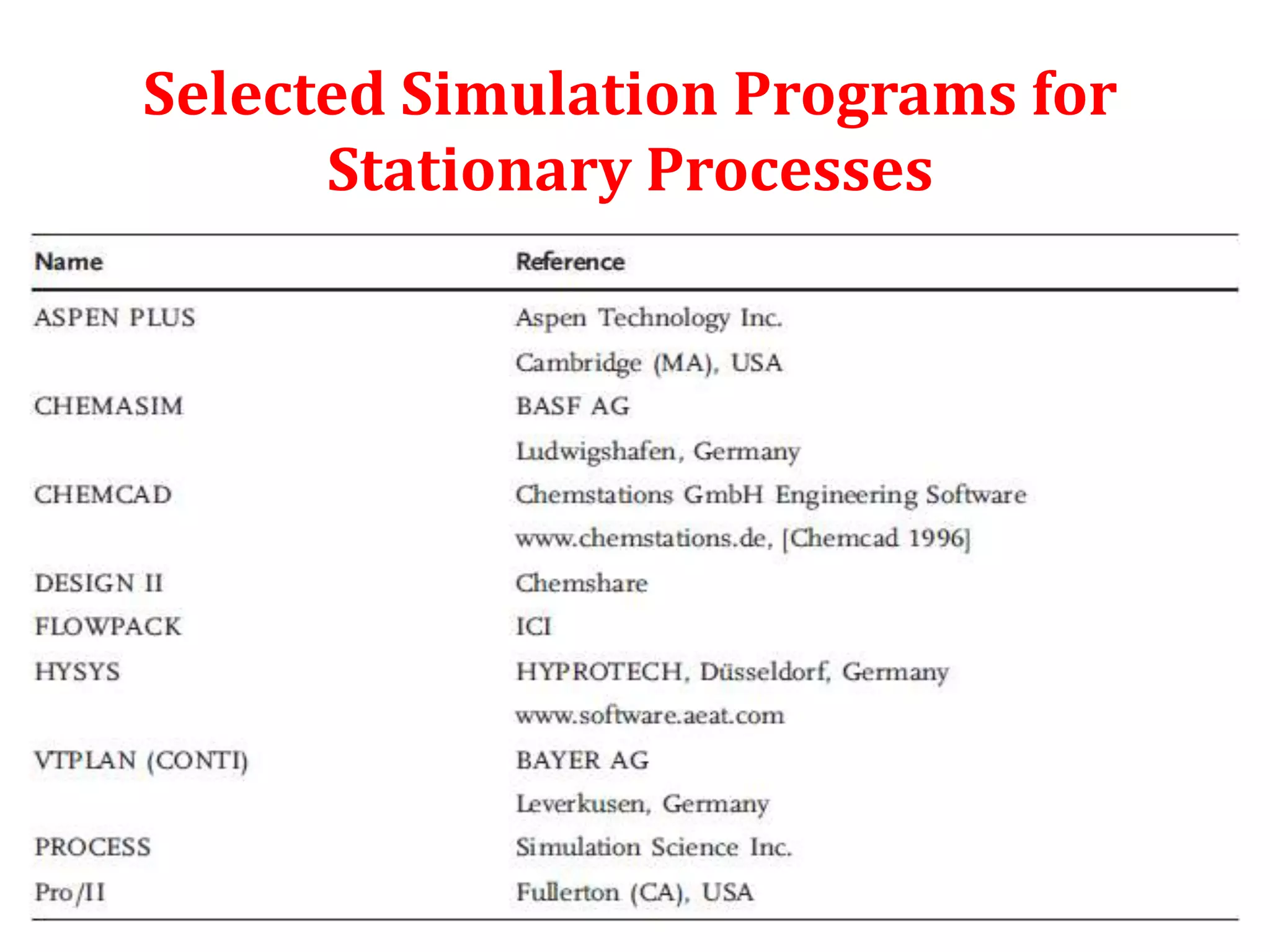
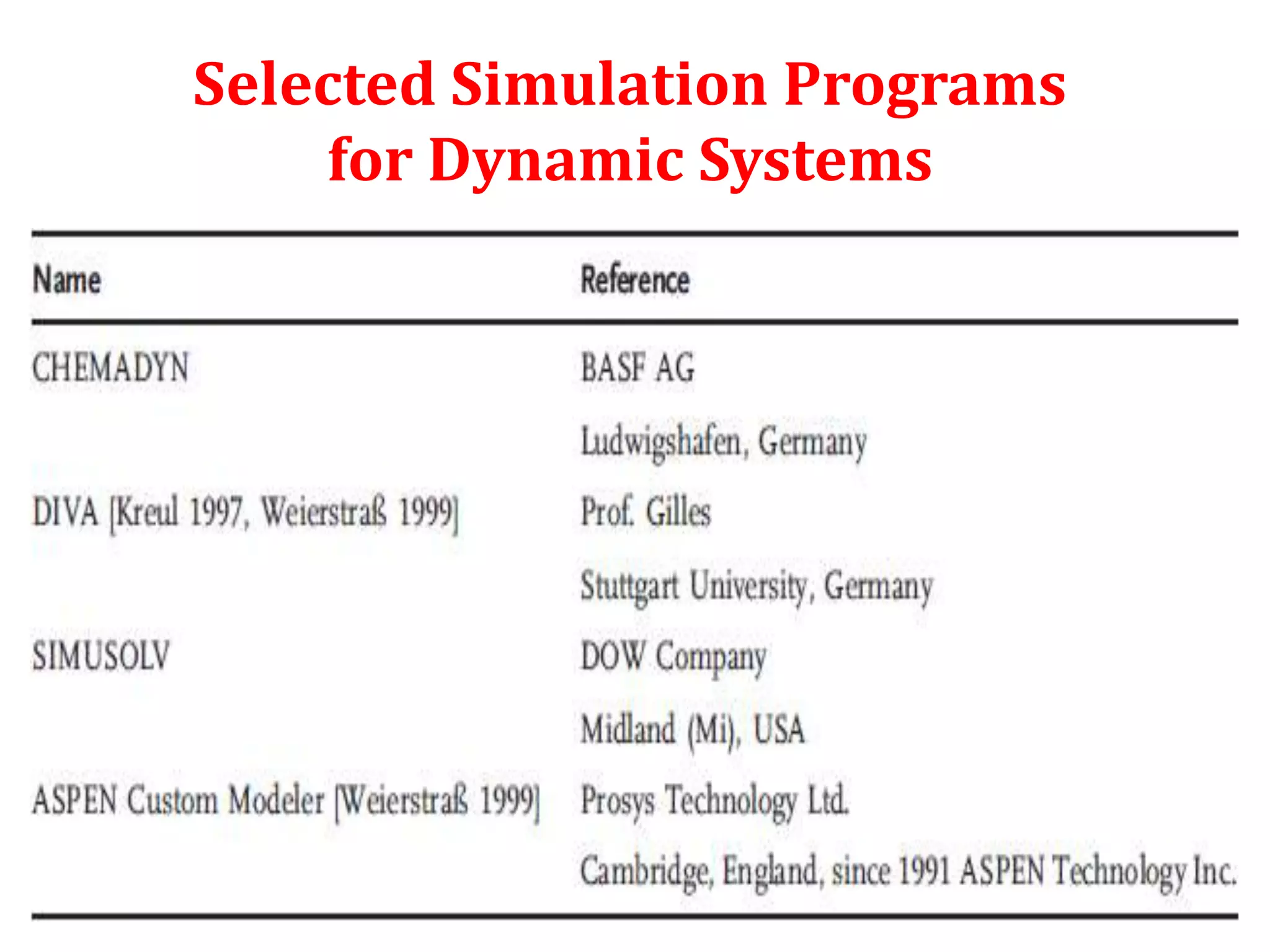
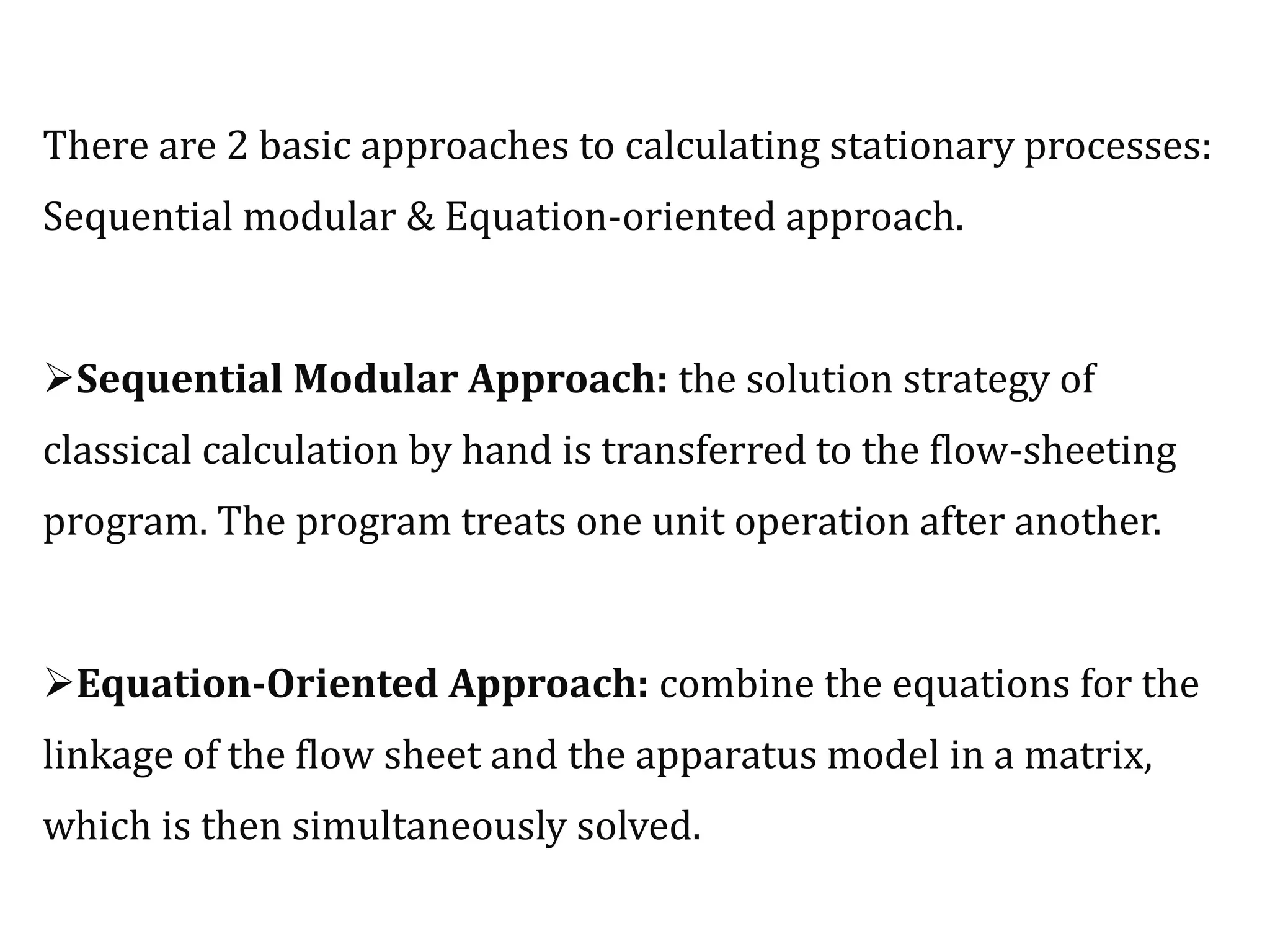
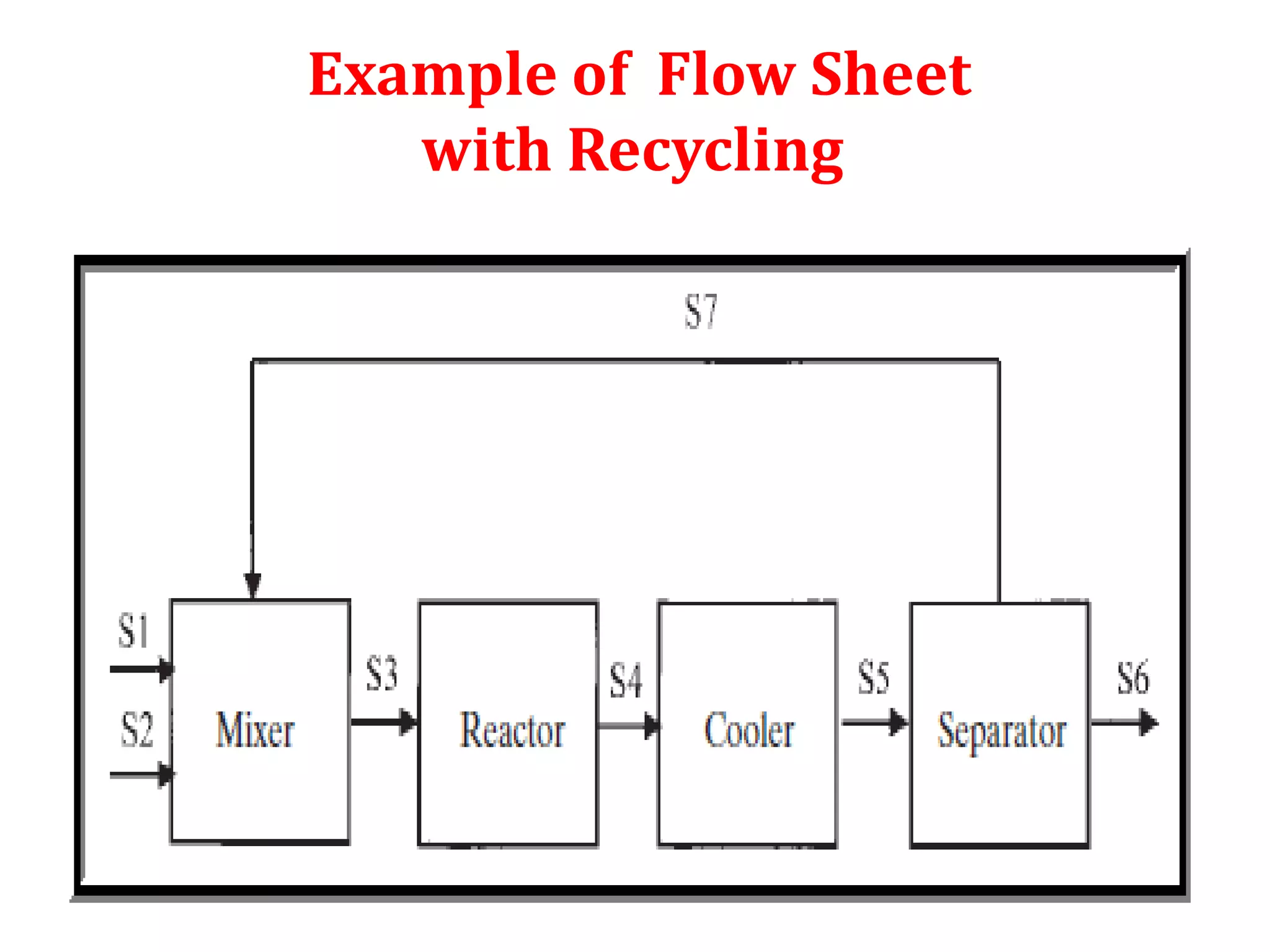
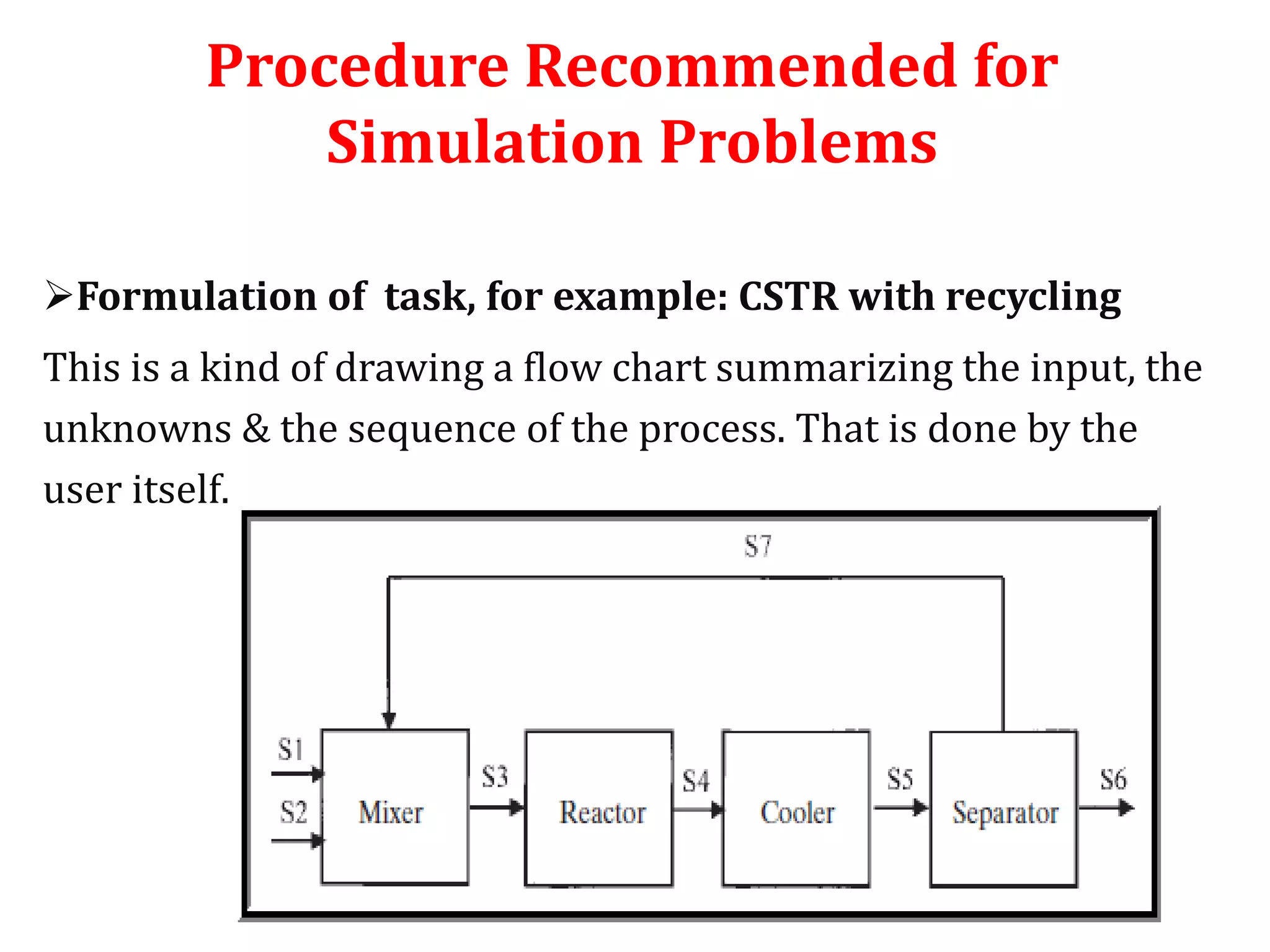
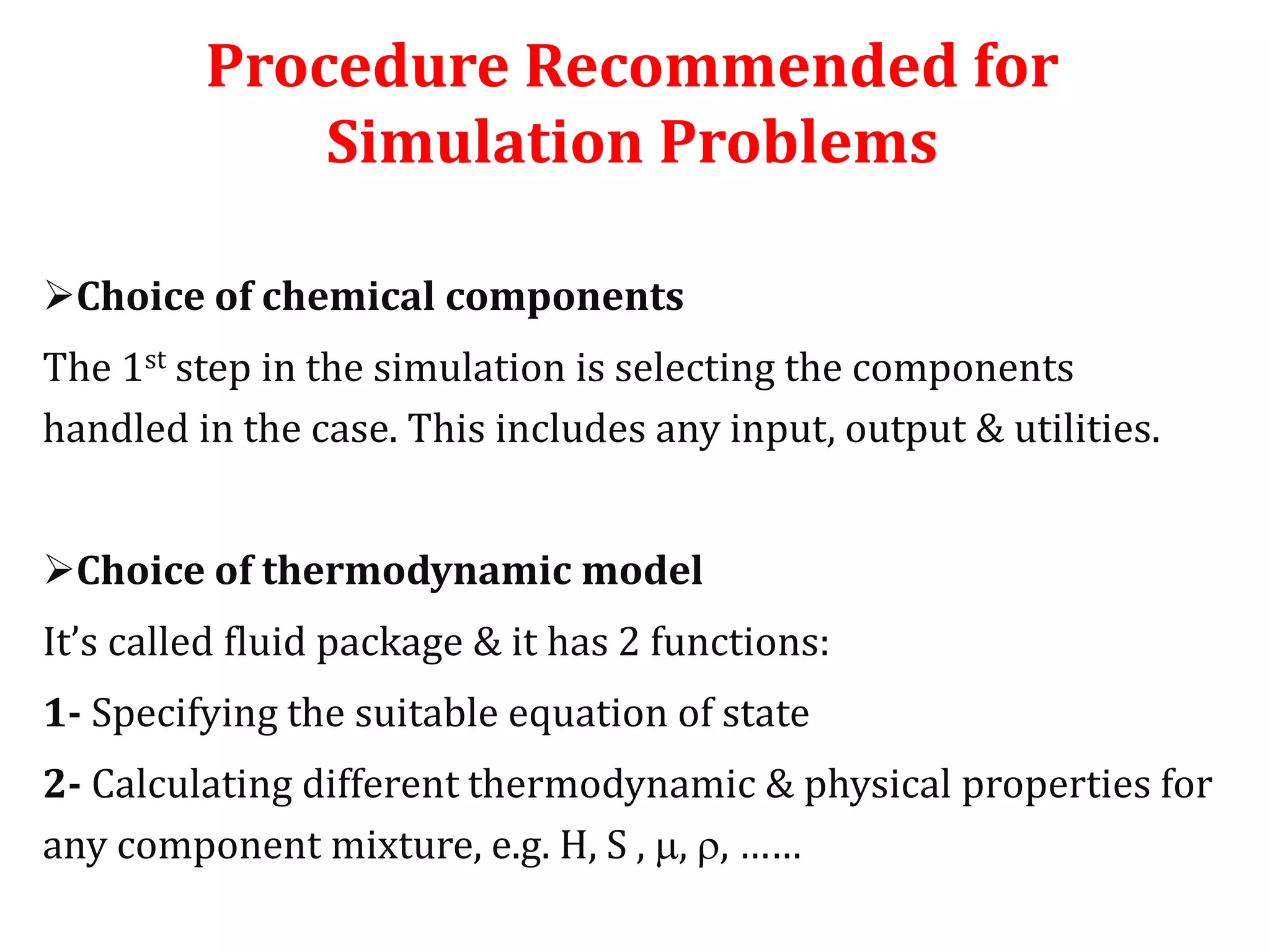
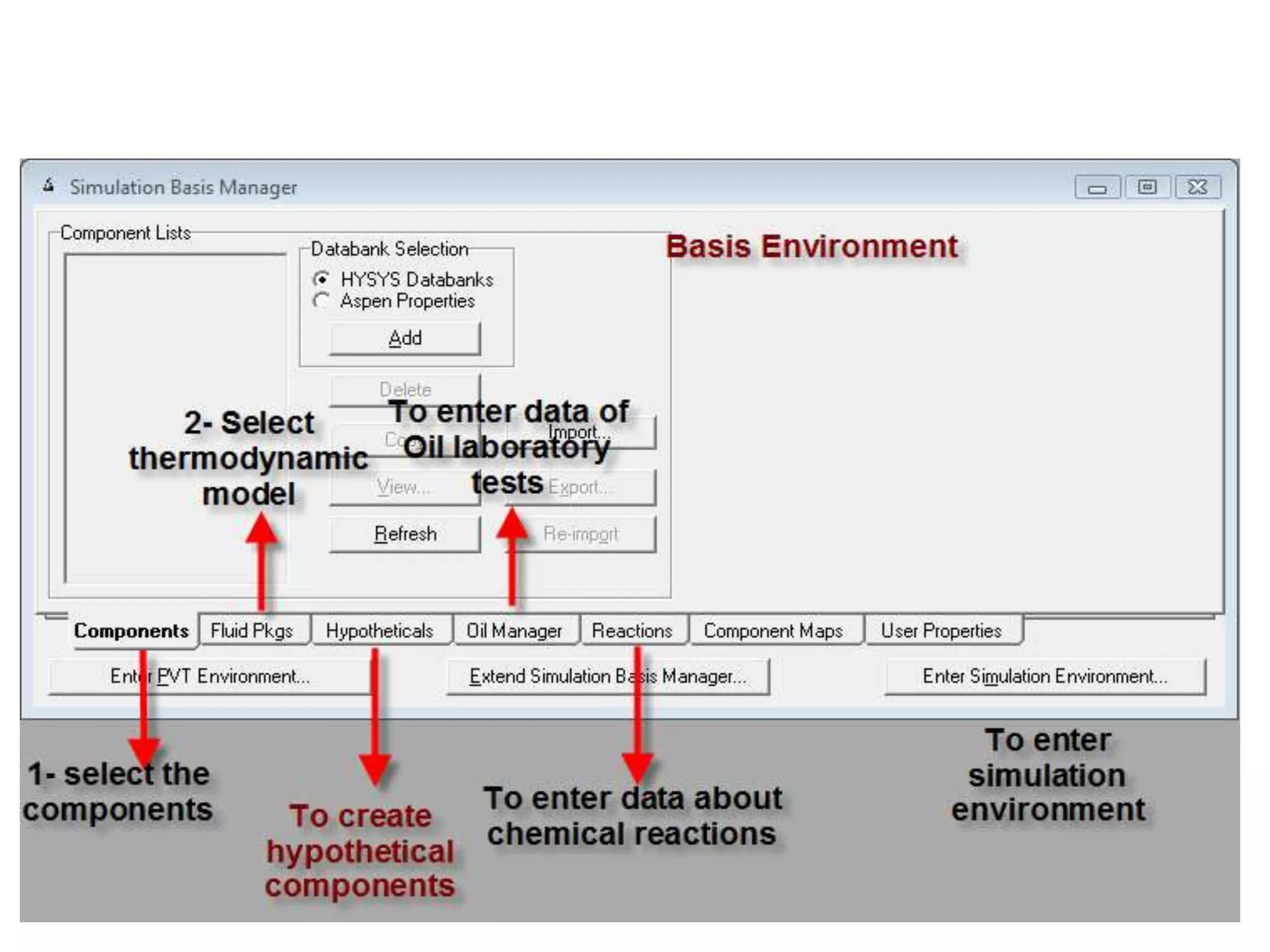
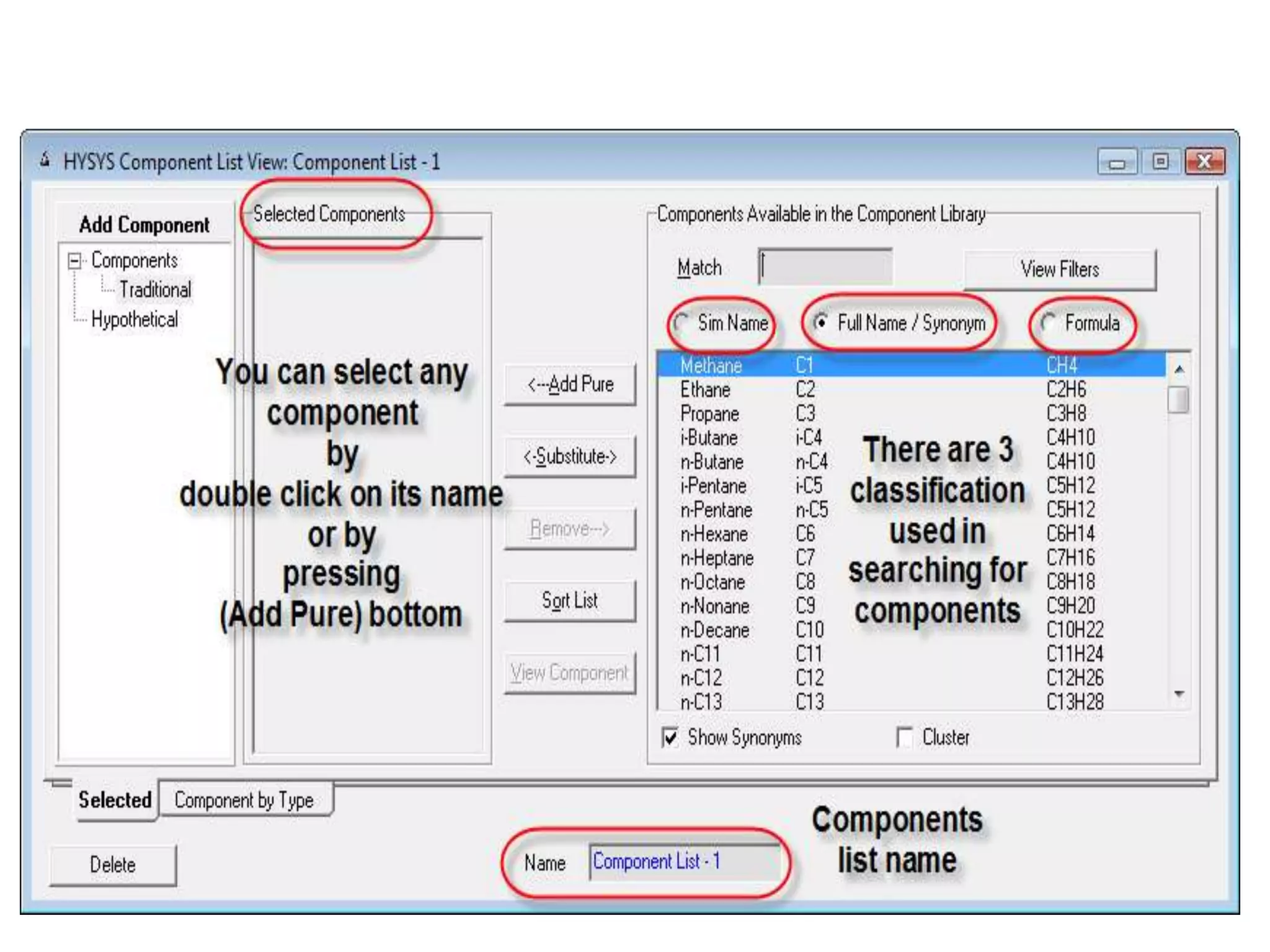
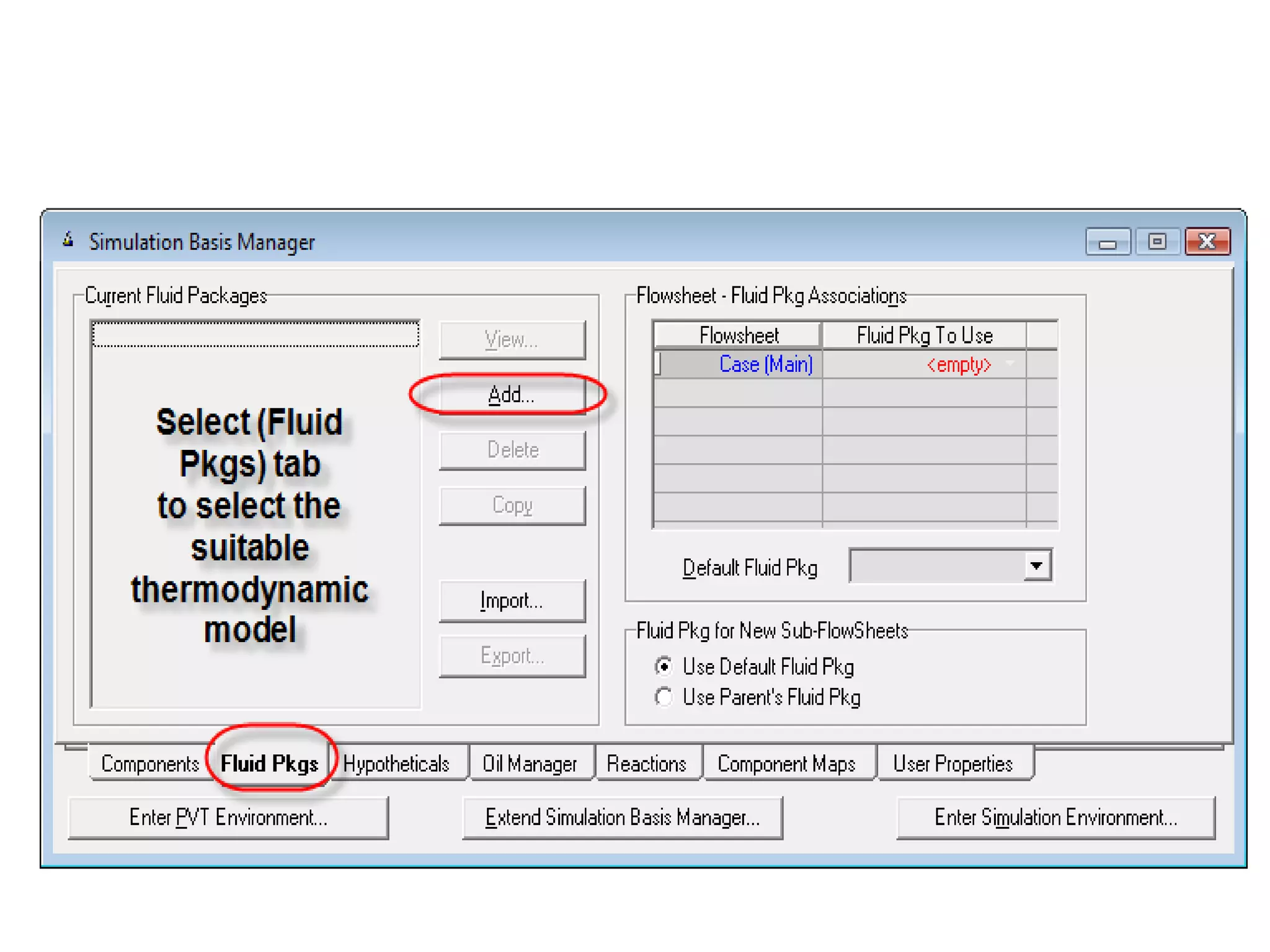
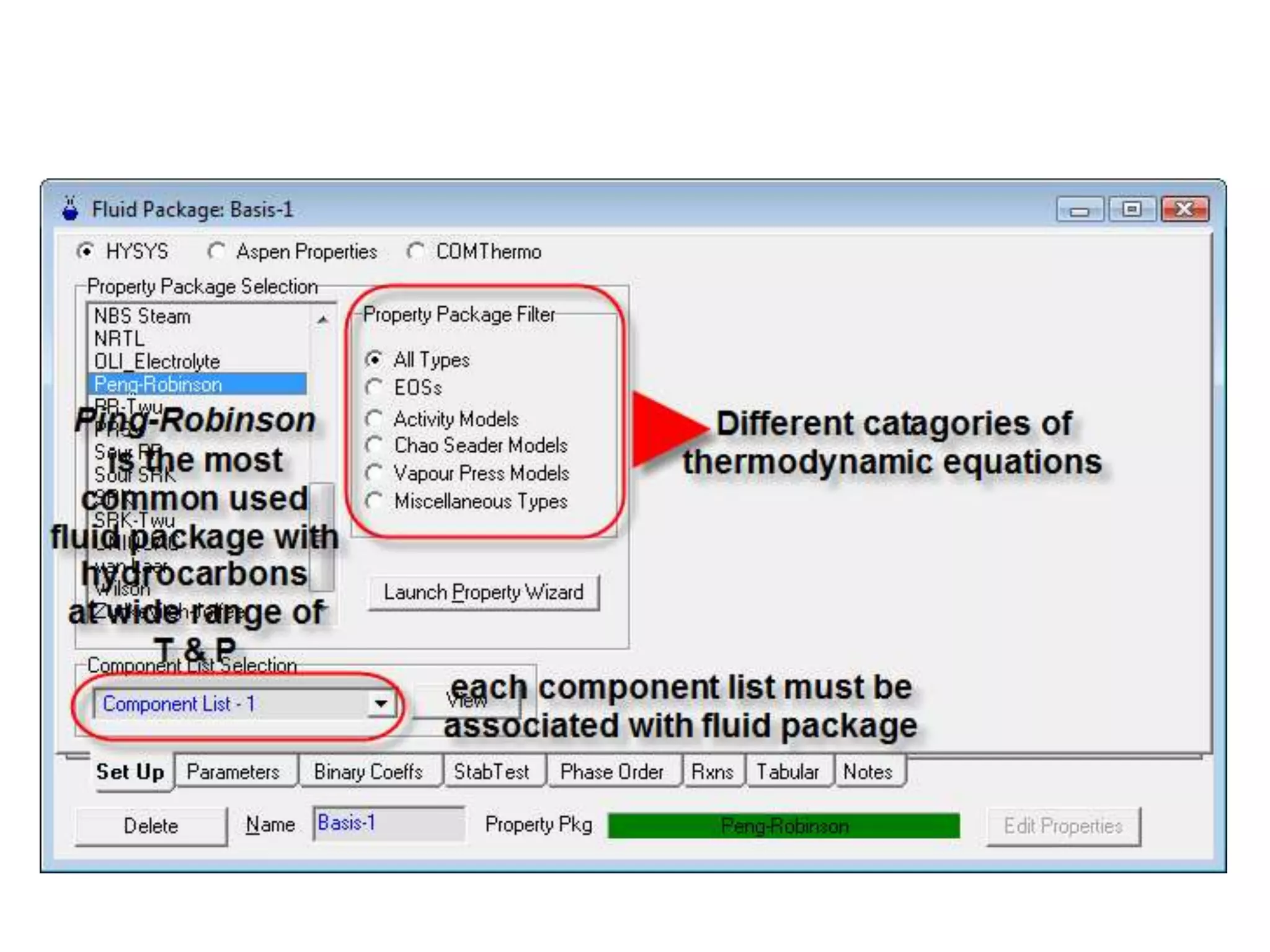
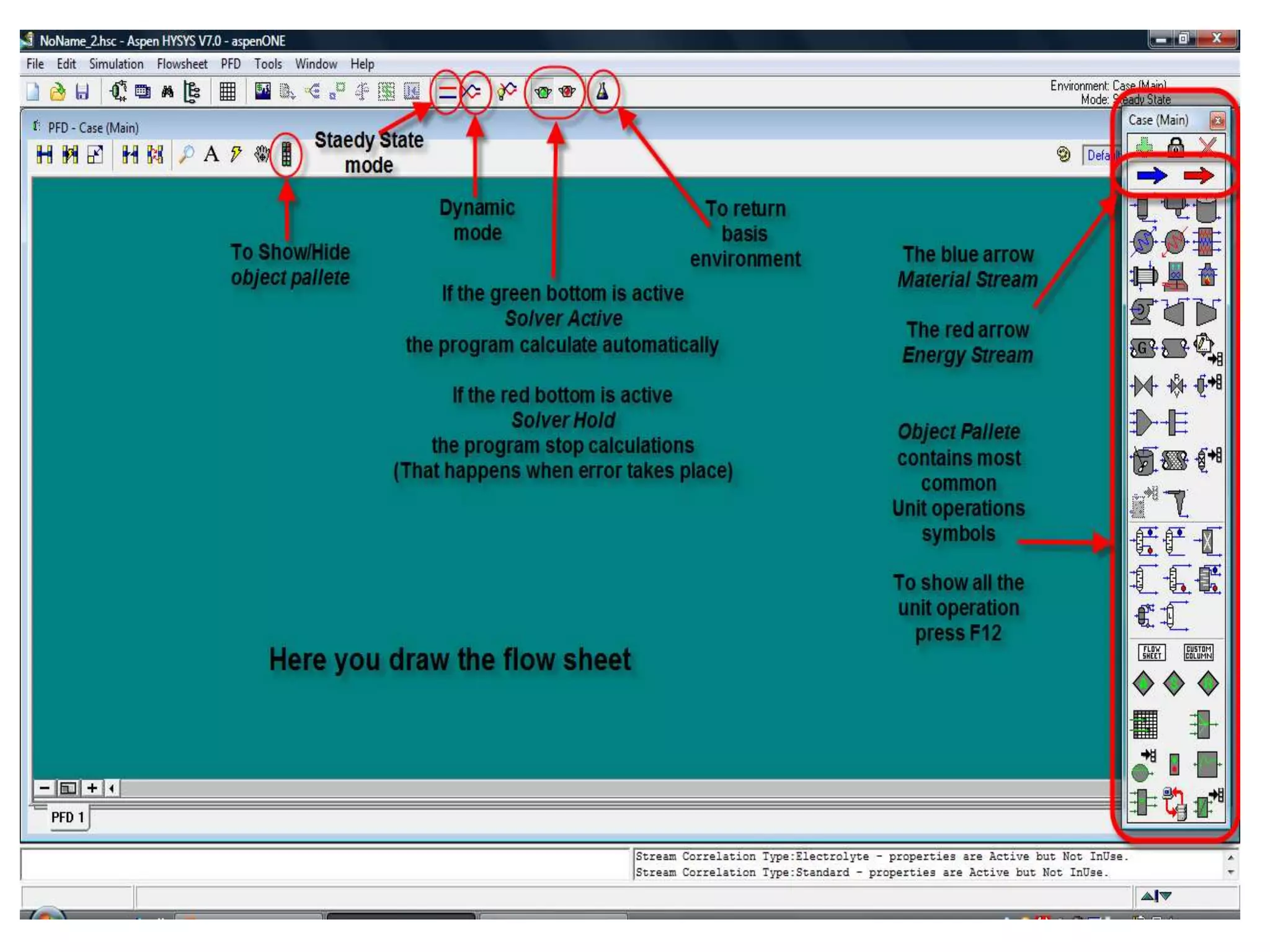
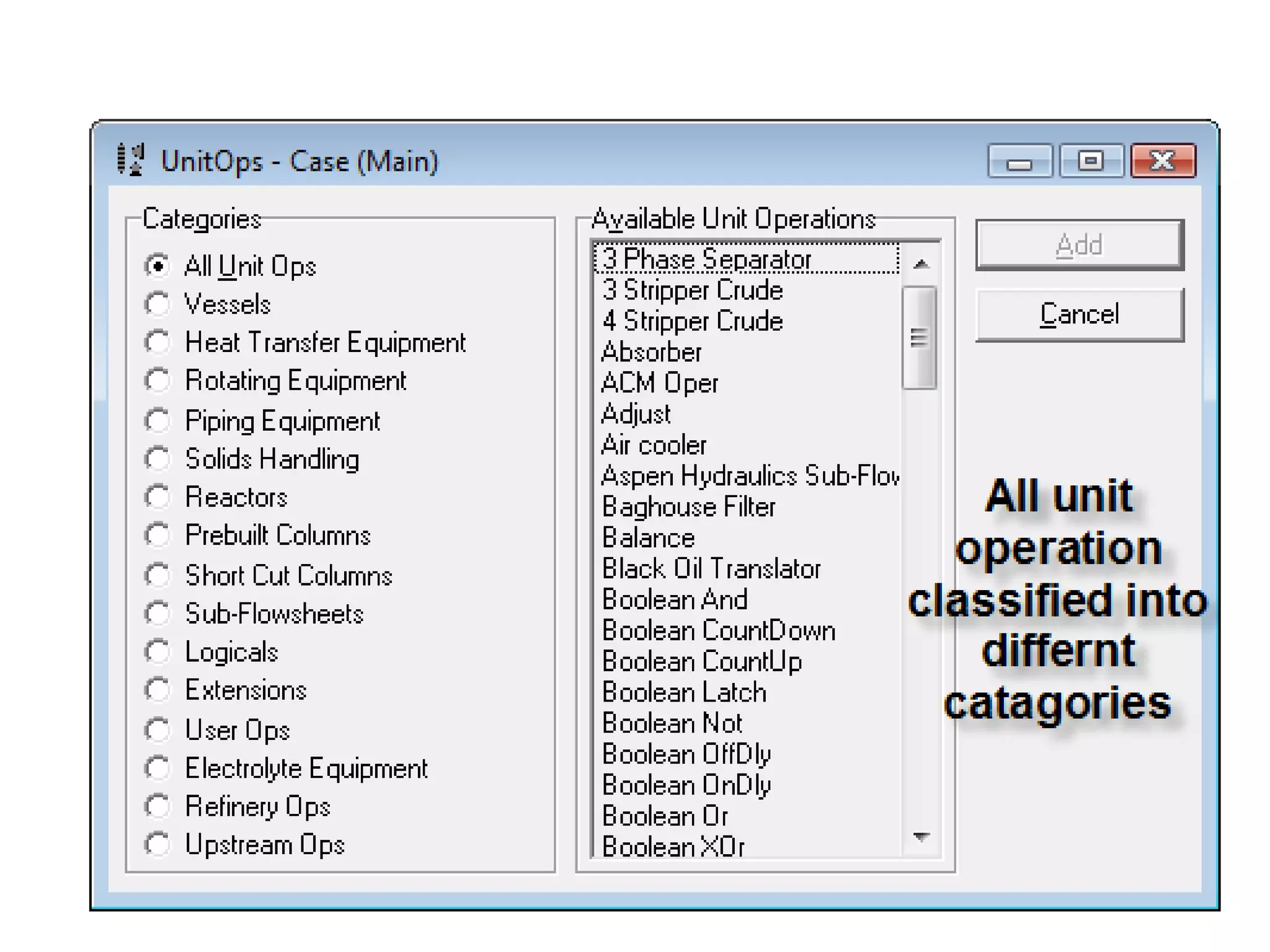
Simulation programs provide process engineers with an effective tool for process development besides experiments and trial plants. Modern simulation programs allow engineers to simulate individual units as well as networks of units. There are advantages to using simulation tools such as better understanding safety aspects, time and cost savings, and optimization of process control. Simulation programs can be divided into two groups: stationary programs suitable for steady state processes, and instationary programs for dynamic systems. Common simulation programs and the basic approaches of sequential modular and equation-oriented are described.