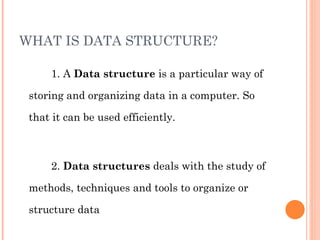
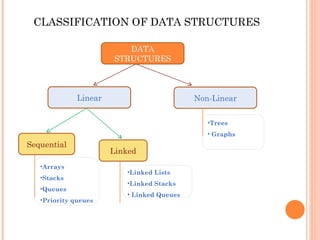
This document provides an introduction to data structures and algorithms. It defines an algorithm as a set of steps to solve a problem and describes data structures as organized ways to store and access data. Common data structures include arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, trees and graphs. Abstract data types define the fundamental operations on data objects in a data structure independently of their implementation. Linear data structures like arrays represent lists in one dimension while non-linear structures represent two-dimensional relationships. Stacks follow the last-in, first-out principle with push and pop operations, while queues are first-in, first-out. Selection of the appropriate data structure depends on the application.




![ABSTRACT DATA TYPES [ADT] WHAT IS DATA TYPES? A data type refers to the type of values that variables in a programming language hold. WHAT IS ADT? Abstract data type refers to the data objects (refers to the list of elements such as list of integers or list of alphabetical strings) which comprise the data structure, and their fundamental operations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-ds-110727020339-phpapp01/85/Intro-ds-6-320.jpg)




![TYPES OF ARRAY One-dimensional A[1:5] Two dimensional B[1:3][1:4] Multi dimensional C[1:3][1:6][1:8]….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-ds-110727020339-phpapp01/85/Intro-ds-12-320.jpg)





![Implementation of push operation on a stack Procedure PUSH(STACK,n,top,item) if(top=n) then STACK_FULL; else { top=top+1; STACK[top]=item; } end PUSH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-ds-110727020339-phpapp01/85/Intro-ds-18-320.jpg)
![Implementation of pop operation on a stack Procedure POP(STACK,top,item) if(top=0) then STACK_EMPTY; else { item=STACK[top]; top=top-1; } end POP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-ds-110727020339-phpapp01/85/Intro-ds-19-320.jpg)

