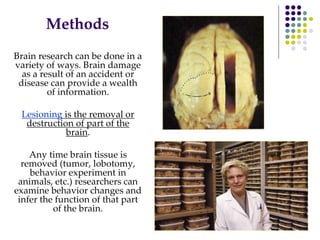
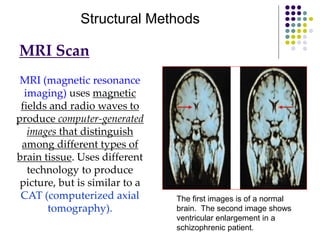
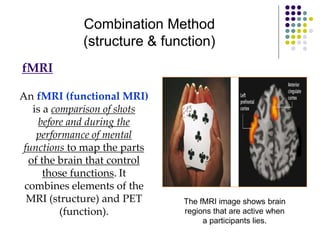
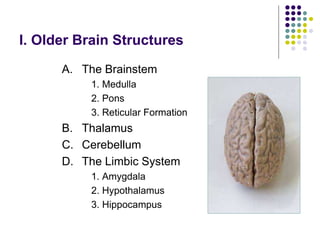
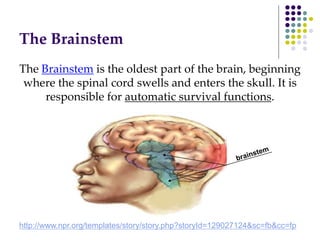
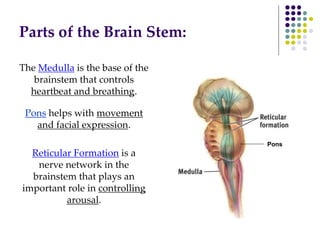
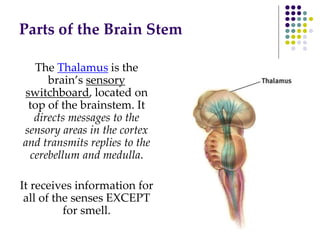
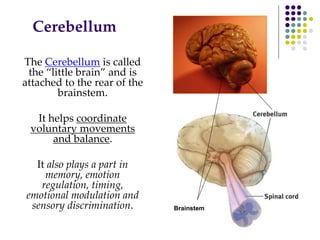
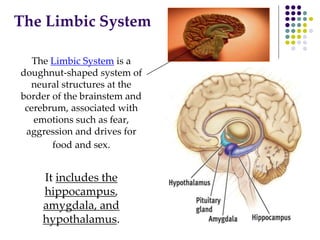
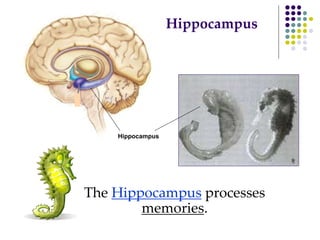
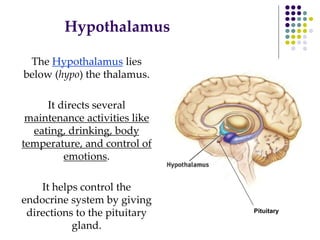
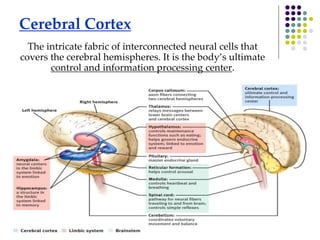
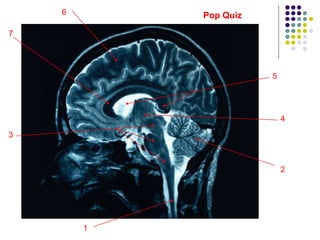
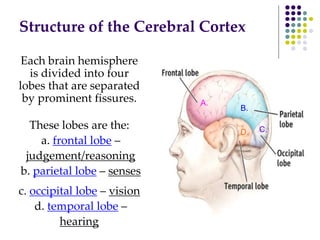
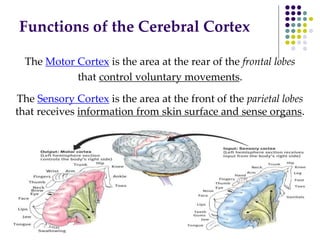
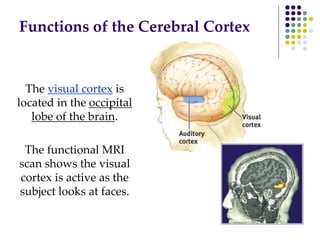
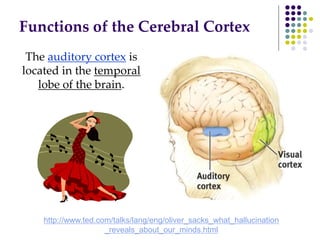
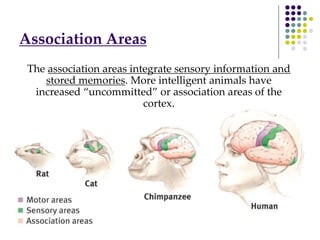
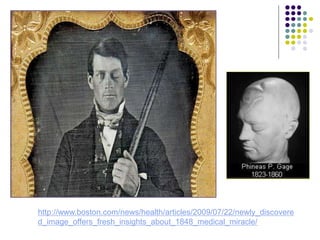
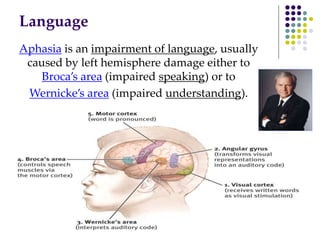
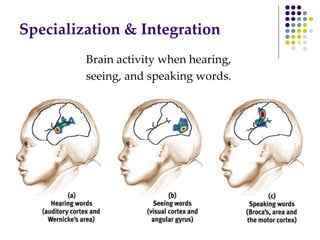
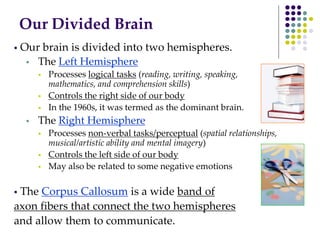
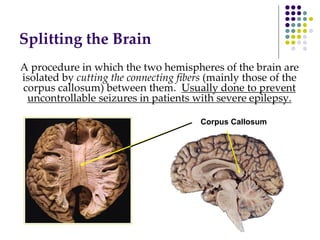
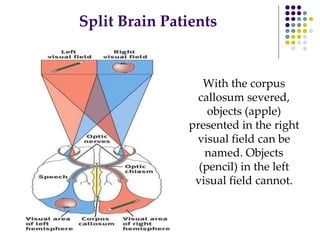
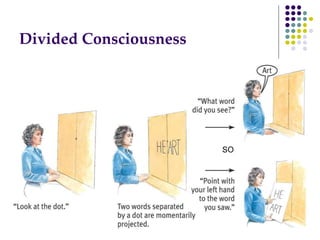
The document discusses various techniques for studying the brain, including examining behavior changes after brain damage or removal of brain tissue. It also describes functional brain imaging methods like EEG, PET scans, MRI scans, and fMRI that map brain activity. The major structures of the brain are outlined, including the brainstem, cerebellum, limbic system, and cerebral cortex. Functions of different brain regions are explained, such as the motor cortex controlling movement and sensory cortex processing sensory information. The plasticity of the brain is noted, along with lateralization of functions between the left and right hemispheres.