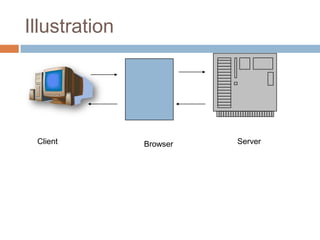
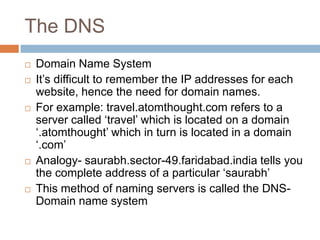
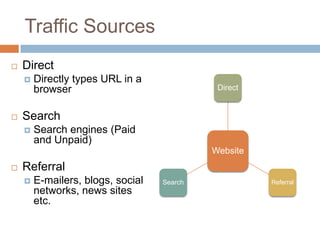
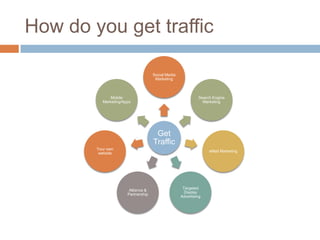
The document discusses how the internet, domain names, and the world wide web work. It explains that web pages are stored on web servers connected to the internet. These servers are identified by unique IP addresses but are easier for humans to access using domain names. The Domain Name System (DNS) converts domain names into the corresponding IP addresses so browsers can locate the correct server. Traffic to a website comes from people directly typing the URL, links from search engines, referrals from other sites, and other online marketing activities.