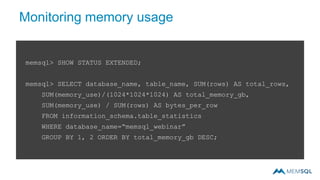
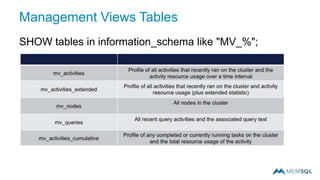
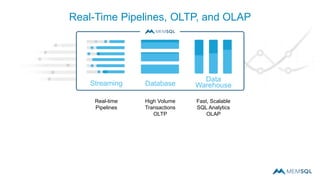
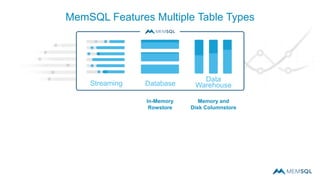
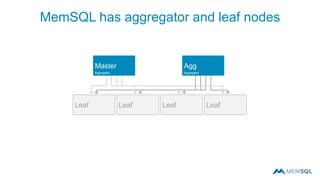
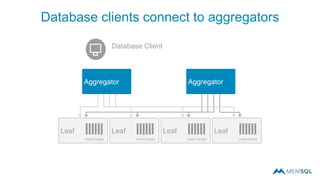
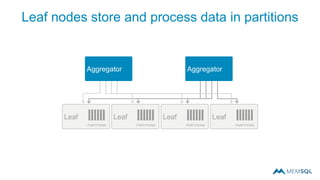
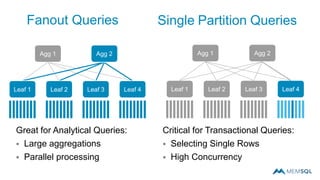
This document summarizes a webinar on advanced tips and tricks for MemSQL. It discusses the differences between rowstore and columnstore storage models and when each is best used. It also covers data ingestion using MemSQL Pipelines for real-time loading, data sharding and query tuning techniques like using reference tables. Additionally, it discusses monitoring memory usage, workload management using management views, and query optimization tools like analyzing and optimizing tables.











![ANALYZE and OPTIMIZE
ANALYZE TABLE
• Calculates table statistics
• Recommended after significant increase/refresh of data
OPTIMIZE TABLE [FULL | FLUSH]
• FULL: Sorts based on primary key (optimal index scans)
• FLUSH (Columnstore only): Flushes in-memory segment to disk
Recommended periodically after large loads](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memsql201webinarjan20181-180129182456/85/MemSQL-201-Advanced-Tips-and-Tricks-Webcast-30-320.jpg)