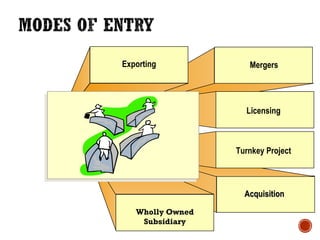
The document discusses international marketing, defining it as business activities that involve the flow of goods and services across nations for profit. It also covers international trade, international business, foreign marketing, and outlines both internal and external environments that affect international operations, including economic, political, legal, cultural, demographic, and technological factors. Additionally, it touches on the roles and functions of international organizations such as the World Bank and the World Trade Organization in promoting trade and economic cooperation among nations.