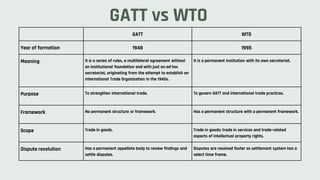
The document discusses key concepts in international business including GATT, WTO, LPG model, MNCs, FDI and challenges faced. GATT was formed after WWII to regulate trade and was transformed into the WTO in 1995. The LPG model introduced in 1991 aimed to liberalize, privatize and globalize the Indian economy. MNCs can benefit countries through technology transfer but also present risks. FDI is an important form of investment that supports economic growth. International businesses face challenges from uncertainties, complex regulations and rapidly changing technology and supply chains.