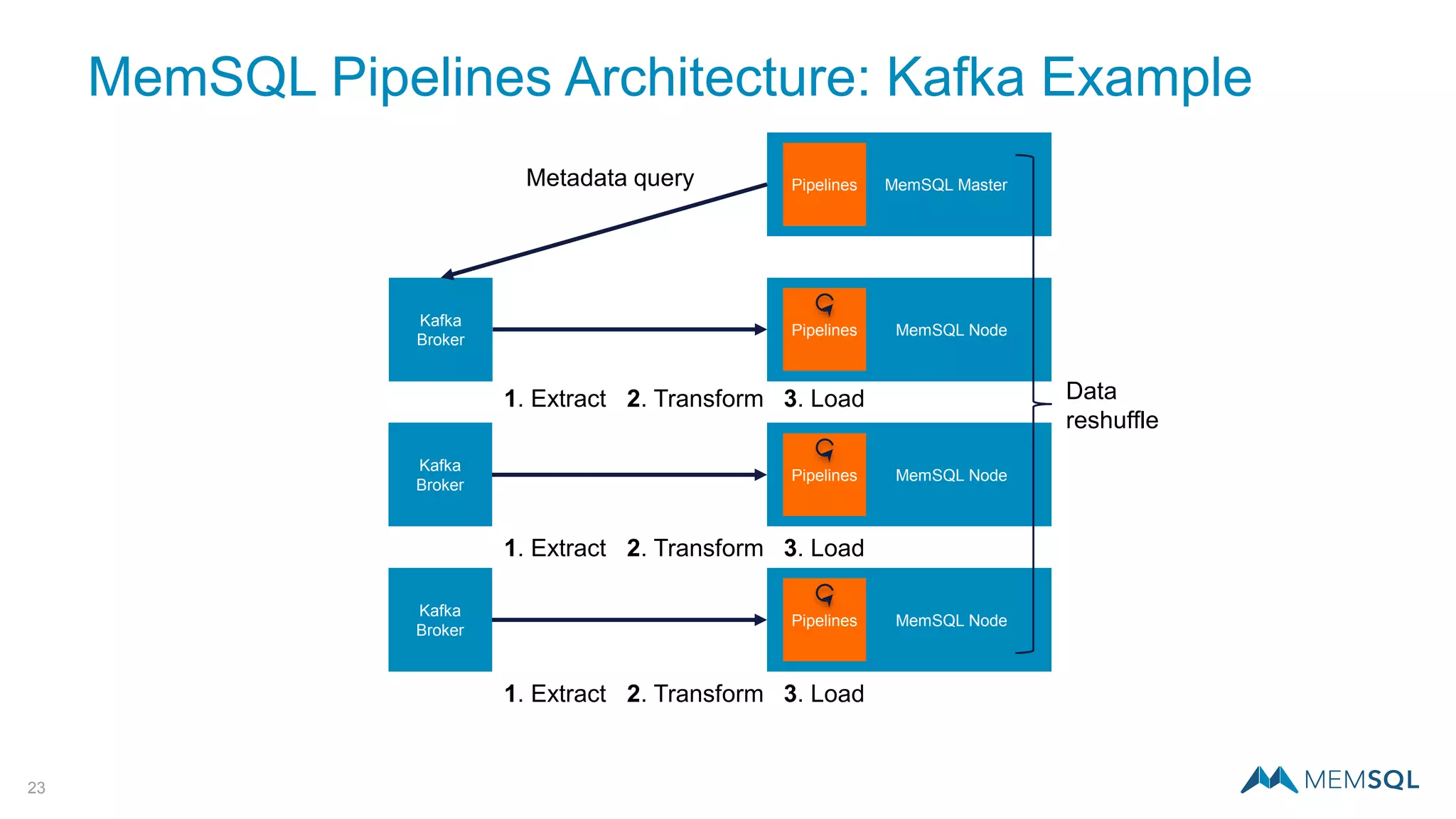
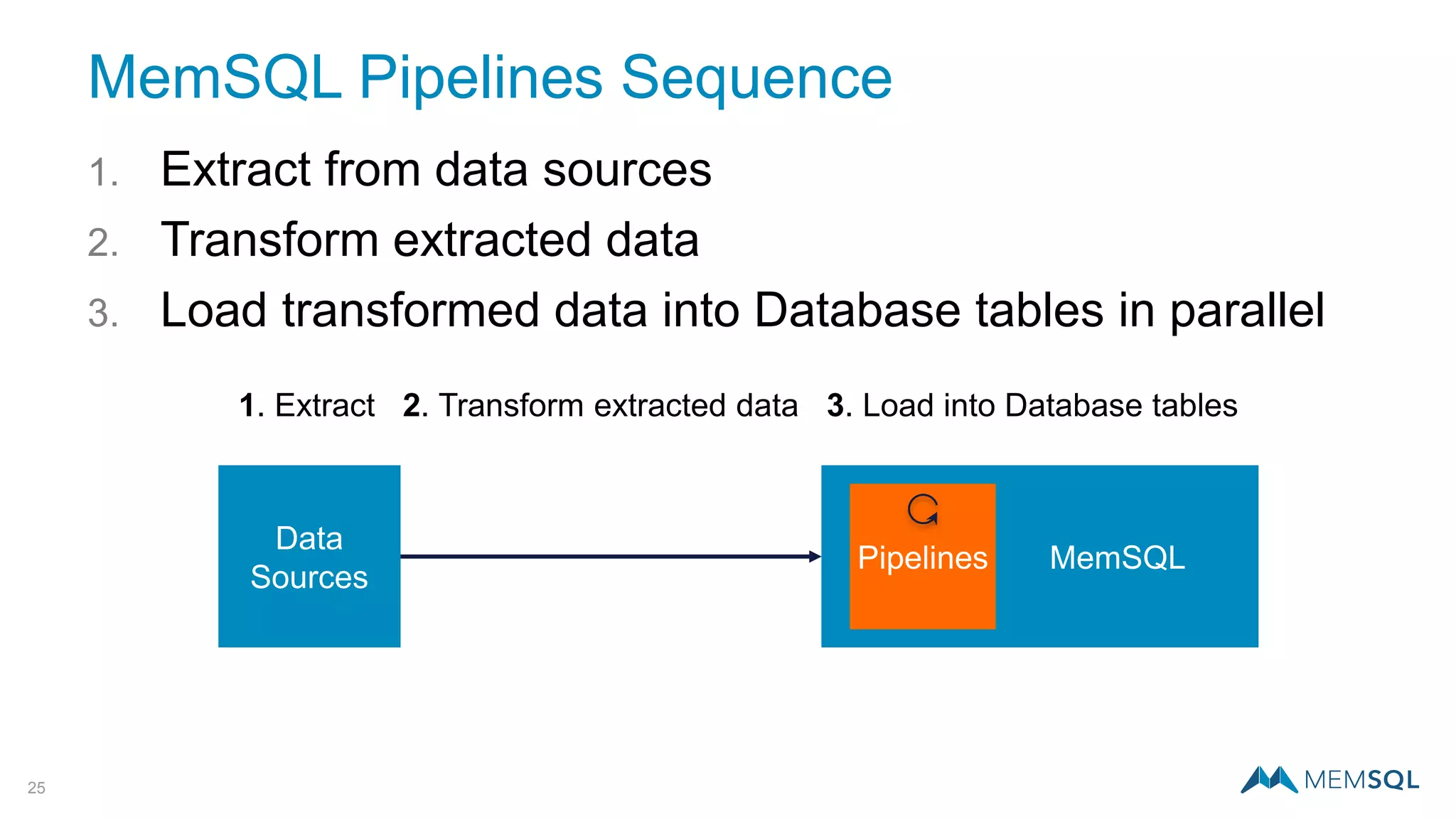
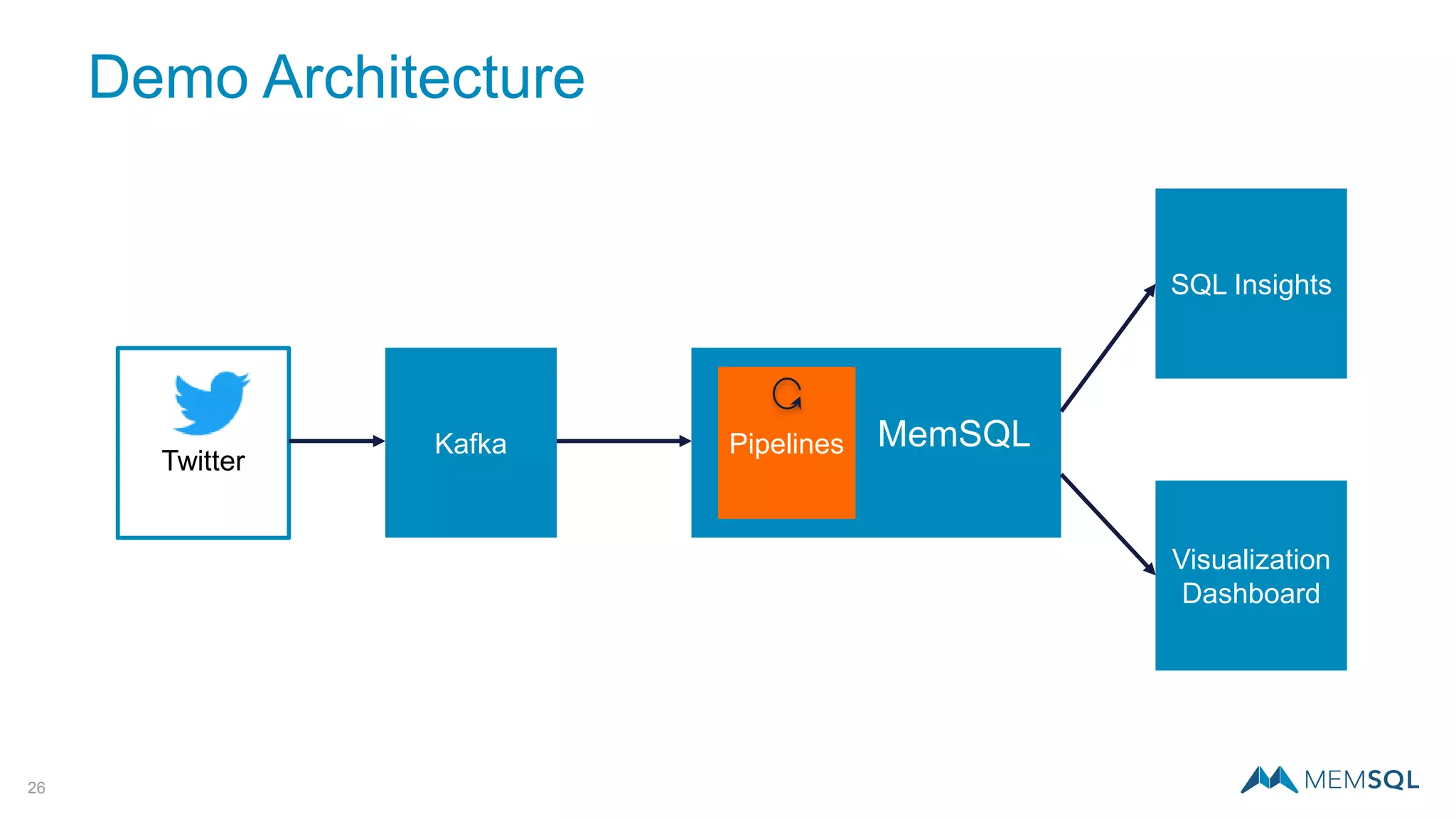
This document introduces MemSQL Pipelines, which allow for exactly-once data ingestion semantics when streaming data from Kafka into MemSQL. MemSQL Pipelines provide a native way to extract, transform, and load external data into MemSQL tables. They offer a scalable and highly performant ETL process across a distributed cluster. The document explains streaming semantics like at least once and exactly once delivery, and how MemSQL Pipelines coordinate with Kafka to enable exactly-once ingestion through offset tracking. It presents the architecture of MemSQL Pipelines and demonstrates their use through a live demo.