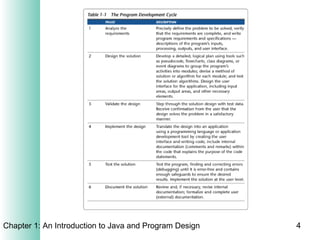
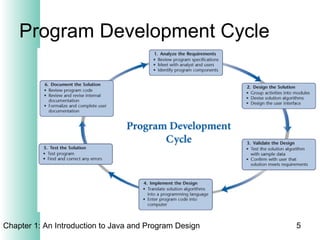
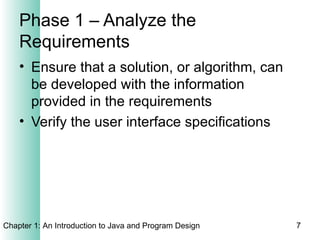
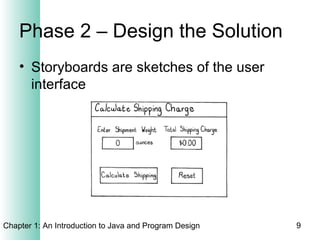
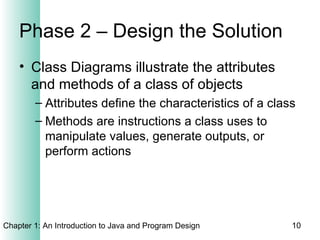
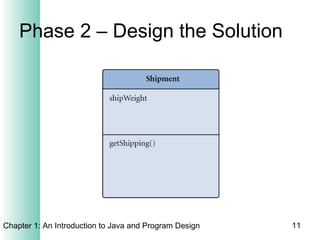
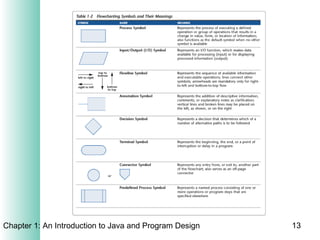
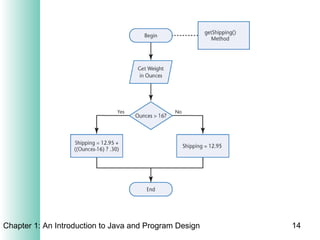
This document provides an overview of the program design process. It discusses the six main phases: (1) analyzing requirements, (2) designing the solution, (3) validating the design, (4) implementing the design, (5) testing the solution, and (6) documenting the solution. Key aspects of each phase like flowcharts, pseudocode, unit testing, and integration testing are explained at a high level.