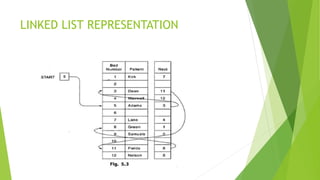
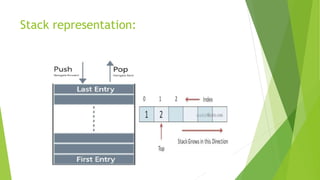
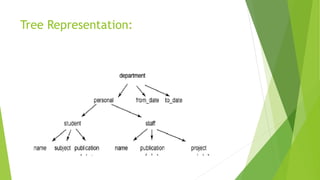
The document defines data structures as organizational schemes for storing and retrieving data in a computer's memory, highlighting the impact of organization on program performance. It categorizes data structures into primitive (such as char, int, float) and non-primitive types, with examples including linear structures like arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues, and non-linear structures like trees and graphs. The document further explains operations such as searching, insertion, and deletion for various data structures.