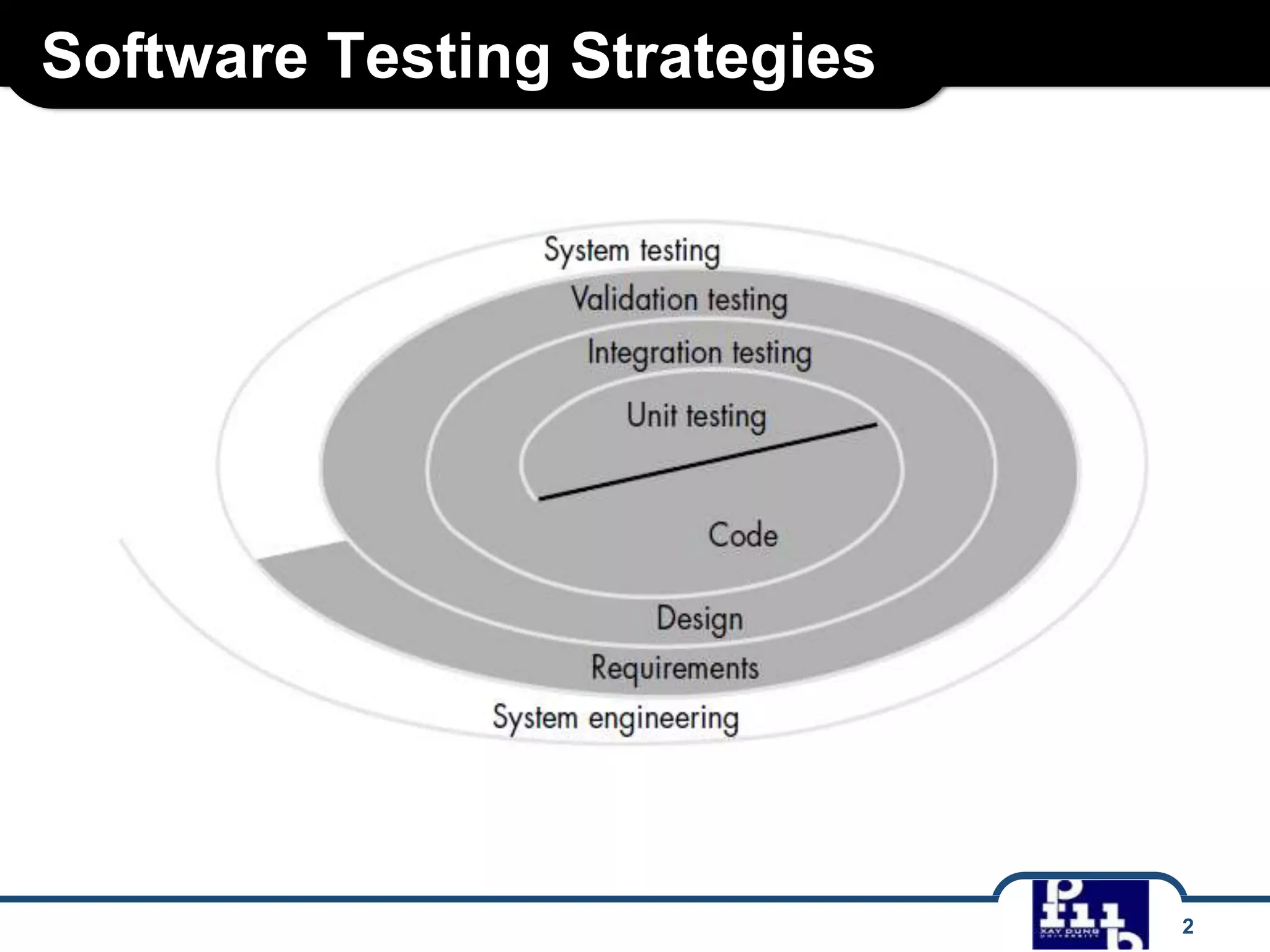
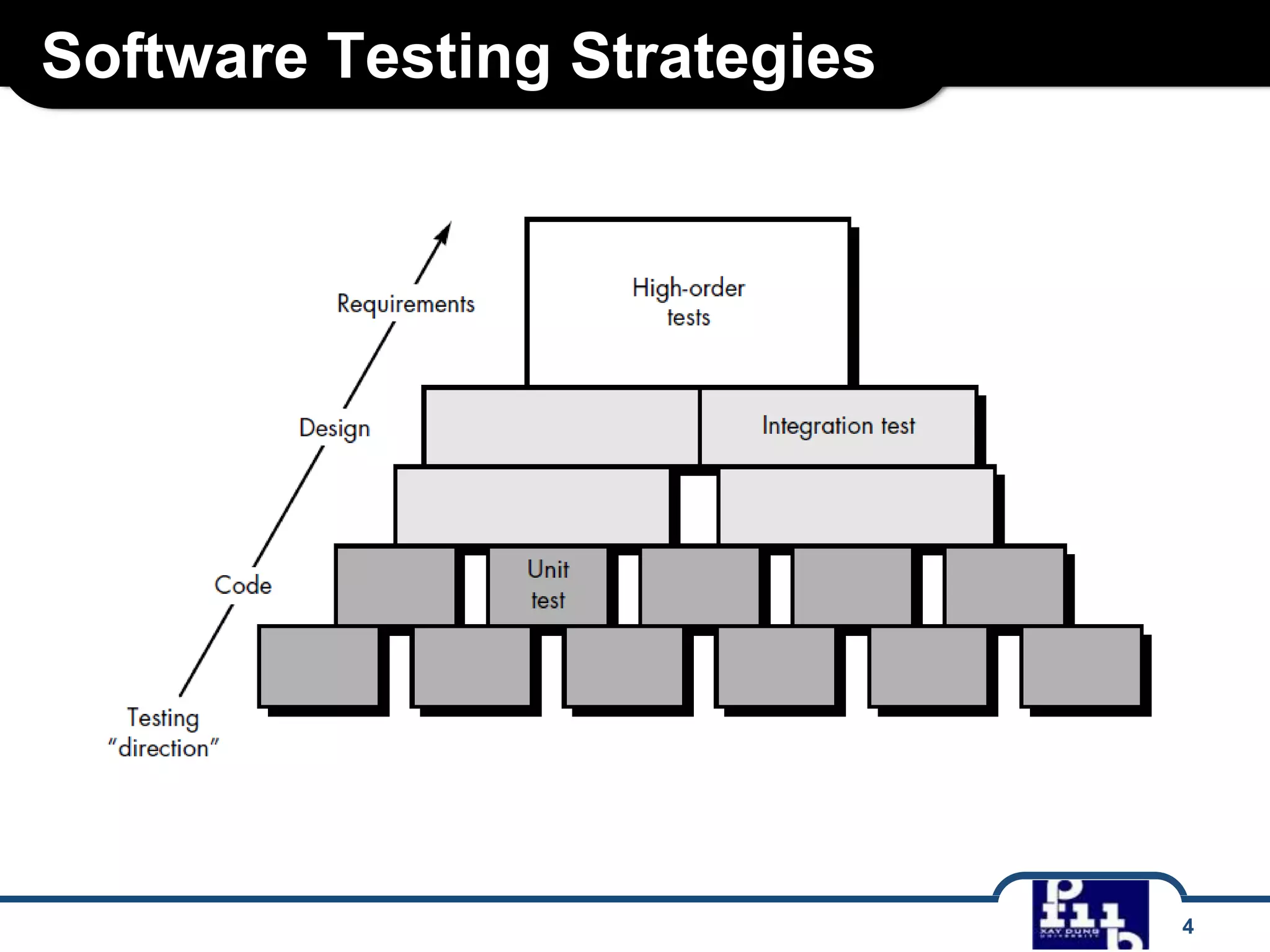
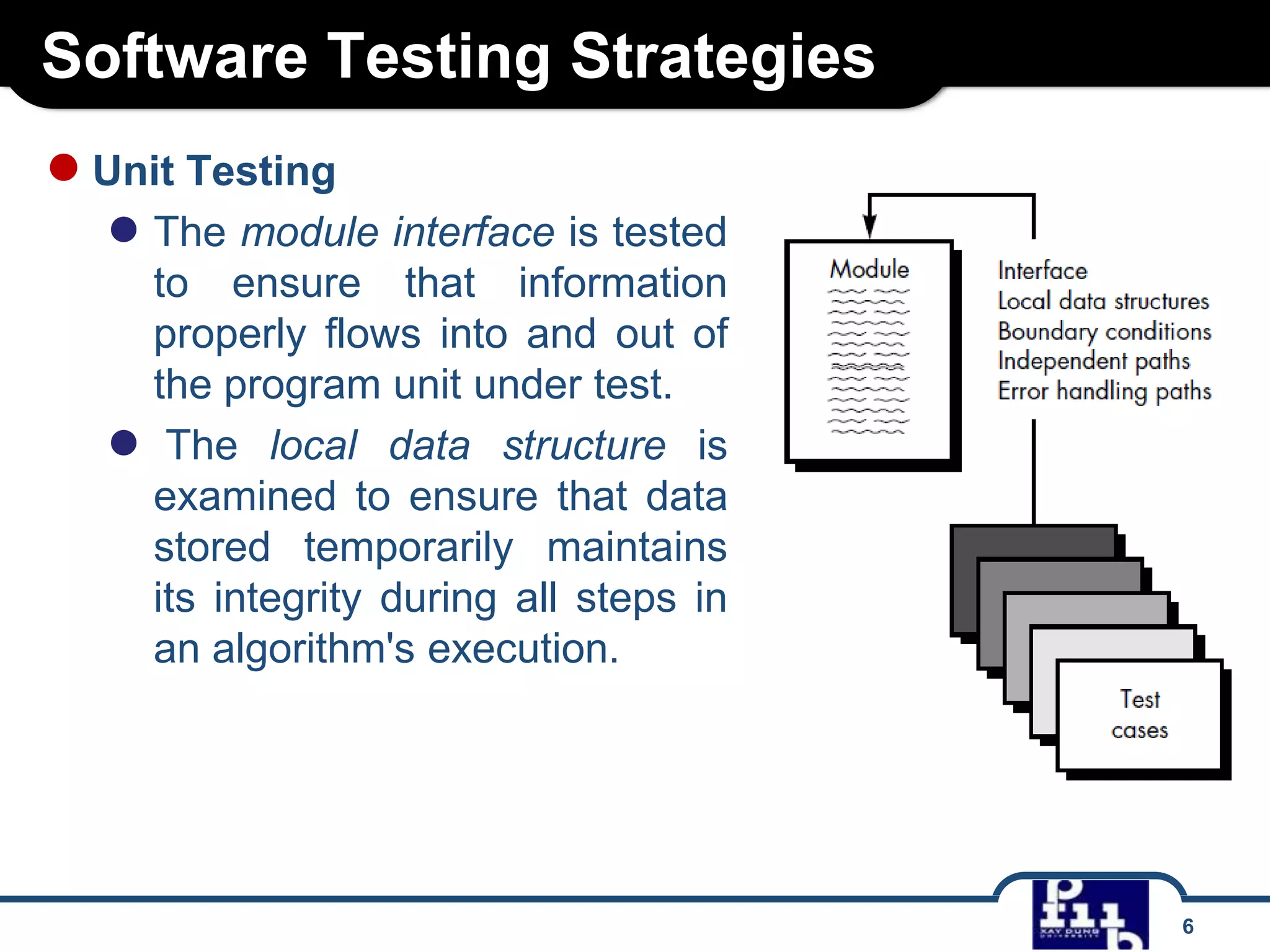
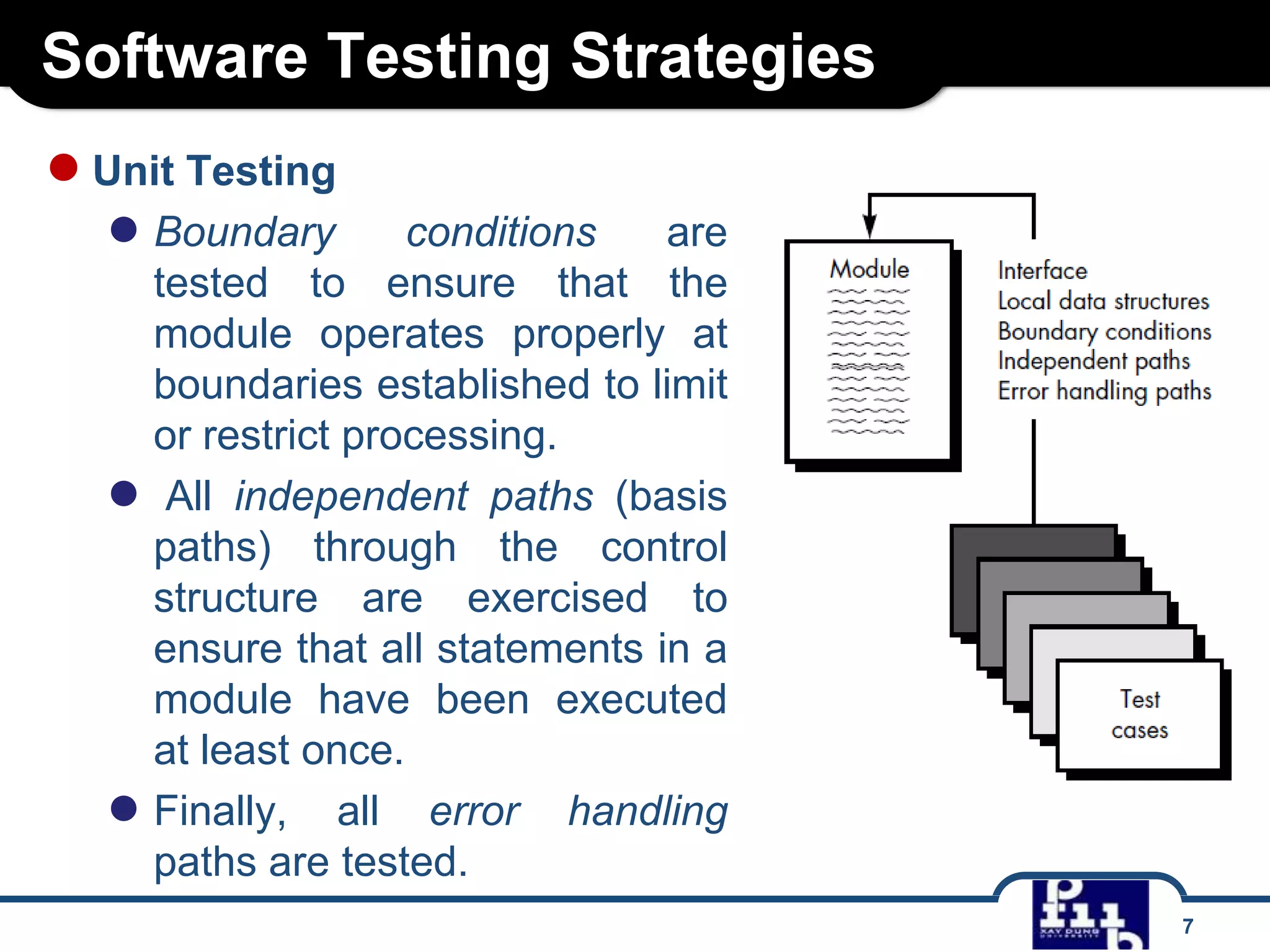
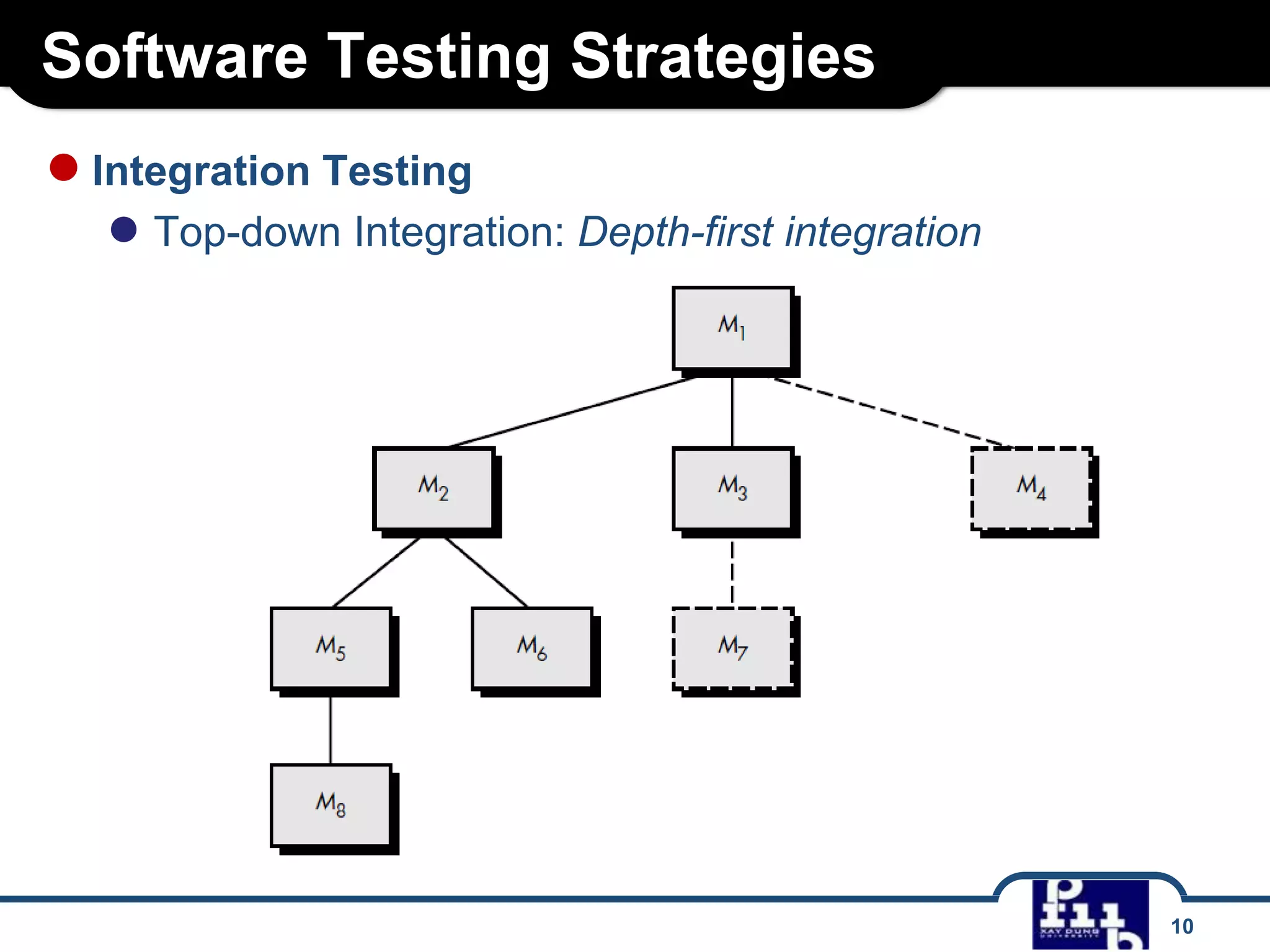
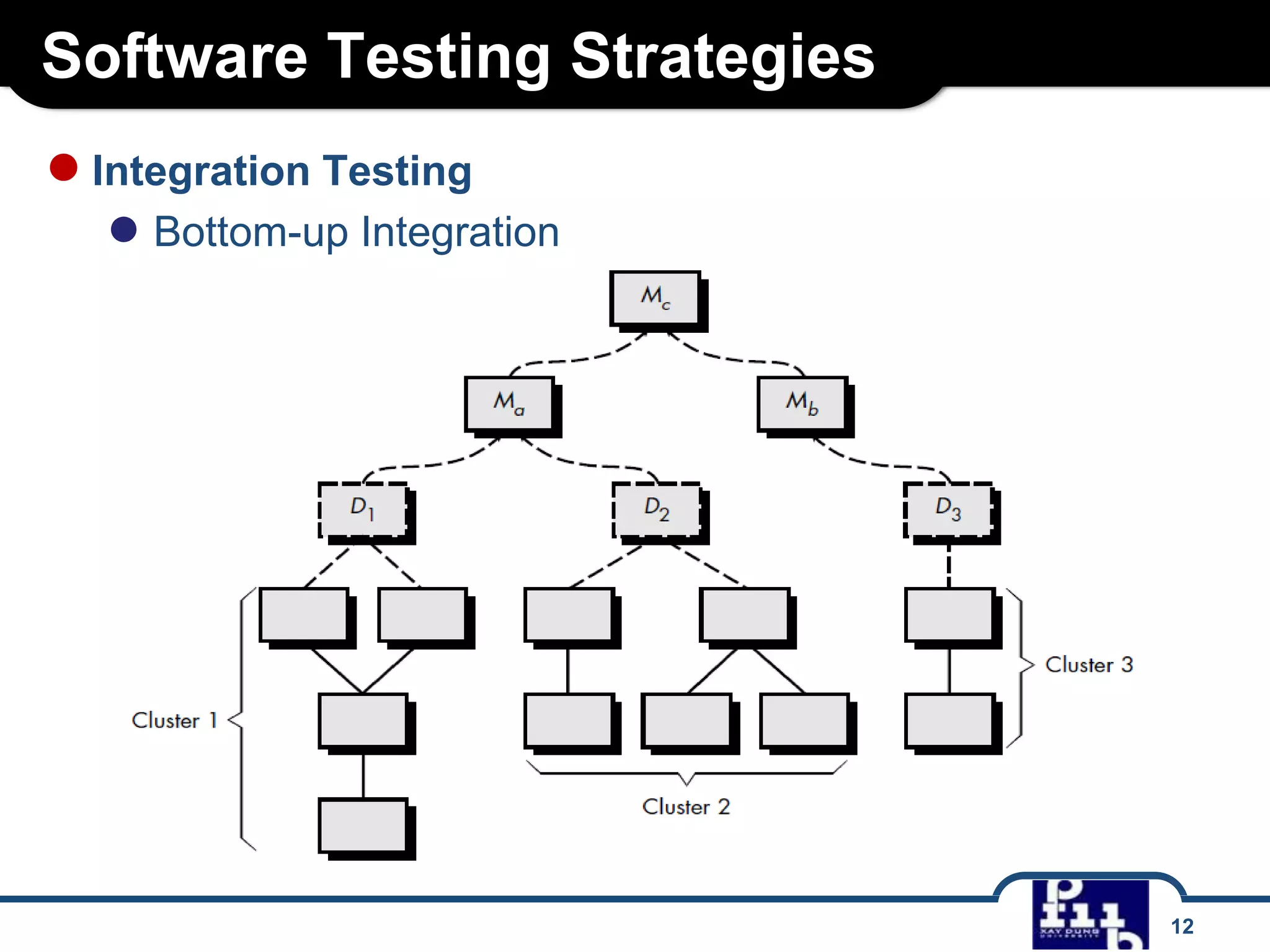
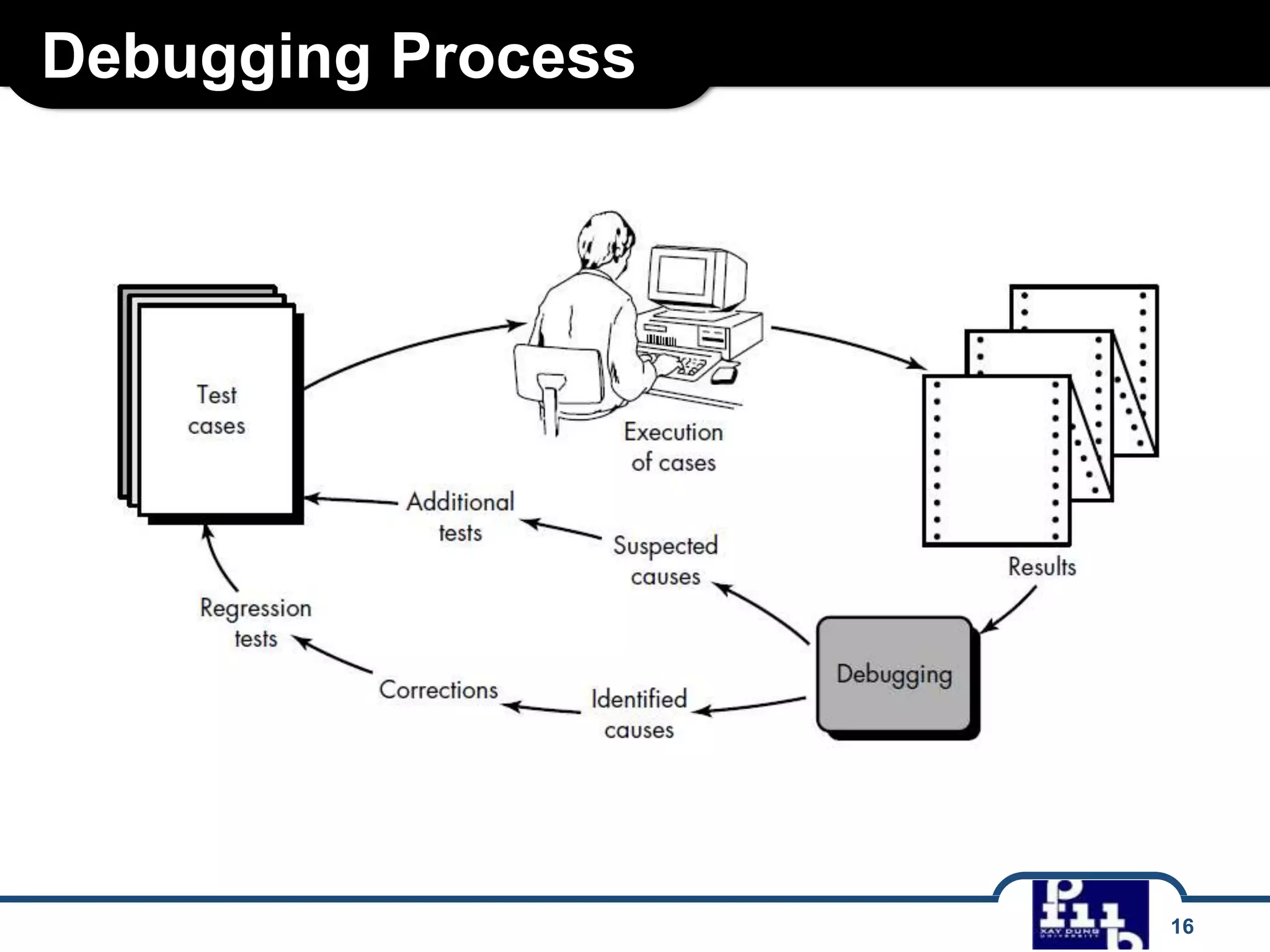
The document outlines various software testing strategies, including unit testing, integration testing, validation testing, and system testing, detailing the focus and methodologies for each type. It describes the purposes of each testing stage and key techniques like top-down and bottom-up integration, along with alpha and beta testing. Additionally, it highlights specific testing aspects such as recovery, security, stress, and performance testing.