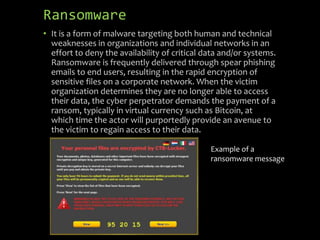
Internet fraud can take many forms, including business email compromise, data breaches, denial of service attacks, malware, and phishing/vishing. These schemes steal millions from victims each year. Business email compromise involves hacking legitimate business emails to conduct unauthorized funds transfers, while data breaches involve leaking sensitive data from secure locations. Phishing uses fraudulent emails or phone calls to steal personal information, and ransomware encrypts files until victims pay a ransom. To prevent fraud, users should keep software updated, be wary of sharing information, verify website legitimacy, use strong passwords, and back up files regularly.