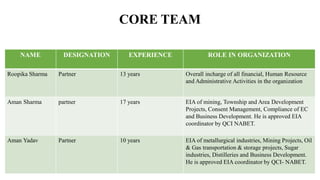
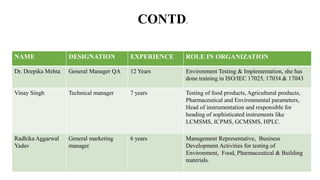
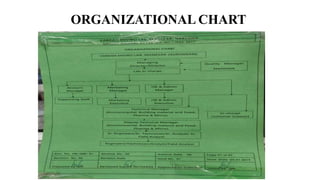
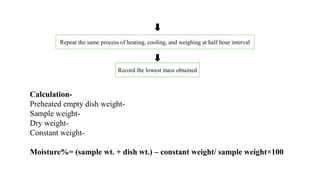
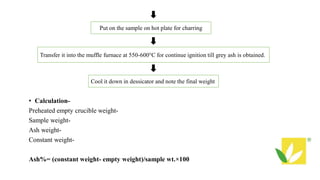
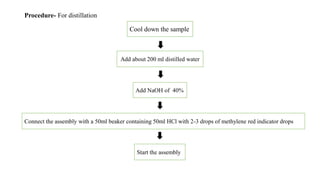
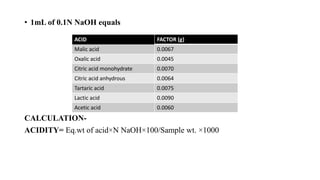
The document provides details about an internship completed by Aafreen Salim at the Food Analysis Laboratory of Vardan Envirolab from February 20th to May 20th, 2023. It includes an acknowledgment, introduction to the laboratory, details of the management team and various departments. Standard operating procedures for proximate analysis methods like moisture, ash, protein, fat, carbohydrate, energy and dietary fiber determination are also outlined.