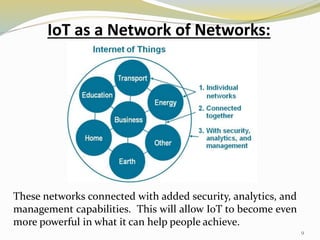
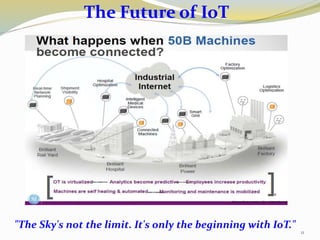
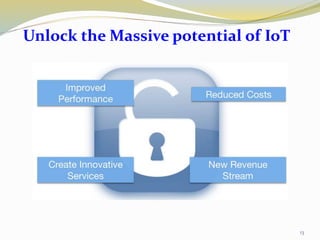
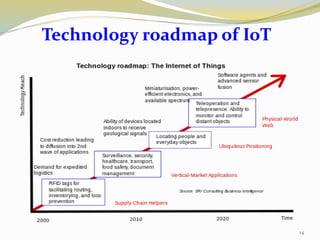
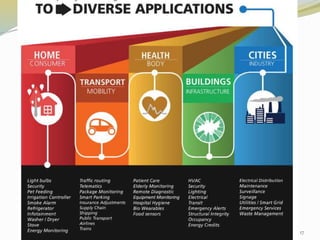
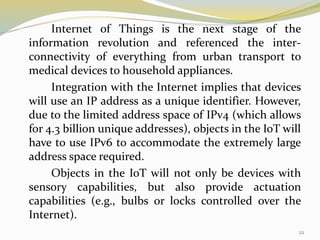
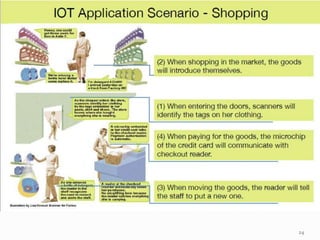
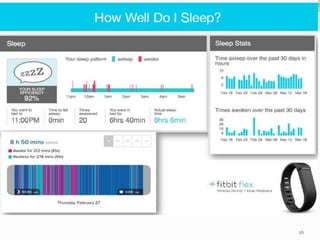
The document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT), including its definition, history, how it works, current status and future prospects. It discusses key enabling technologies like RFID, sensors and nanotechnology. It also outlines the structure of IoT as a network of networks. The document then highlights several applications of IoT and technological challenges. Finally, it notes some criticisms around privacy, security, autonomy and environmental impacts of large-scale IoT adoption.