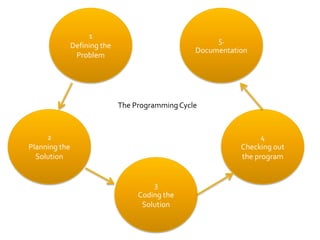
This document outlines the key steps in the programming cycle: 1) Defining the problem by understanding what needs to be solved, 2) Planning the solution through flowcharts to map out processing steps, 3) Coding the solution by writing program instructions, 4) Checking for errors by debugging, and 5) Creating documentation such as problem statements, flowcharts, and operating instructions. Documentation is important for maintaining the program.