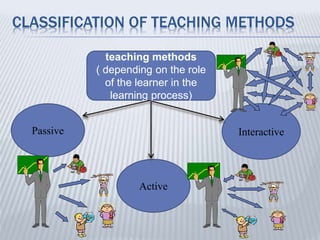
1. The document discusses different teaching methods, including passive, active, and interactive methods.
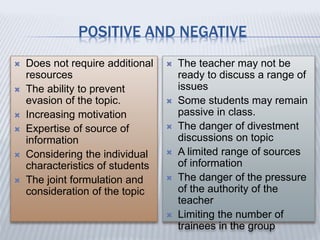
2. Passive methods involve one-way transmission of information from teacher to student through lectures and readings. Active methods engage students through questions and creative tasks.
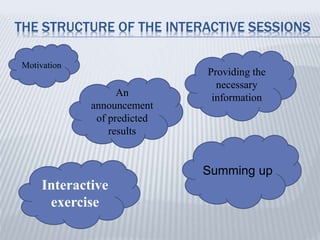
3. Interactive methods are based on cooperation between students and teacher. Learning occurs through interaction and small group discussions, with the teacher taking more of a facilitating role.