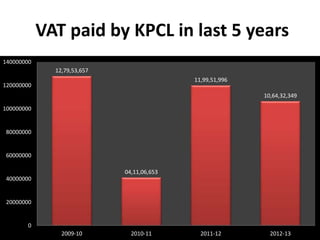
This document summarizes a summer internship project on documenting and understanding the procedures and documentation of sales tax (MVAT) in Kirloskar Pneumatic Company Limited (KPCL). The project involved studying MVAT acts, rules and regulations in Maharashtra and comparing them to procedures followed at KPCL. The intern observed invoice generation, reviewed software and forms used, and analyzed VAT paid over the last 5 years. The intern found KPCL to be compliant with MVAT requirements and did not have any recommendations, noting the topic revolves around government laws and regulations.