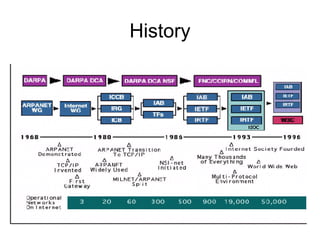
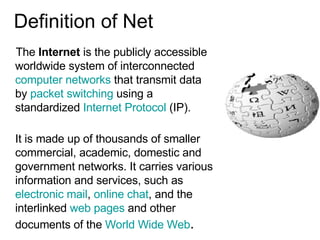
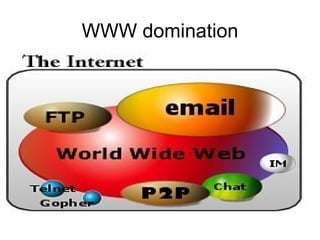
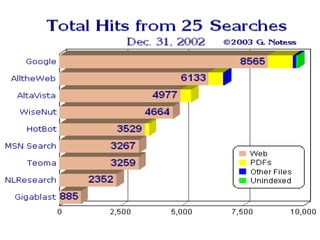
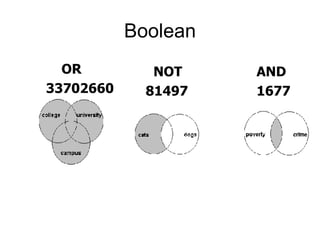
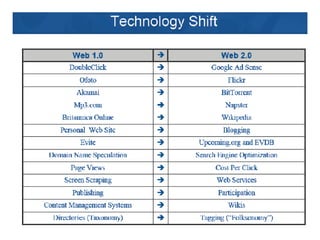
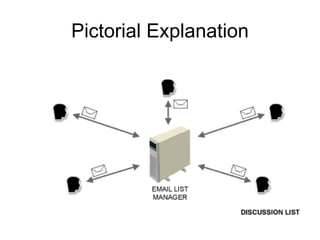
This document provides an overview of internet search strategies, including the history and definition of key concepts like the internet, web browsers, search engines, directories, blogs, multimedia tools, and more. It also briefly discusses issues around internet politics such as viruses, freedom of speech, pornography, and copyright.