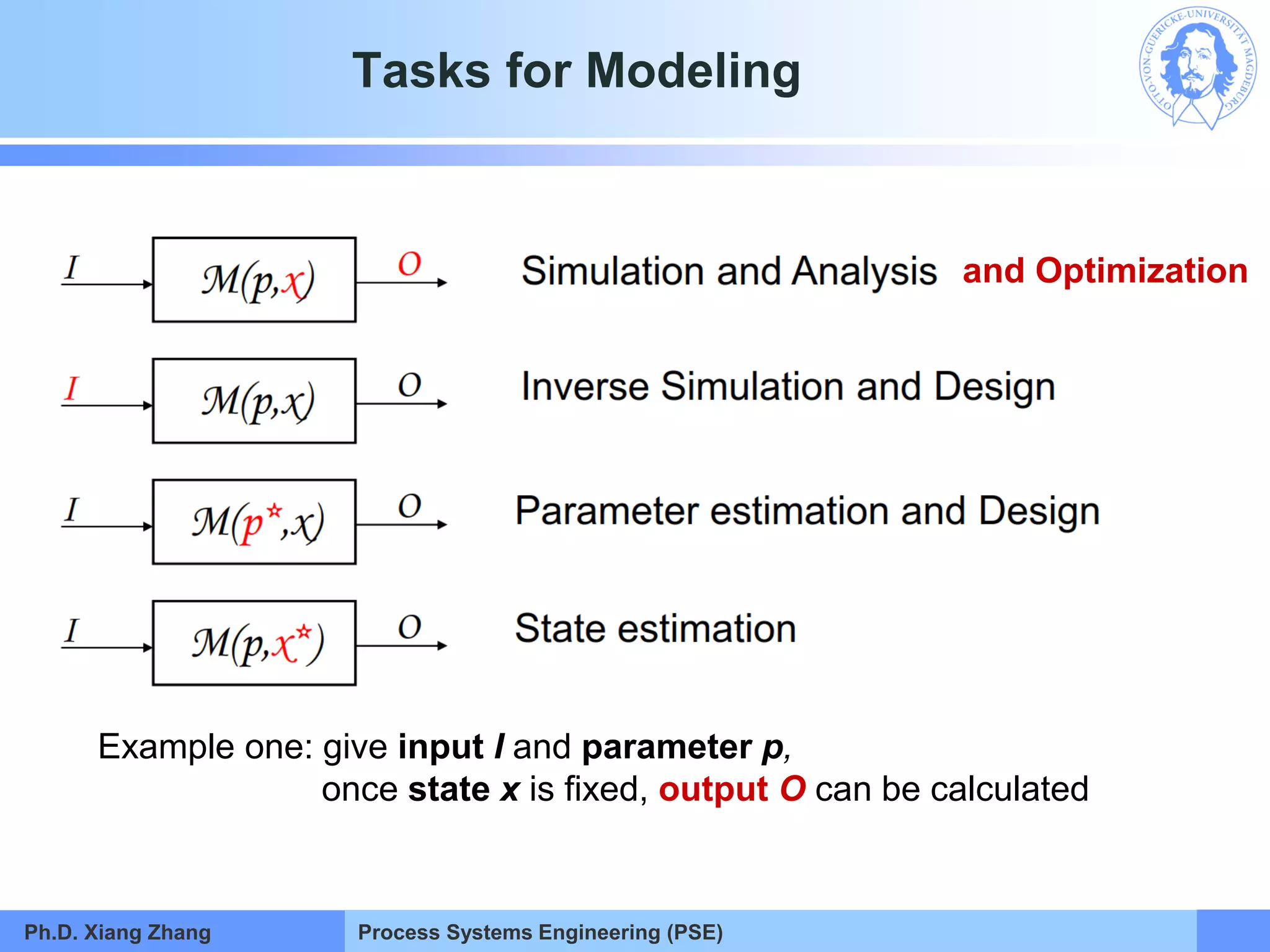
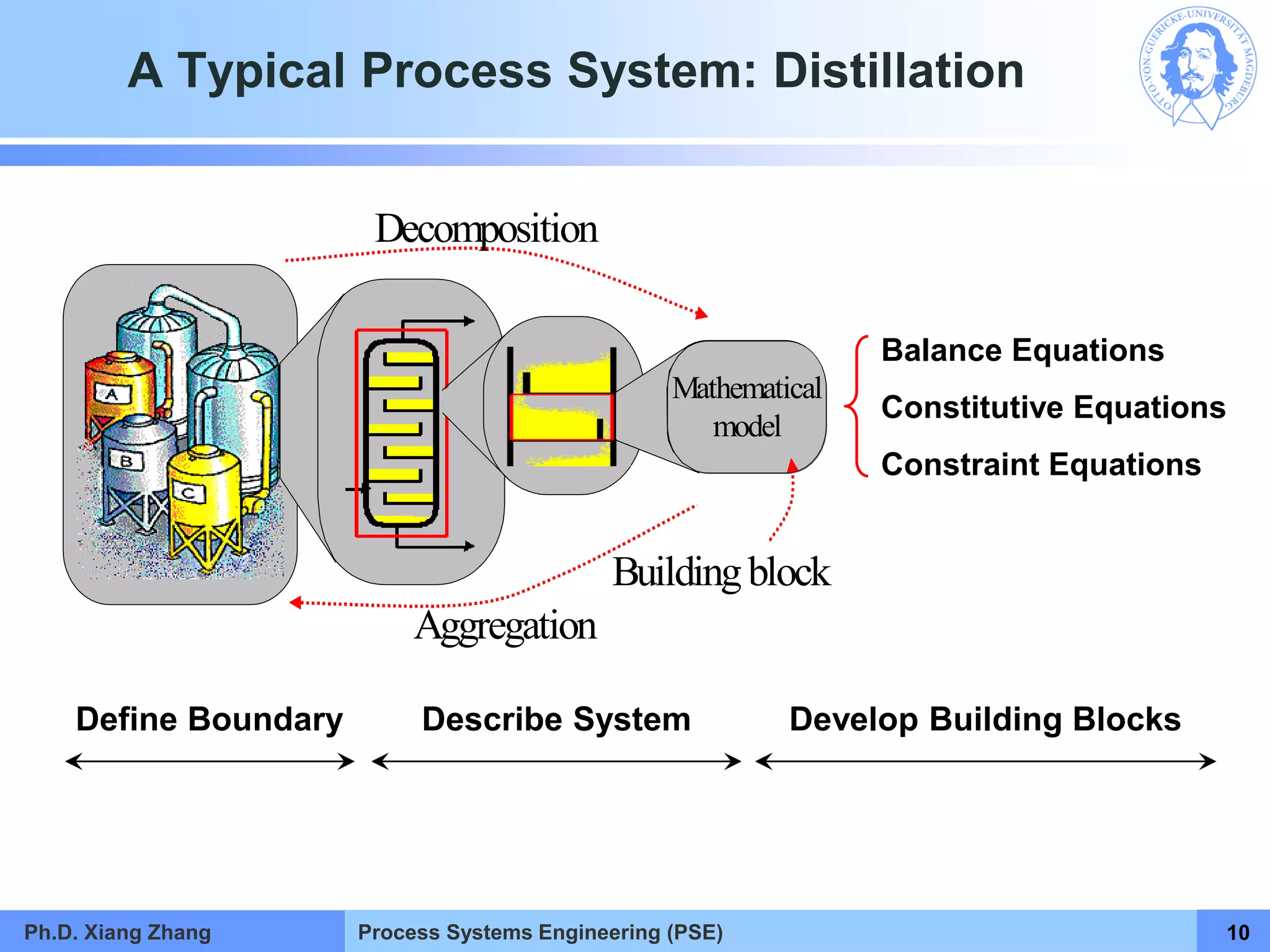
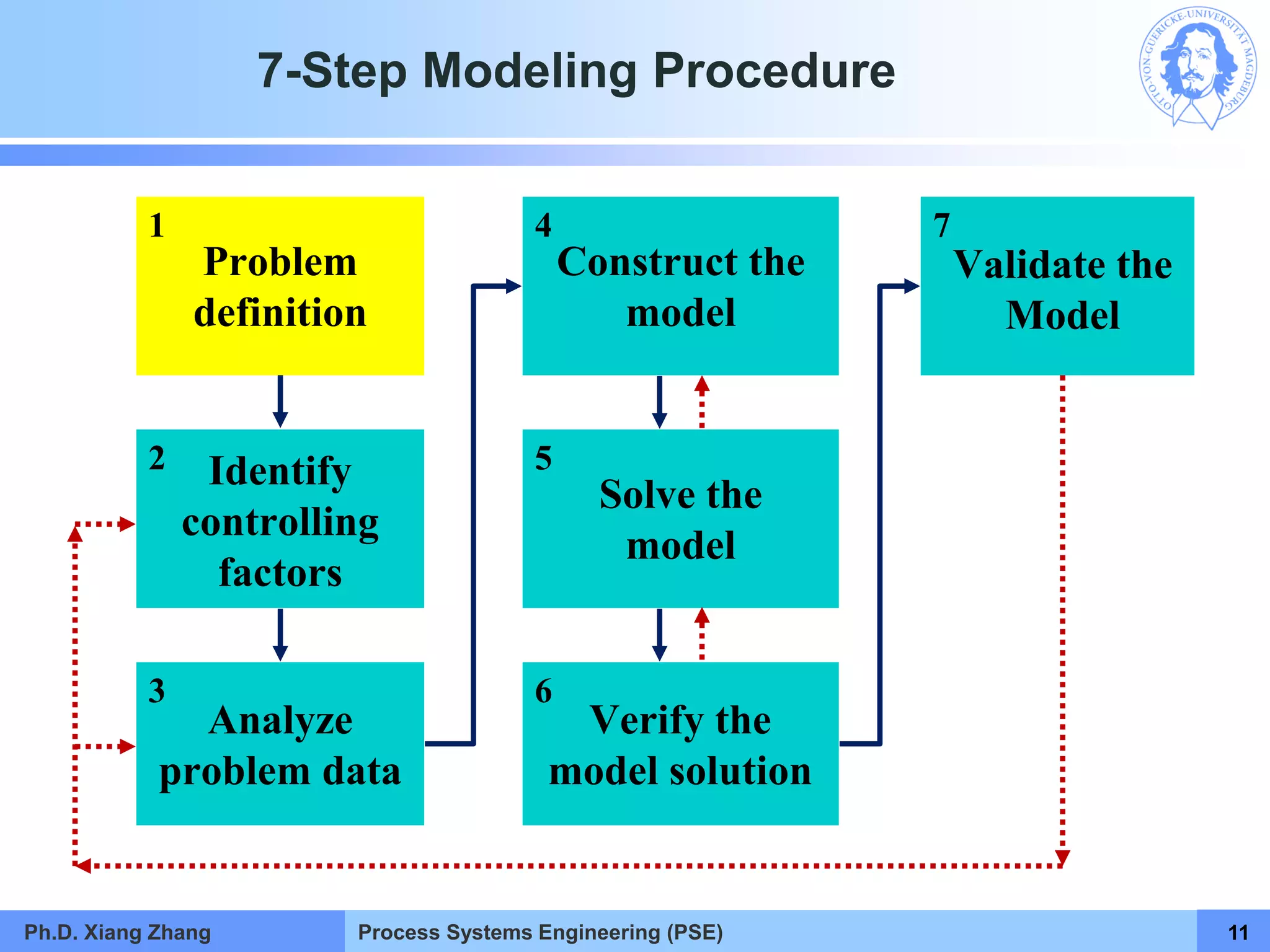
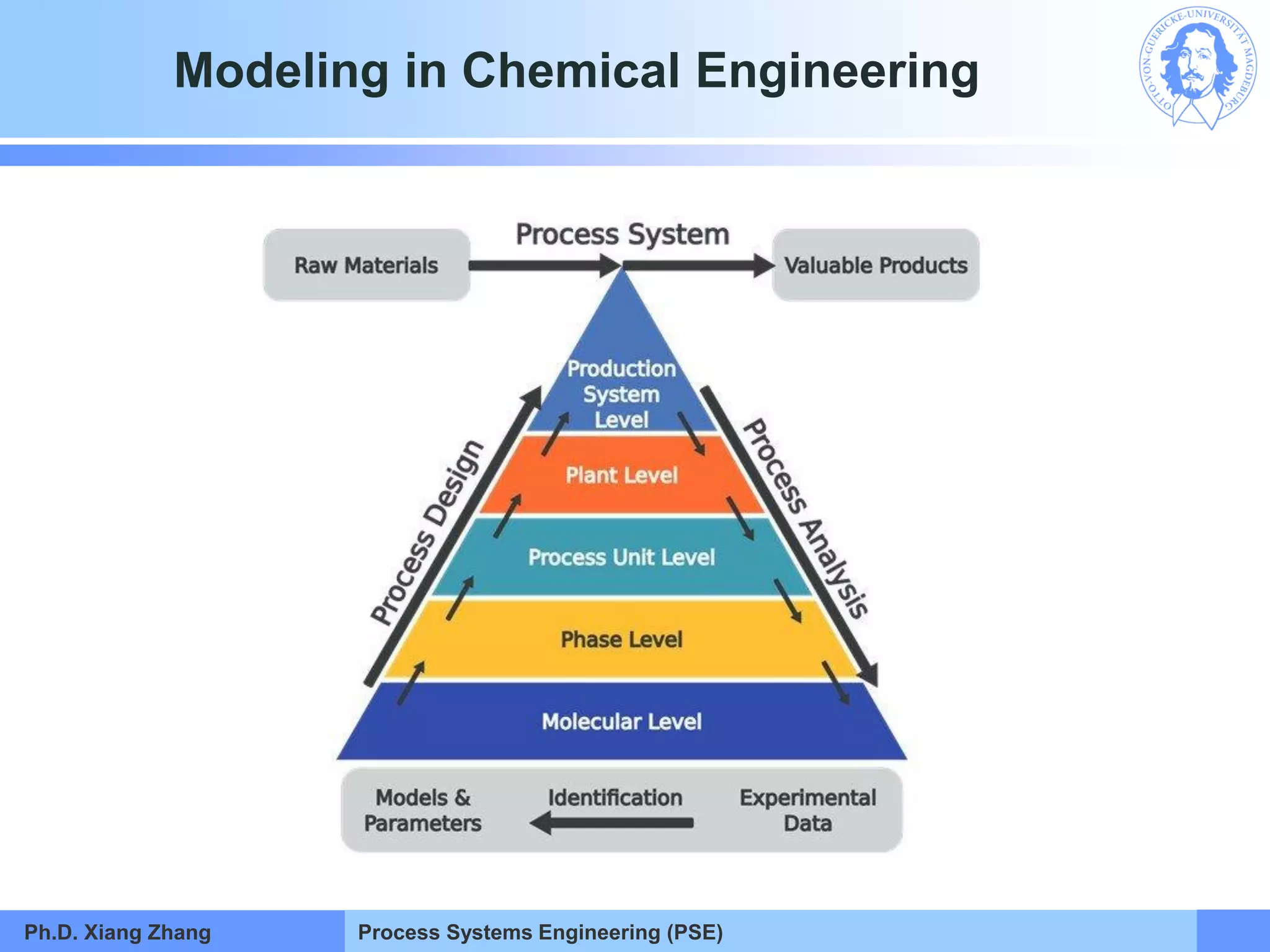
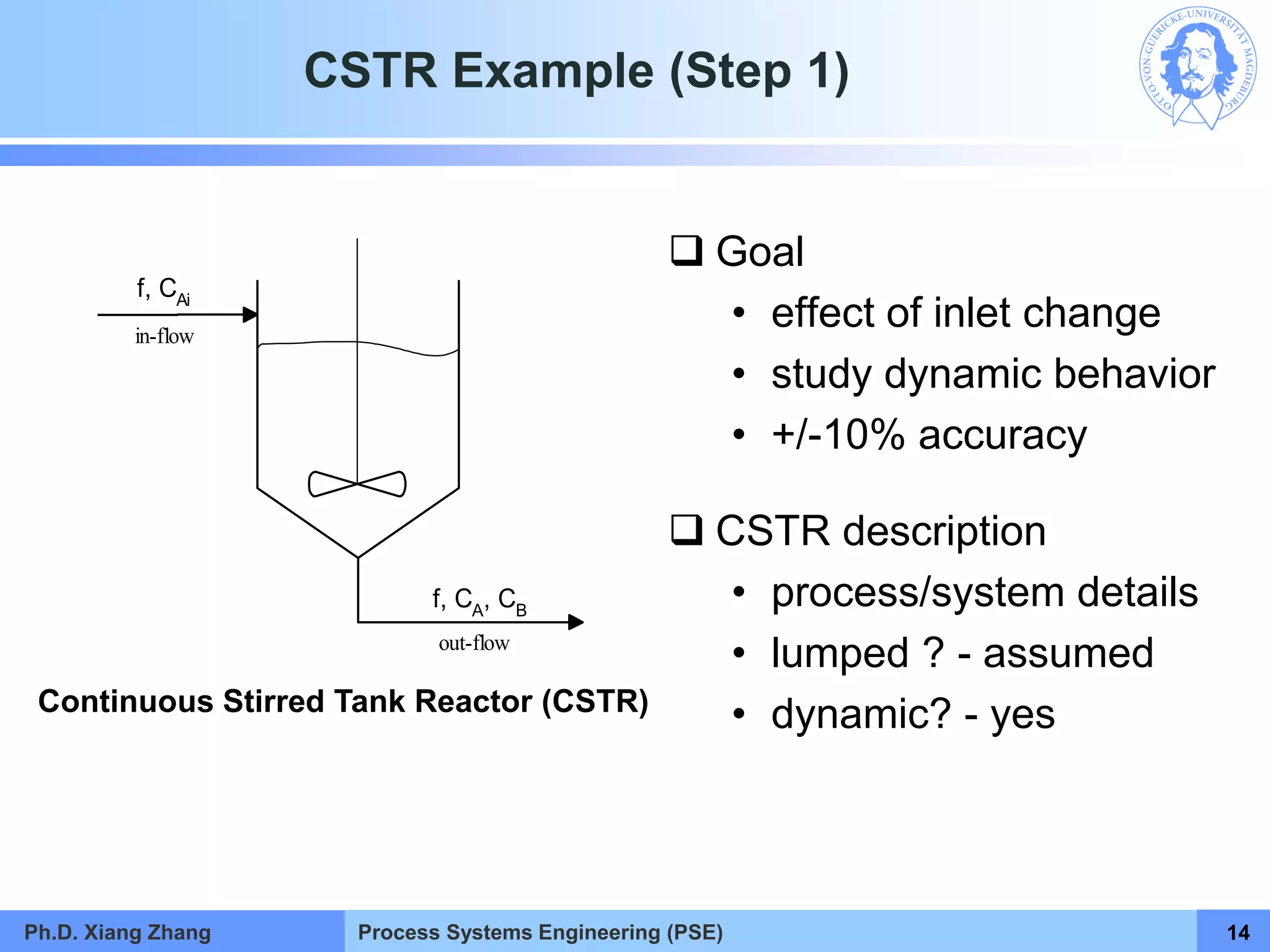
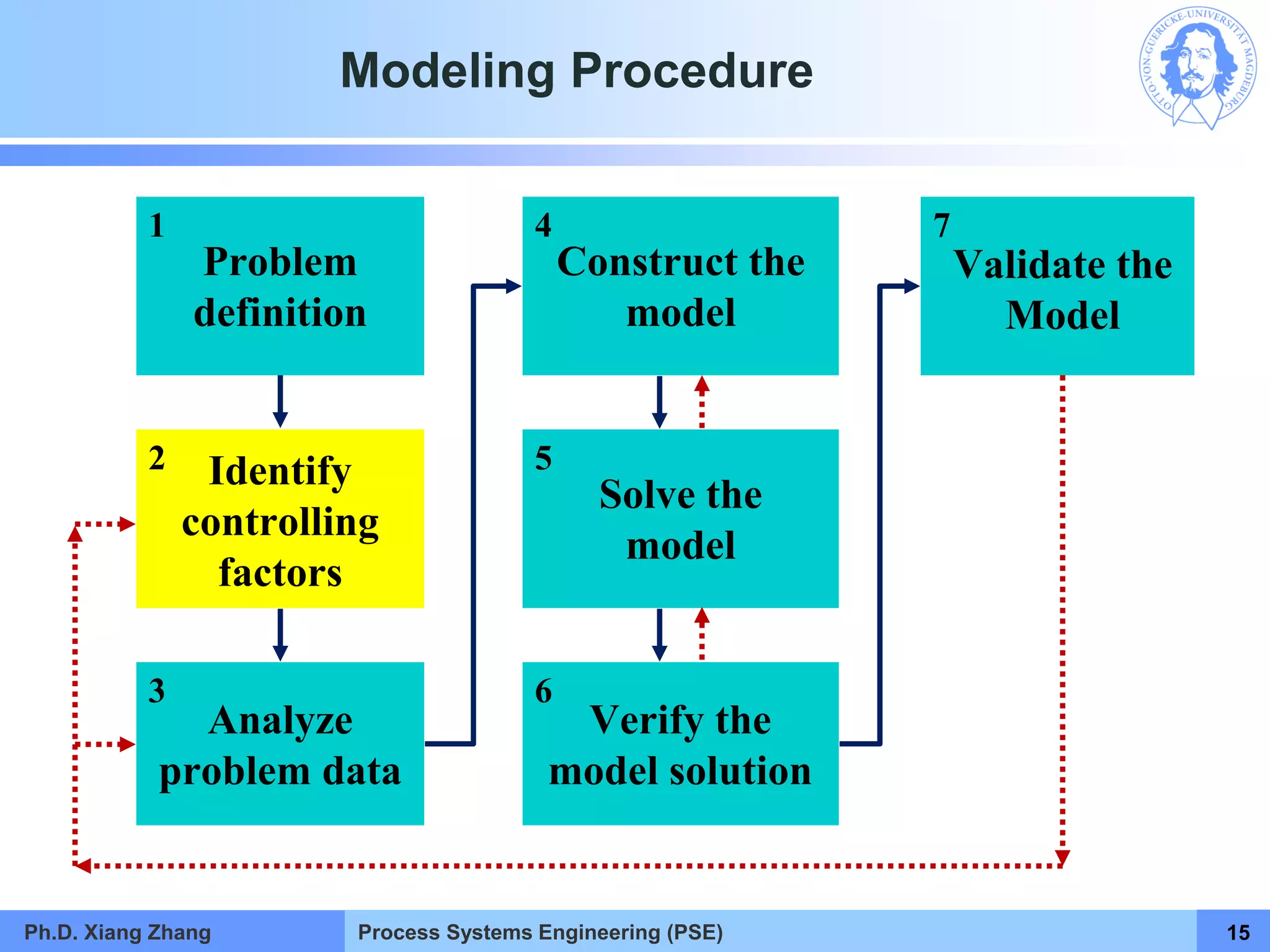
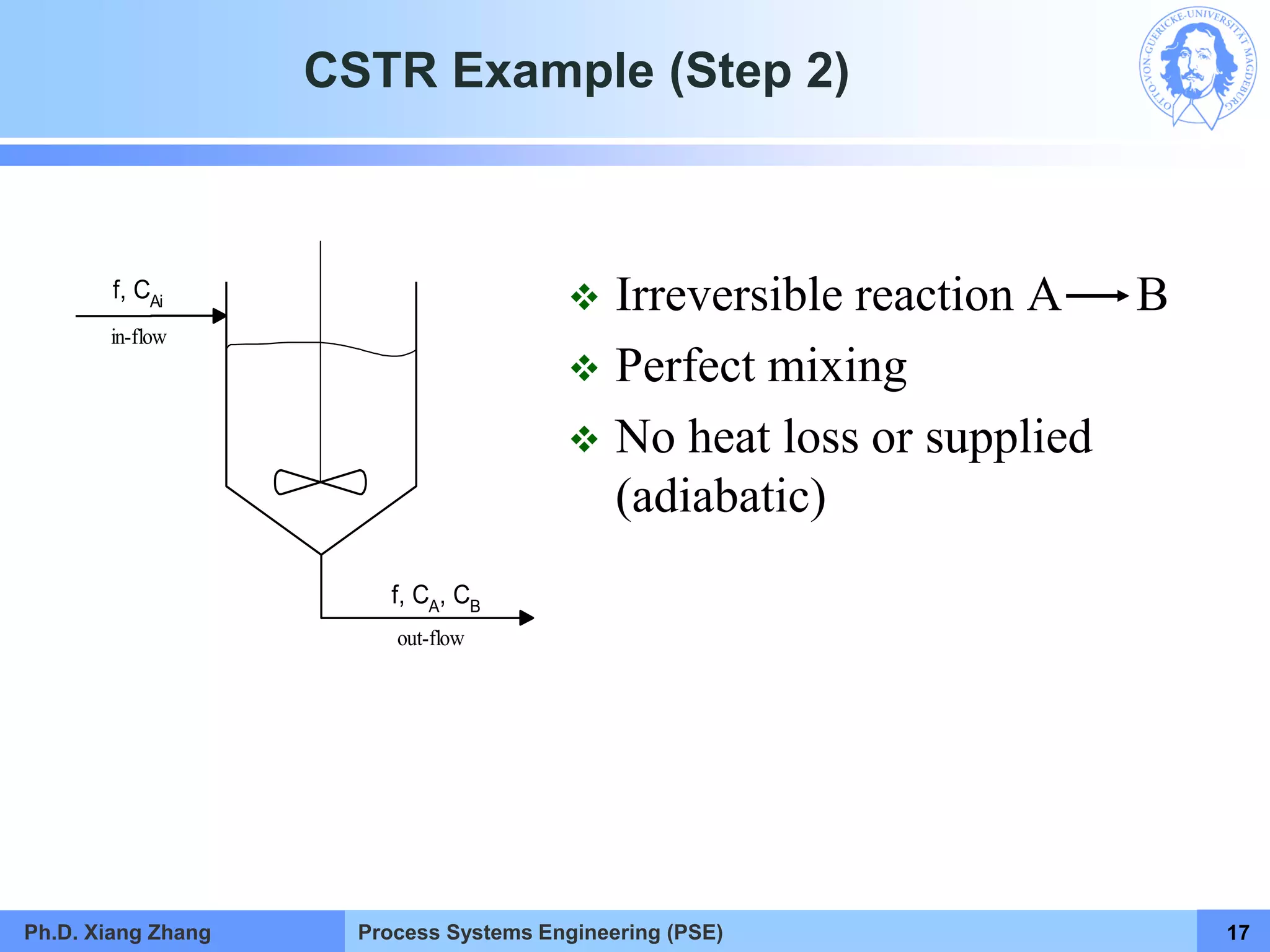
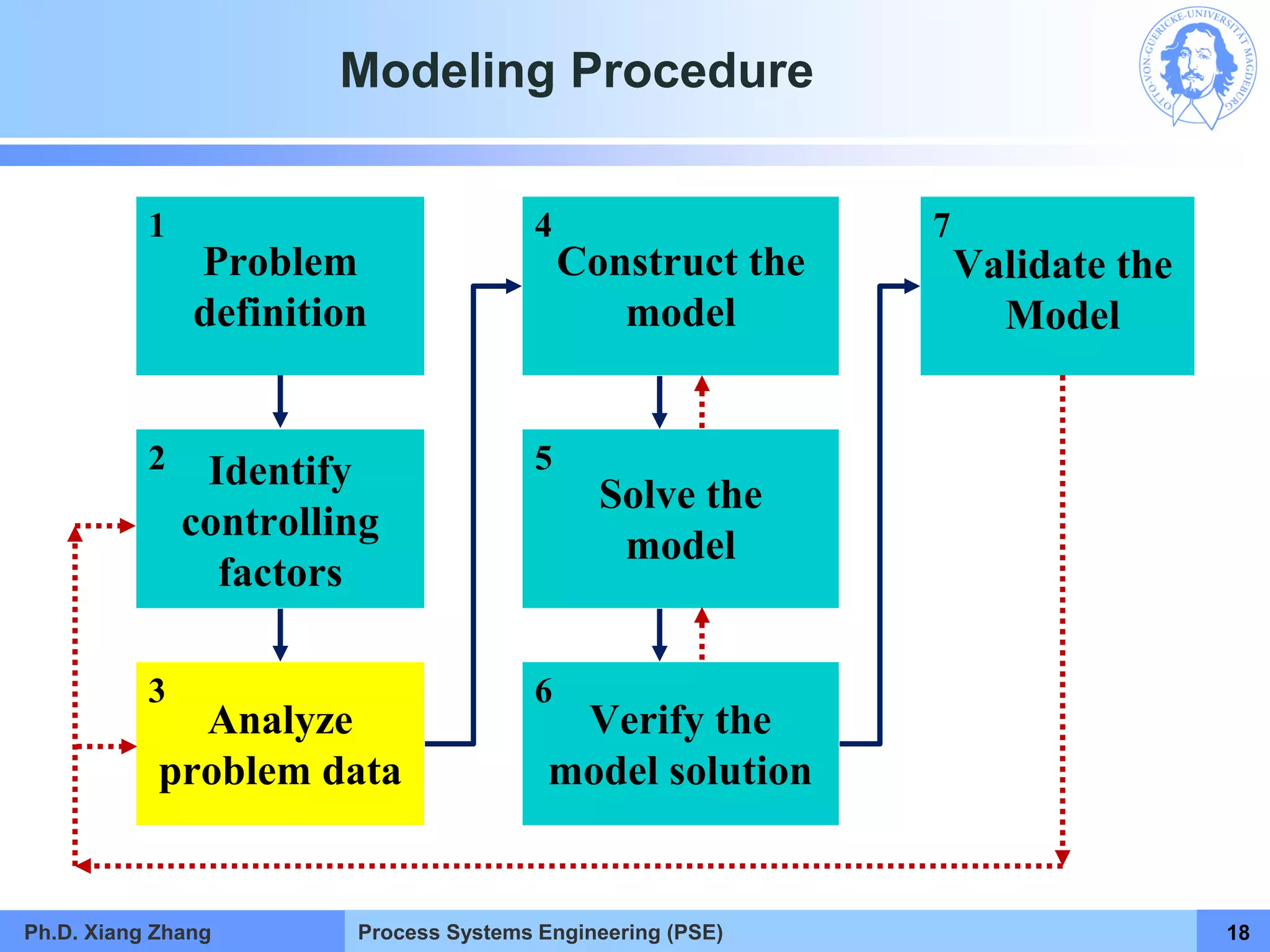
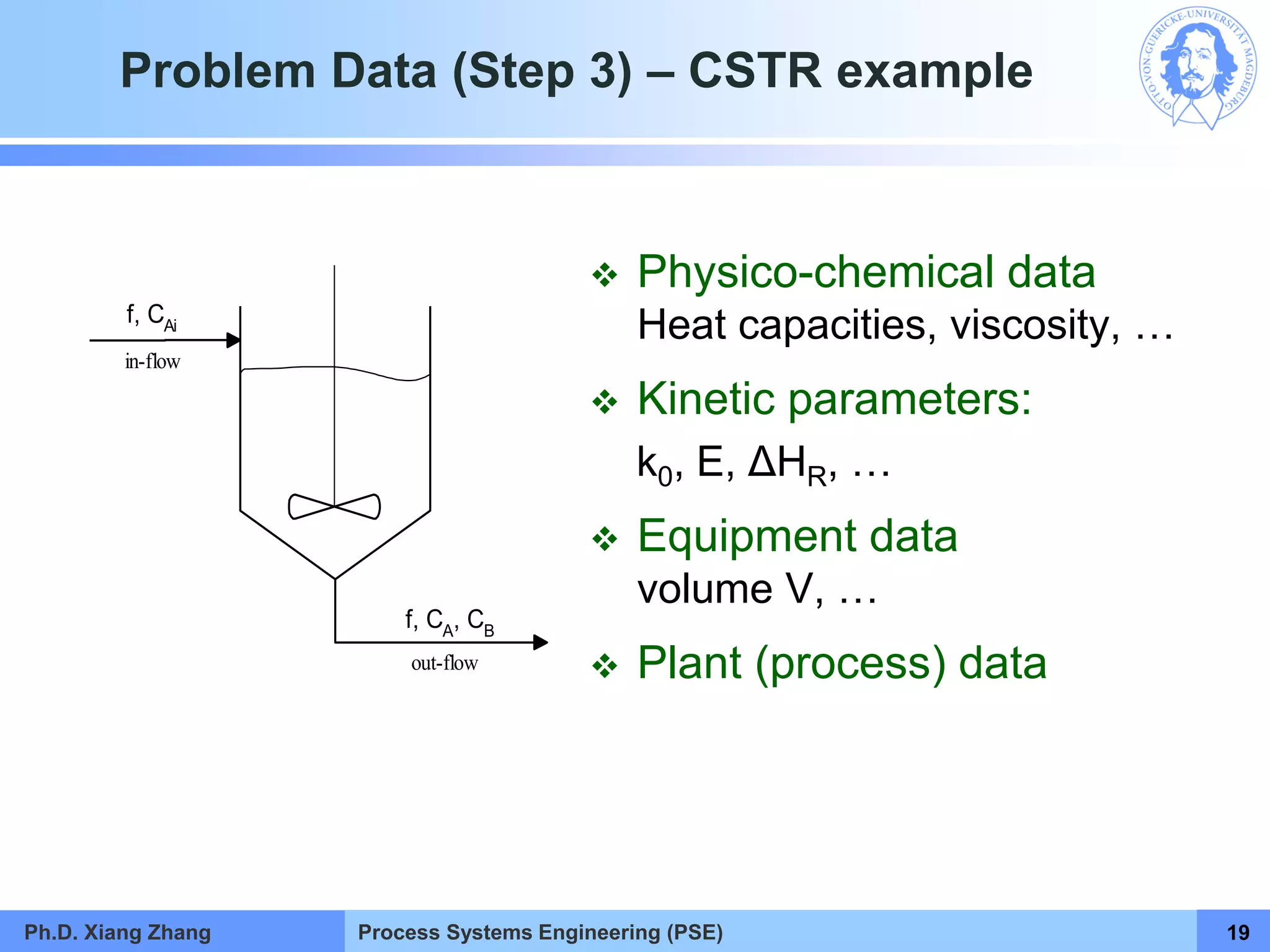
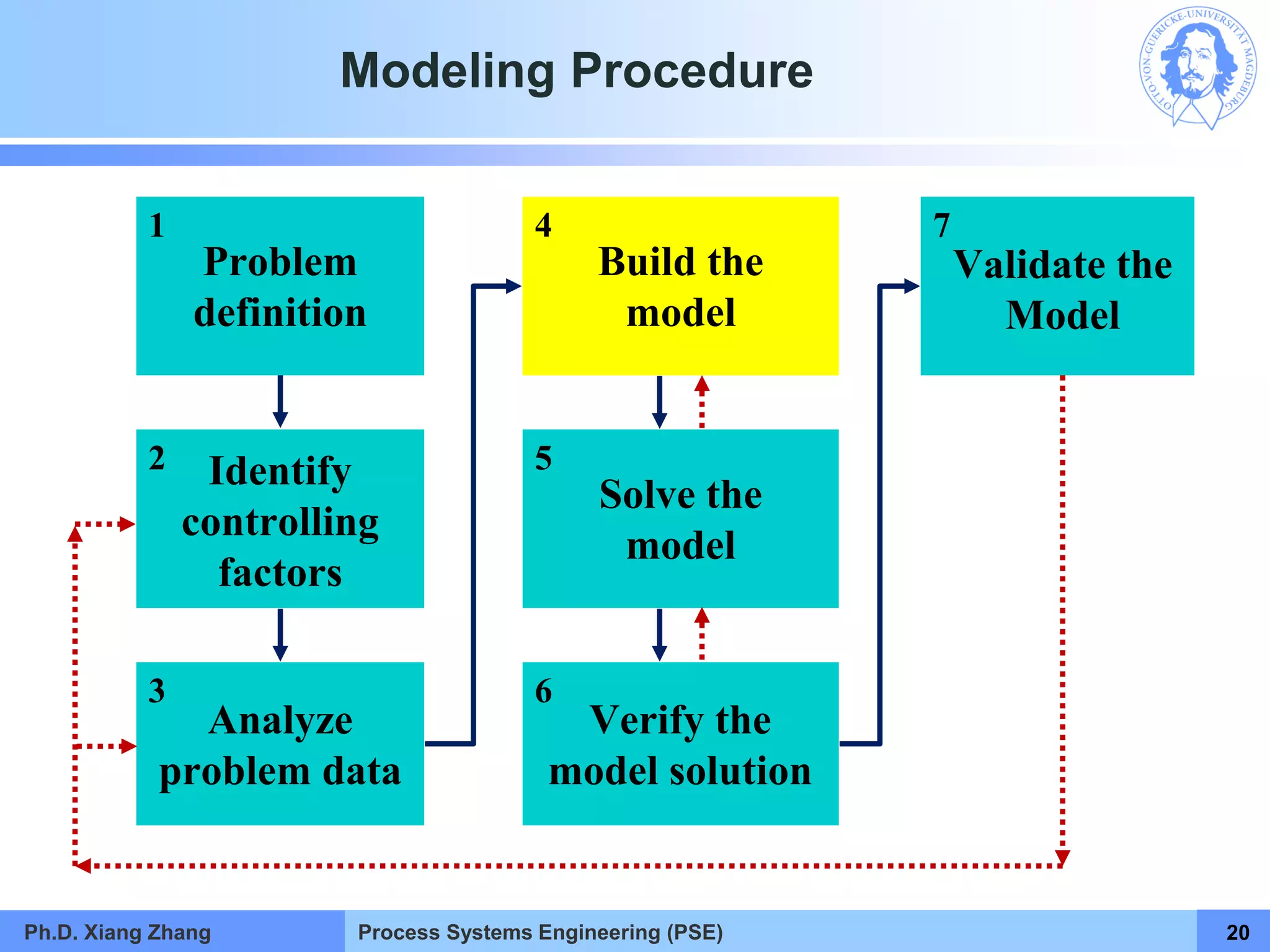
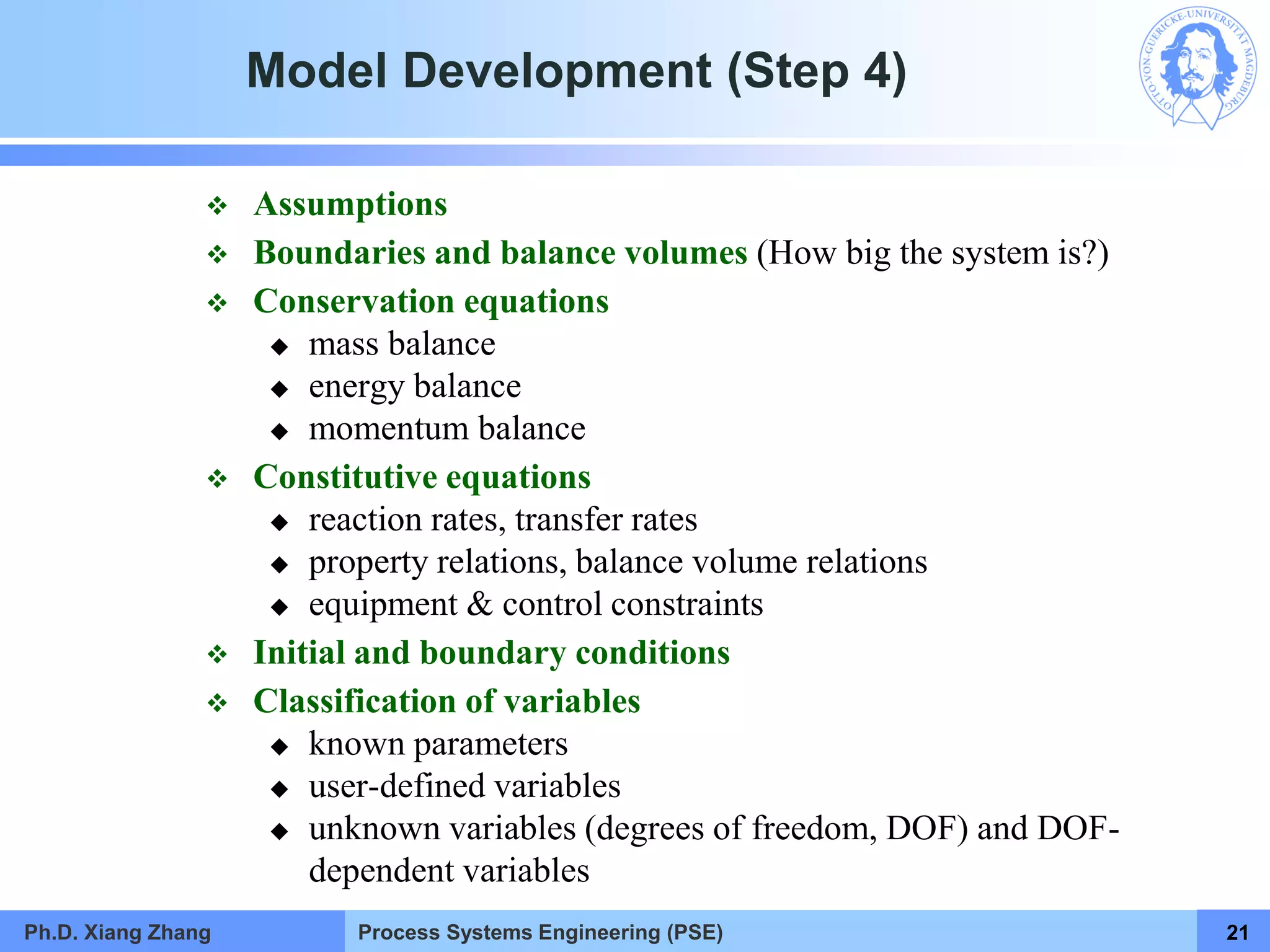
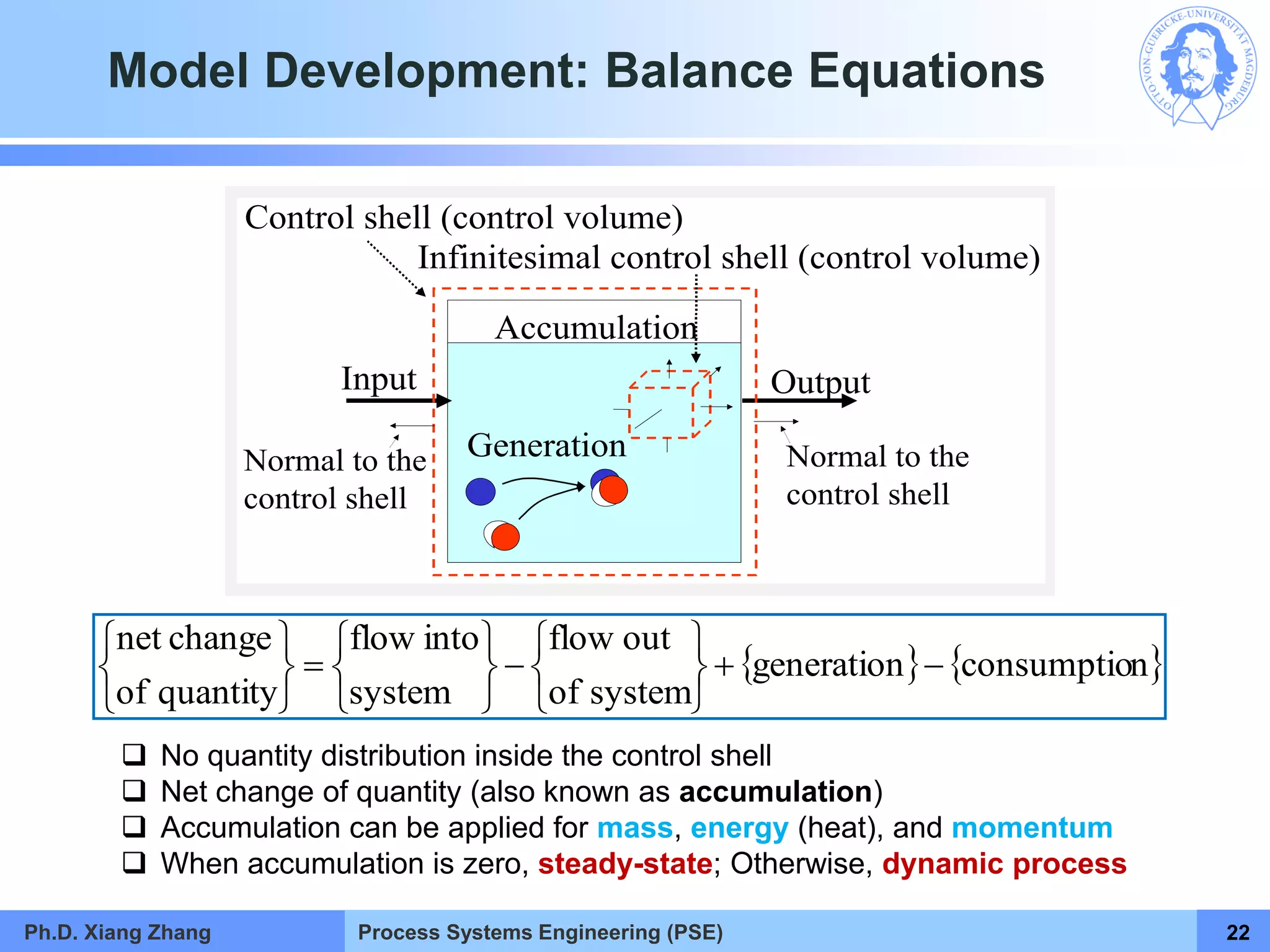
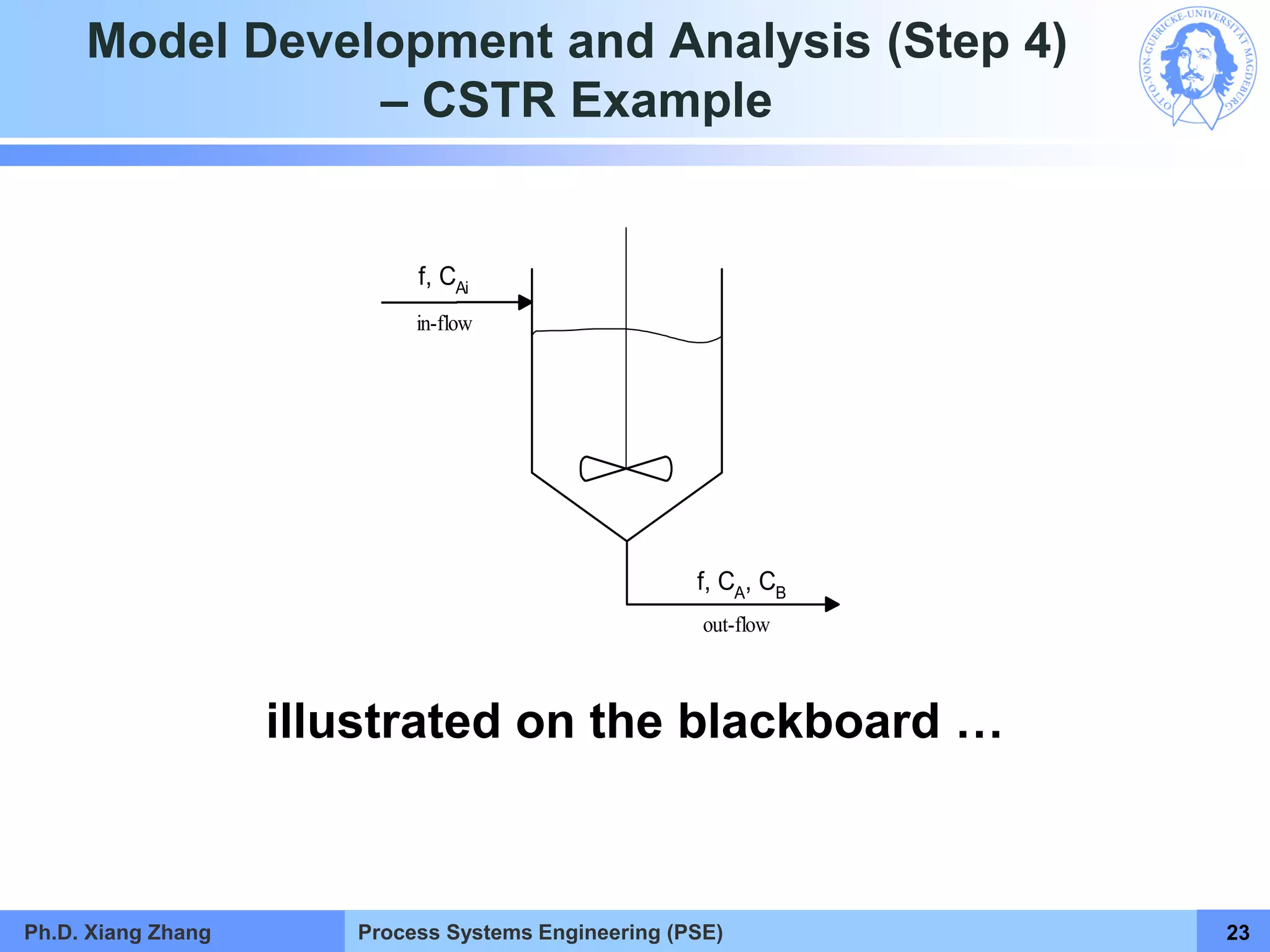
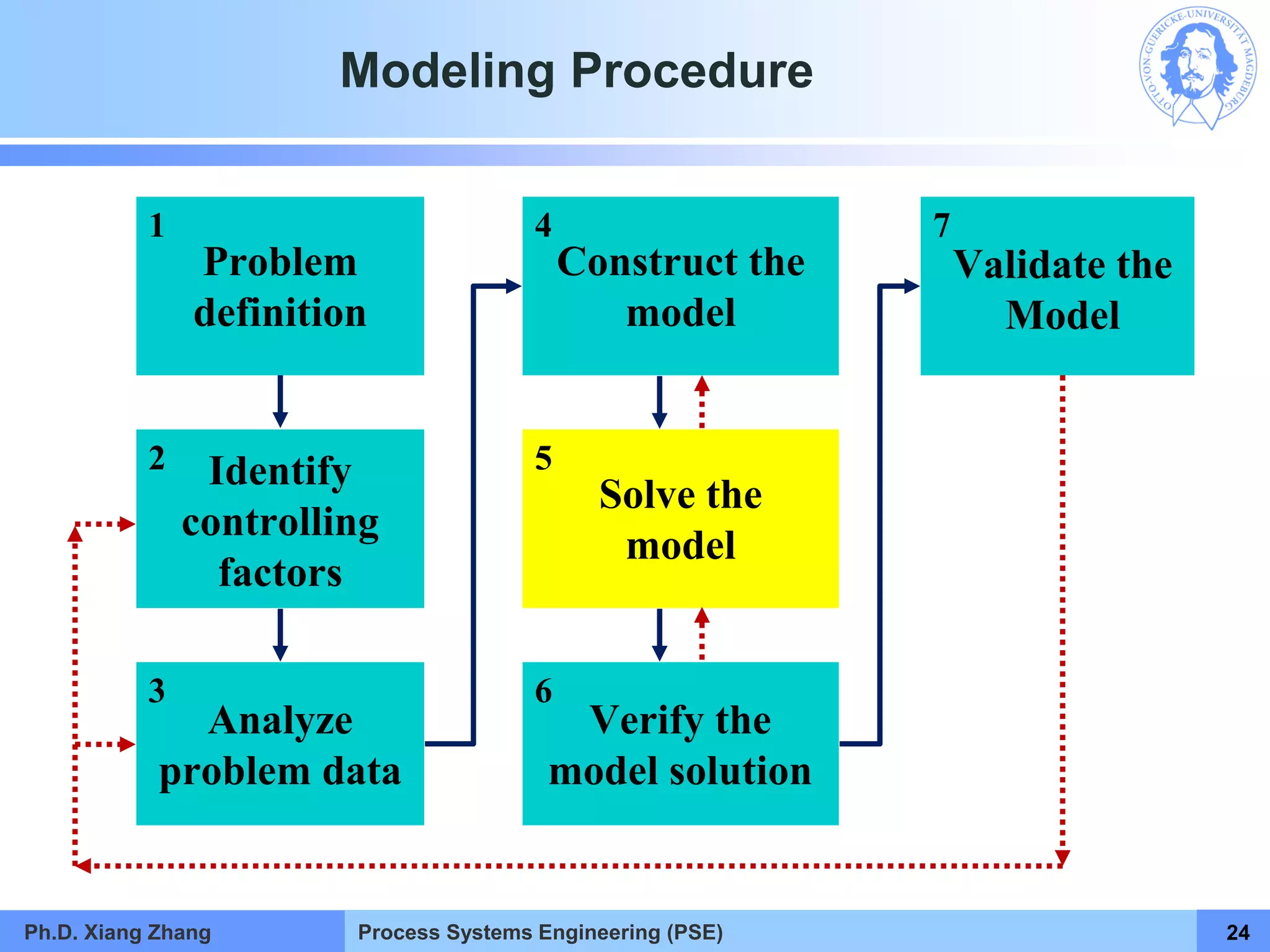
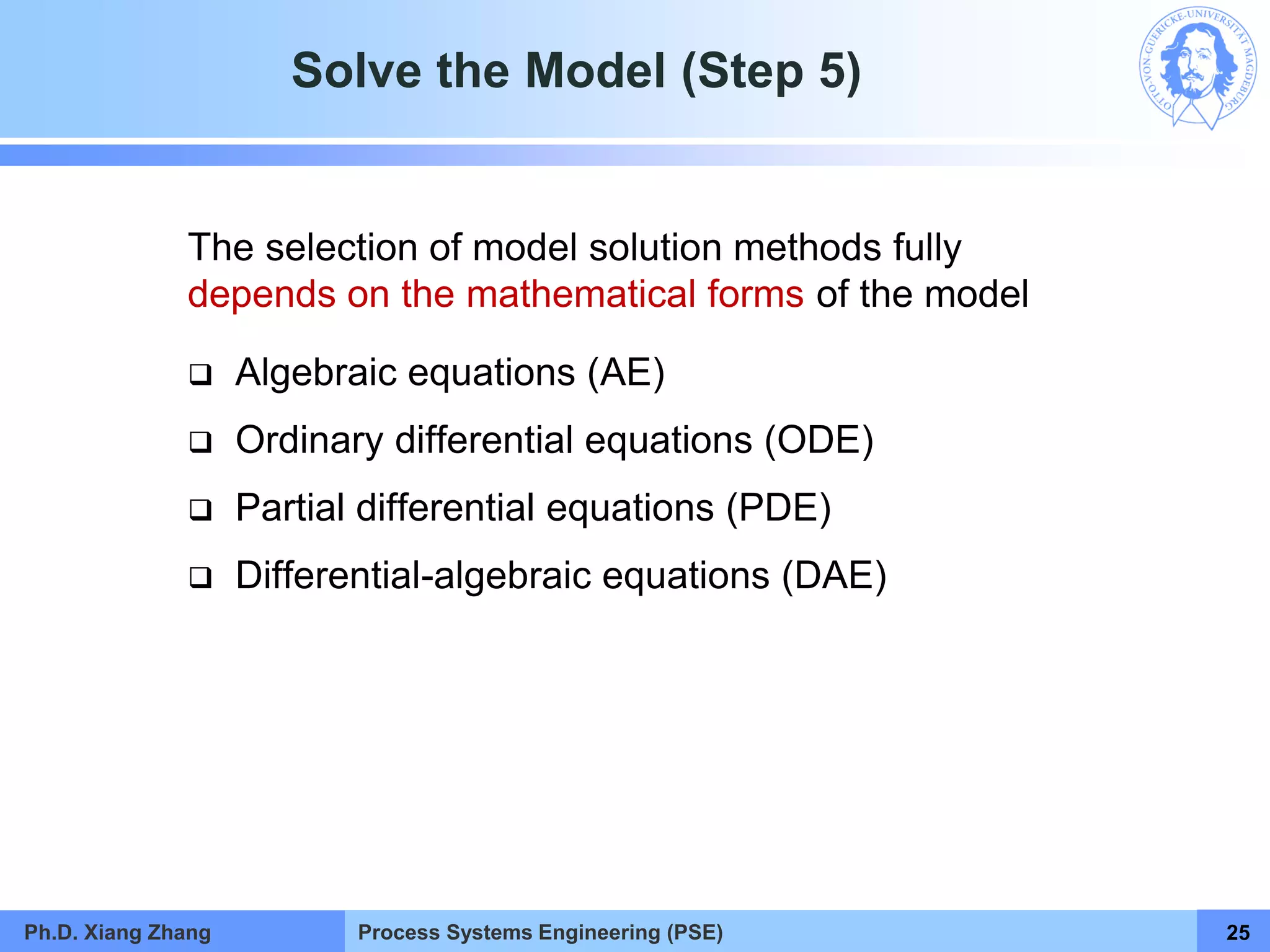
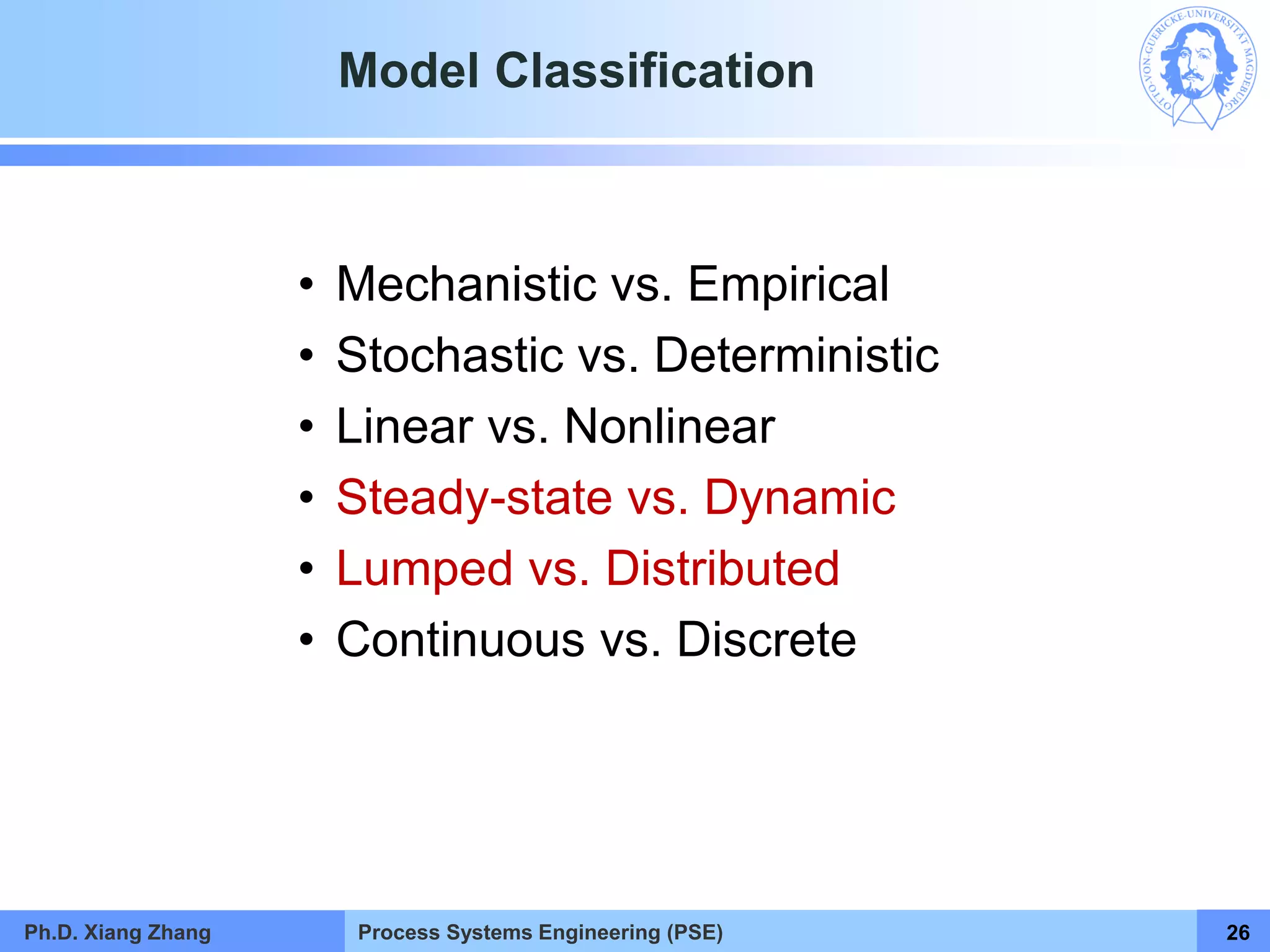
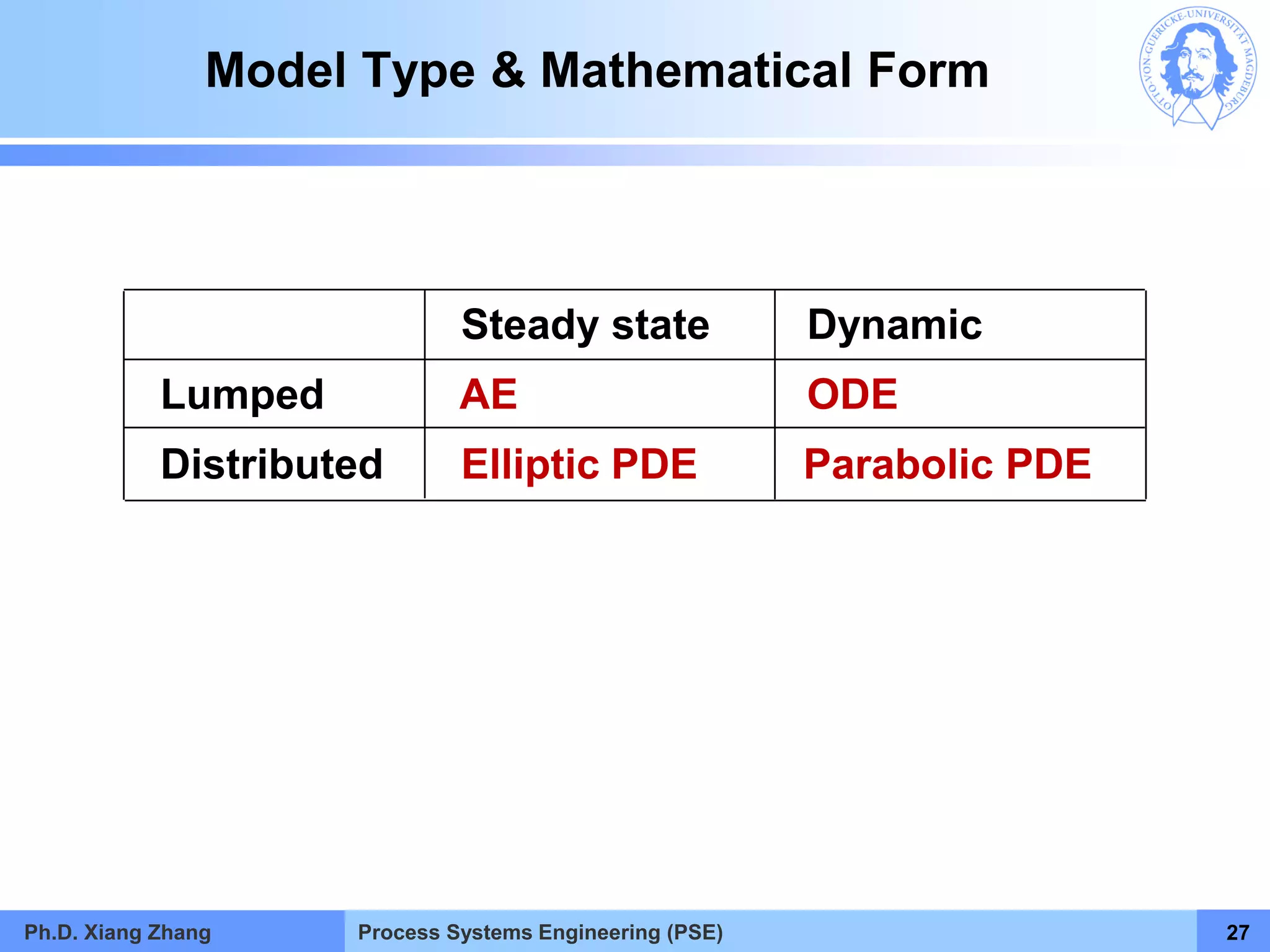
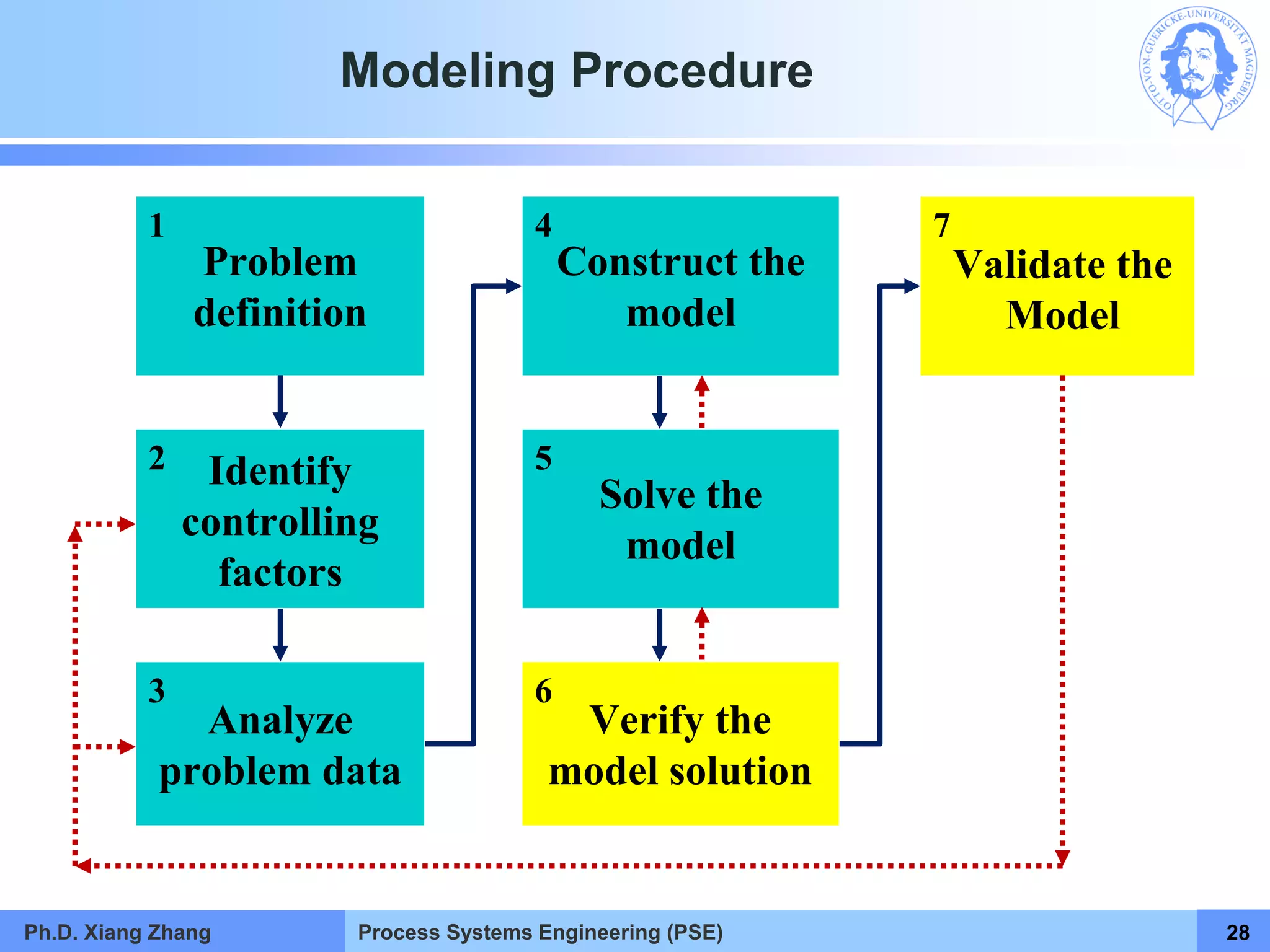
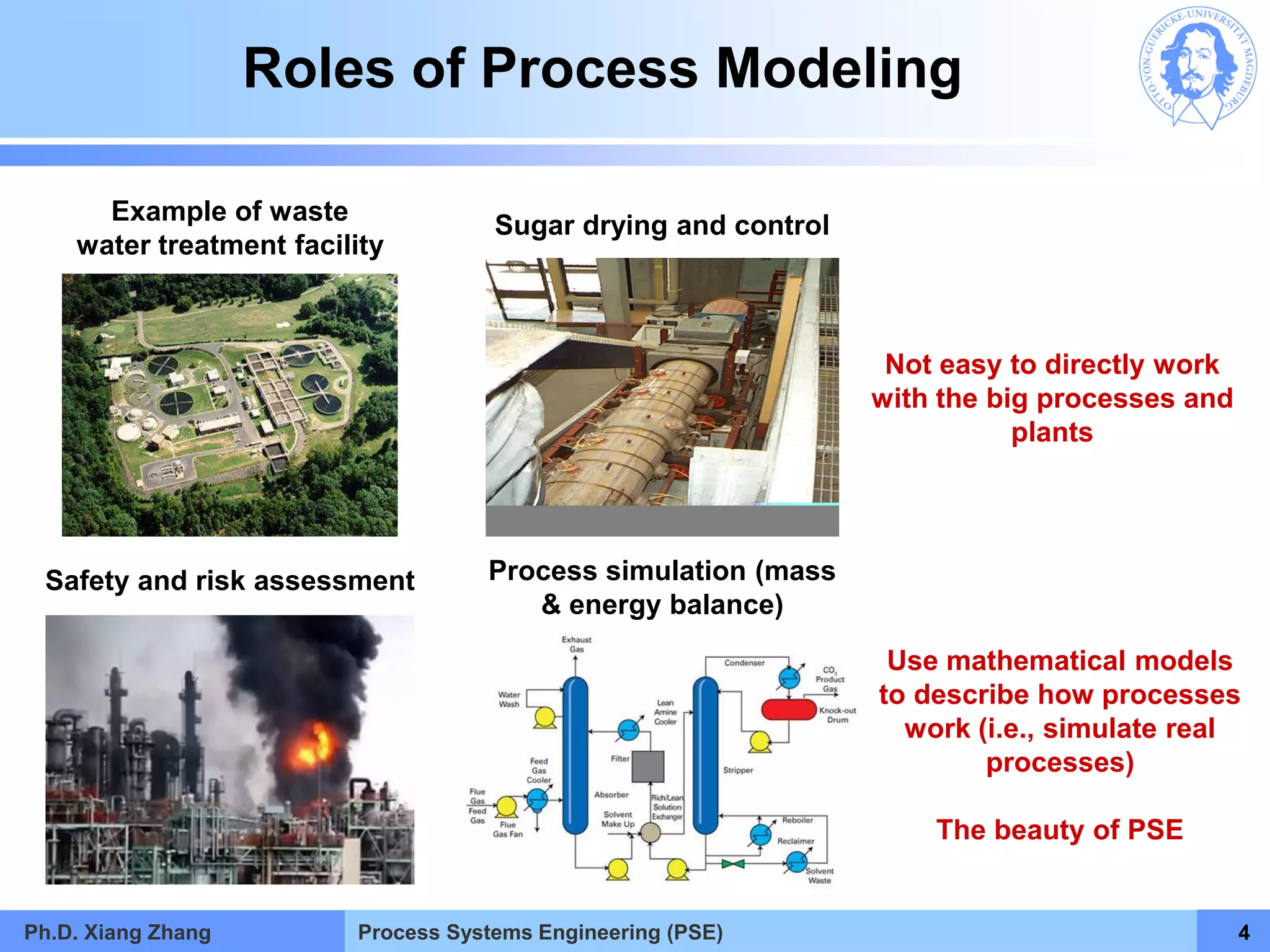
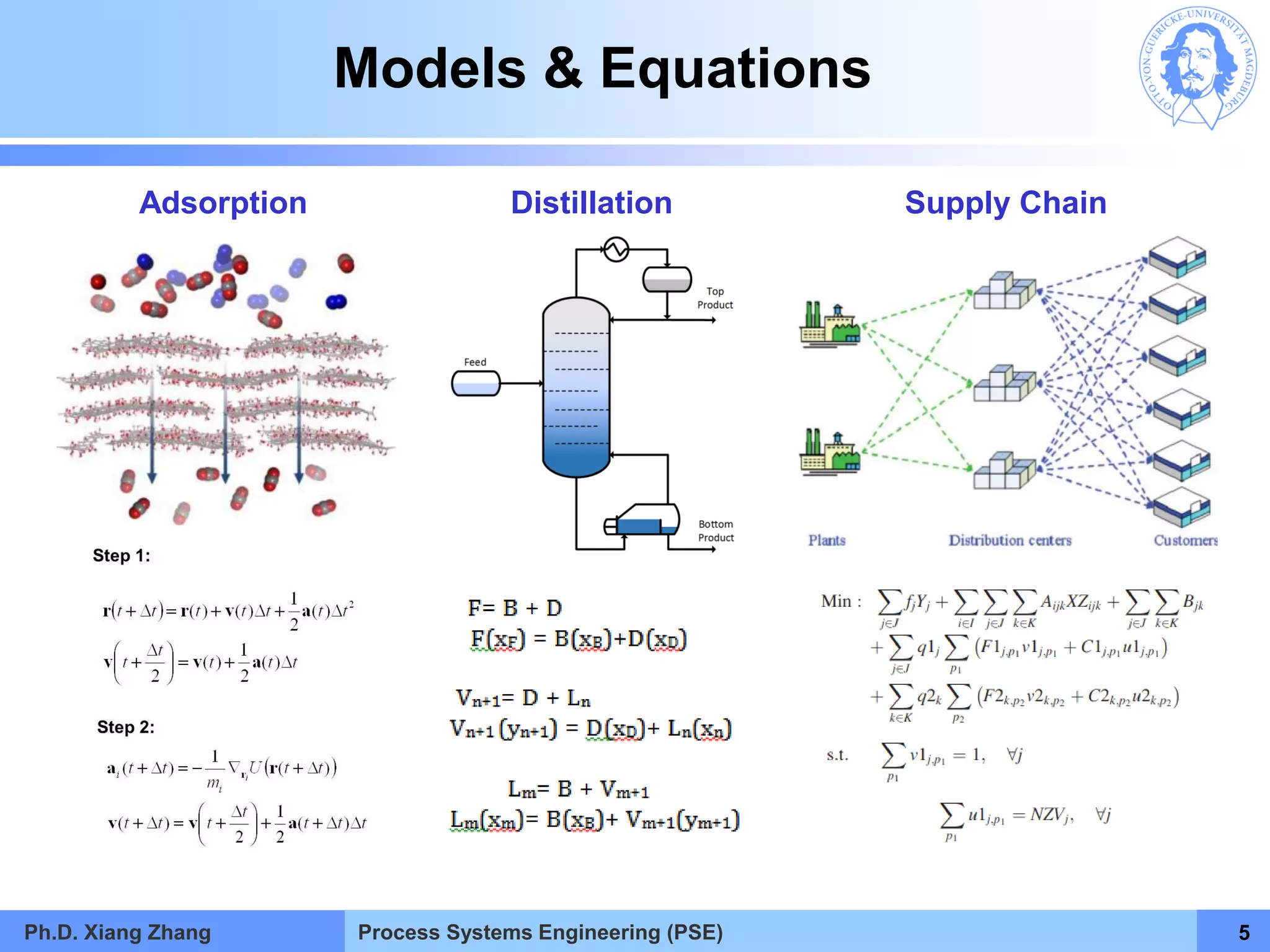
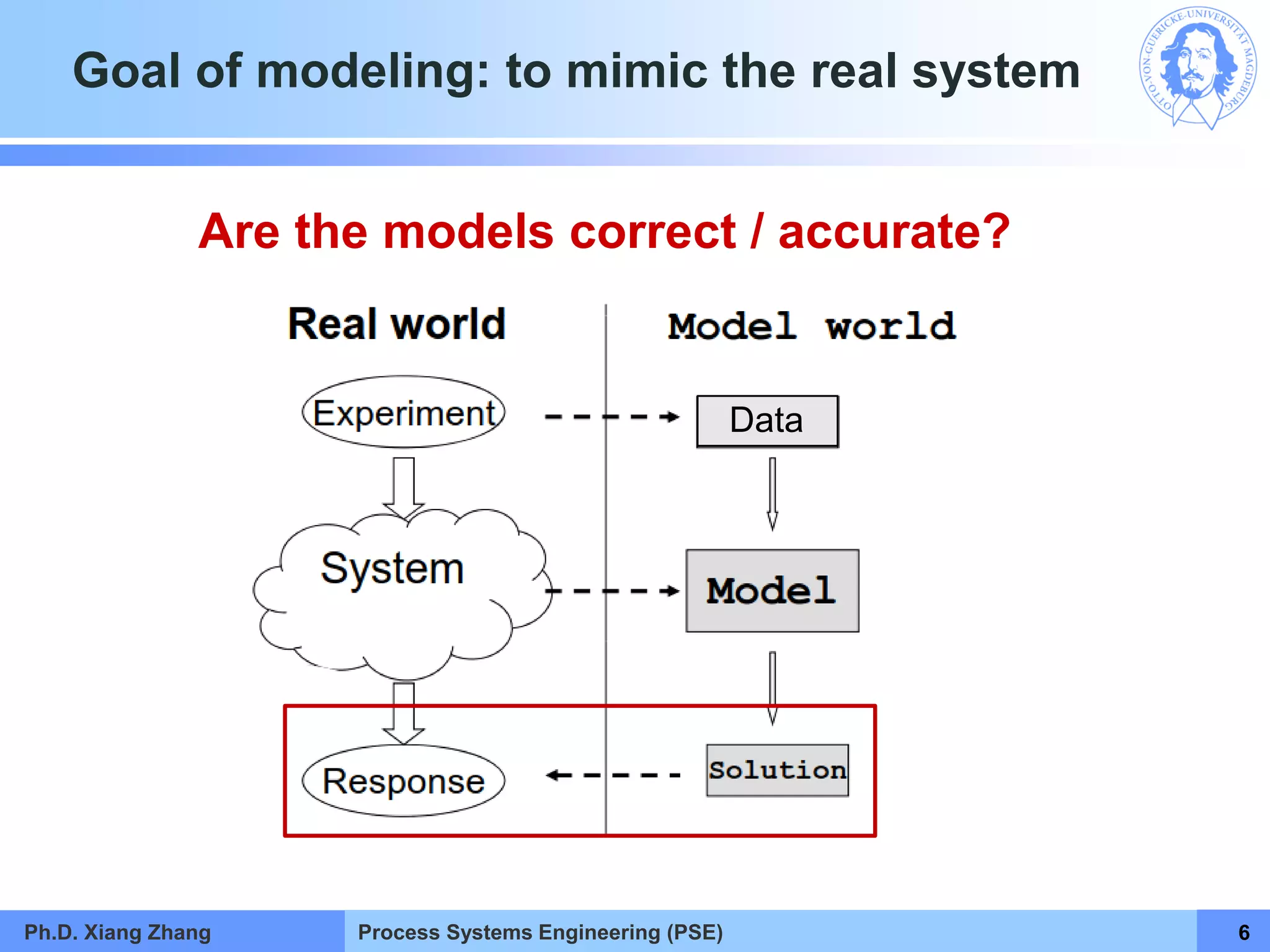
This document provides an overview of a Process Systems Engineering (PSE) course taught by Dr. Xiang Zhang. The course covers process modeling, including steady-state and dynamic modeling of lumped and distributed parameter systems. It describes the main steps of modeling as defining the problem, identifying controlling factors, analyzing data, developing mathematical models, solving models, and verifying solutions. An example of continuous stirred-tank reactor modeling is discussed. The document outlines the course content, lecturers, and examination details.



![Process Systems Engineering (PSE) 8
The Process System
Inputs, u
Outputs, y
States, x
Parameters, p
System (S)
u y
x
y = S[u, x, p, t] (dynamic)
y = S[u, x, p] (steady-state)
A process system can be simply a process unit (e.g., reactor, distillation).
It can also be a chemical plant represented by a process flowsheet.
p
Ph.D. Xiang Zhang](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1introductiontoprocessmodeling-221126231845-1cddc183/75/Lecture-1_Introduction-to-Process-Modeling-pdf-8-2048.jpg)