This PowerPoint presentation provides a comprehensive, evidence-based overview of Interferential Therapy (IFT) as part of Electrotherapy for BPT 2nd-year physiotherapy students.
Key topics covered include:
Principles of Interferential Therapy
Production of Interference Current
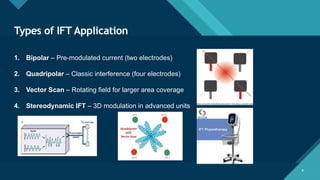
Types of IFT (2-pole and 4-pole)
Physiological effects and therapeutic benefits
Clinical indications and contraindications
Electrode placement techniques
Dosage parameters and treatment protocols
Recent advances and research evidence
This presentation is ideal for physiotherapy students and educators looking to understand the fundamentals and clinical applications of IFT in rehabilitation practice.