Embed presentation
Download to read offline



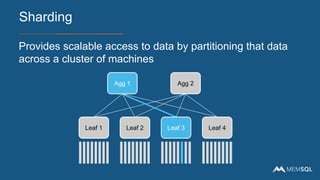





Building scalable software requires designing it so that adding more hardware allows the software to utilize that hardware. Key considerations include avoiding contention over shared resources like CPU, disk, memory and network. Examples of scalable architectures include lock-free skiplist indexes, sharding or partitioning data across multiple machines, distributed query execution, and columnar data stores. Building for scale changes how software features are developed, requiring simple initial designs, leveraging existing resources, ensuring the right technical decisions through code reviews and technical leadership.








