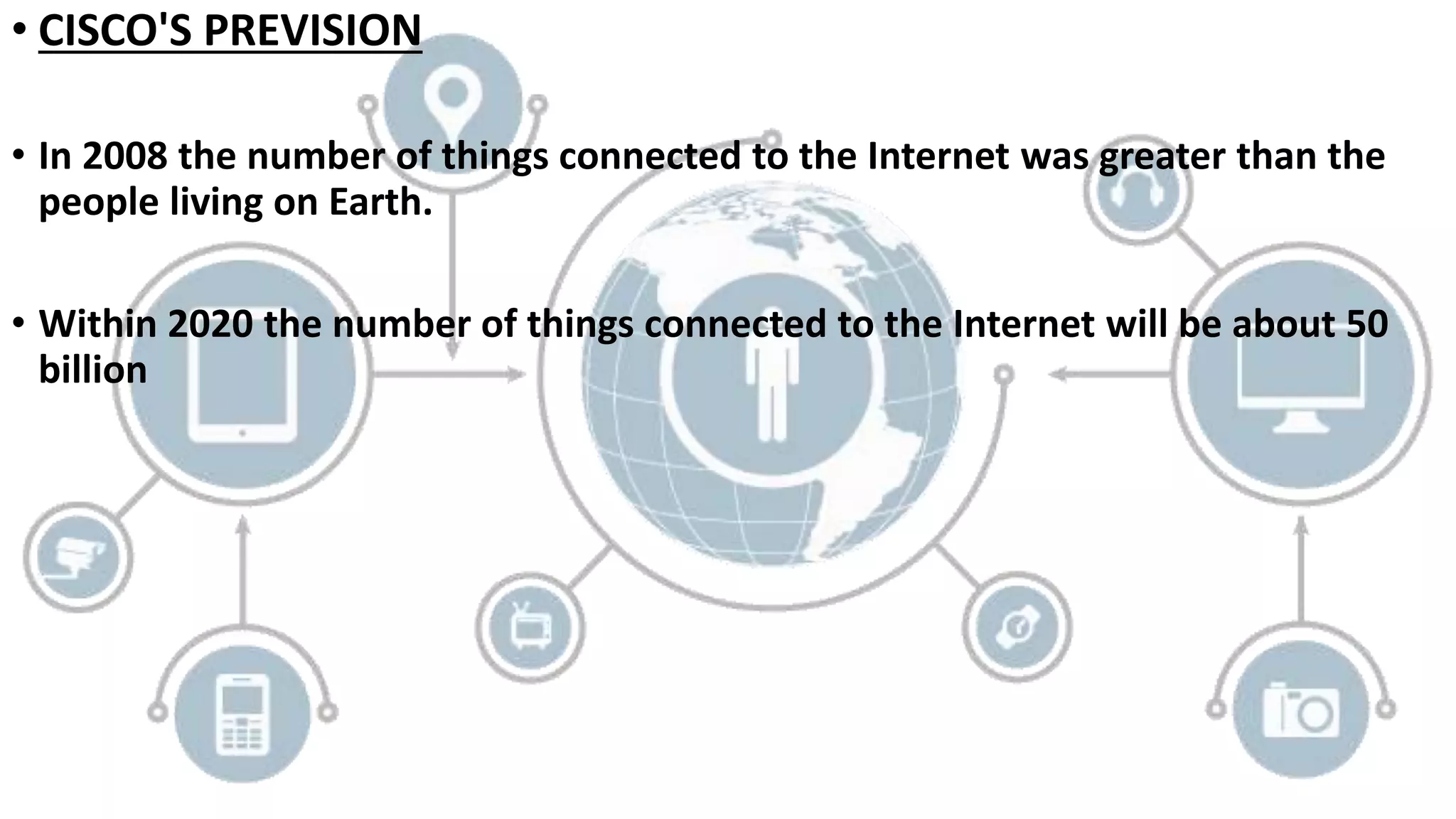
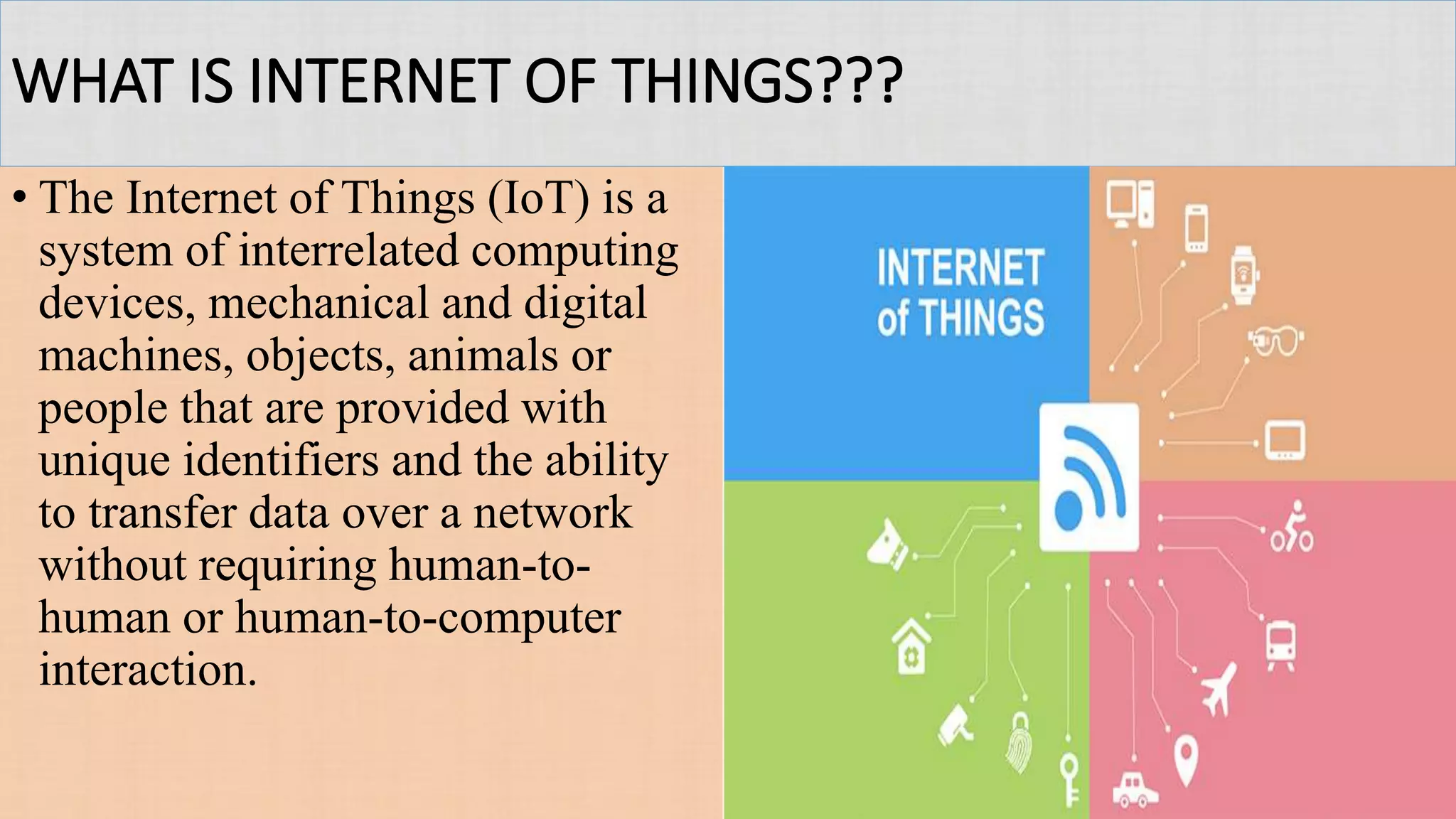
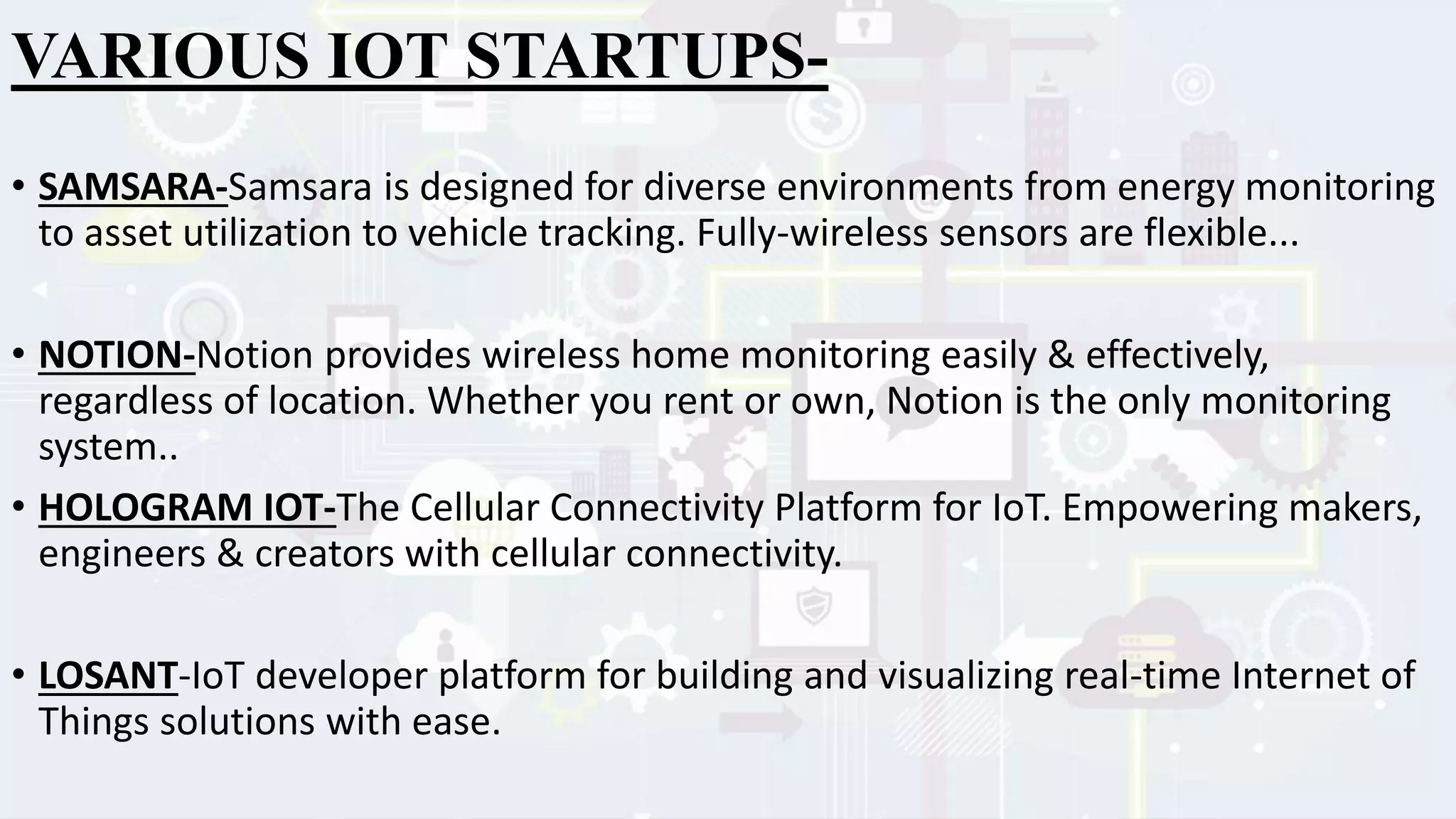
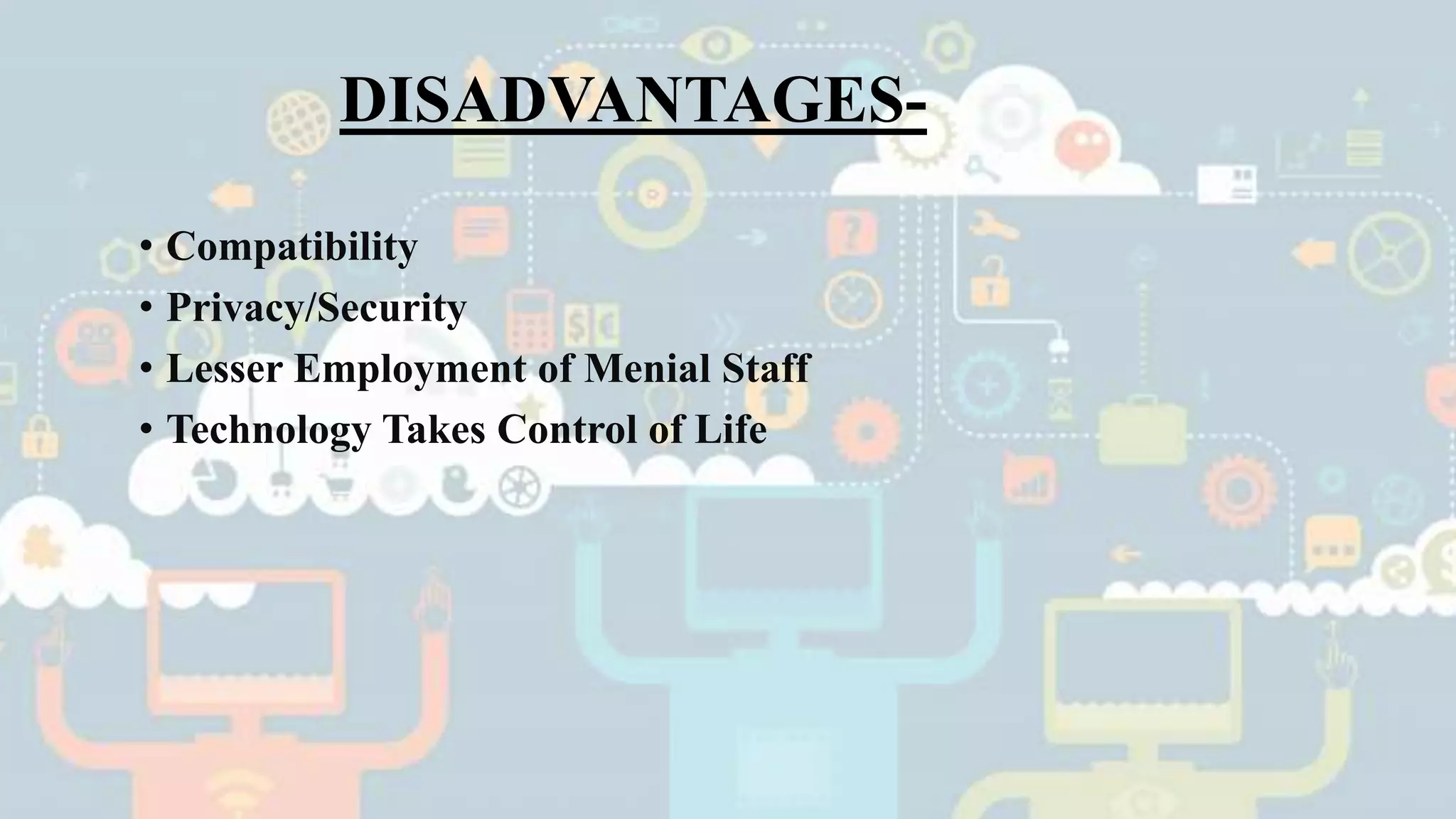
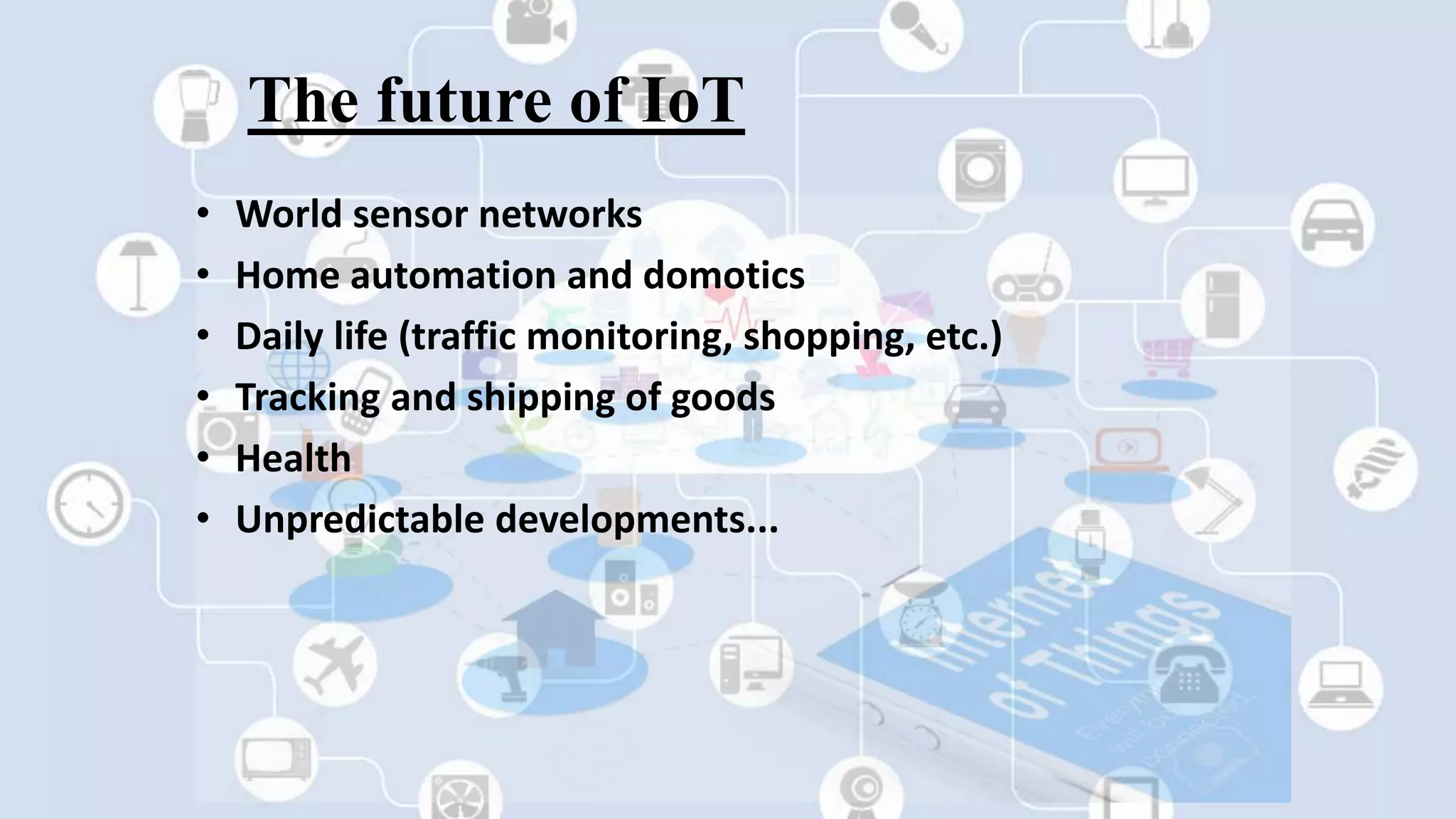
This presentation provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT). It defines IoT as interconnected computing devices, objects, animals or people that are provided with identifiers to transfer data over a network. The presentation outlines key features of IoT like intelligence, connectivity, sensing, expressing, energy and safety. It discusses technologies enabling IoT such as RFID, WiFi, barcodes, ZigBee and sensors. Examples of IoT applications mentioned include environmental monitoring, infrastructure management, industrial uses, energy management, healthcare, home automation and transport. Advantages include improved communication, automation, monitoring and efficiency while disadvantages include compatibility, privacy and security issues. The future of IoT is predicted to include world sensor networks, home