The document discusses the key stages in the program development process:
1. Planning - Identifying requirements, goals, inputs and outputs
2. Coding - Writing the source code based on the planning
3. Testing and Debugging - Thoroughly testing for errors and fixing them
4. Documentation - Providing documentation on how to use and maintain the program
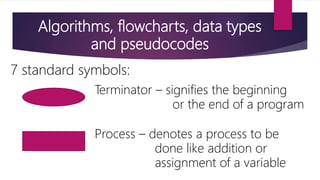
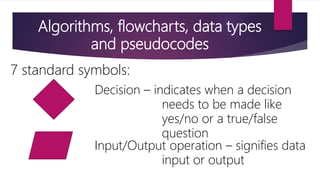
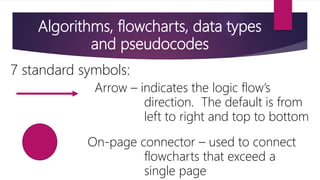
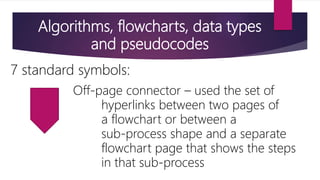
It also covers algorithms, flowcharts, pseudocode and data types which are important tools used in problem solving and representing programs. Algorithms define step-by-step processes, flowcharts provide graphical representation, and pseudocode describes programs using natural language.