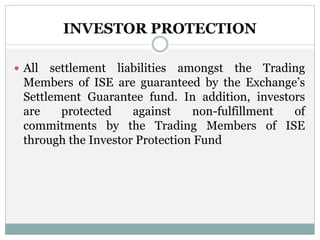
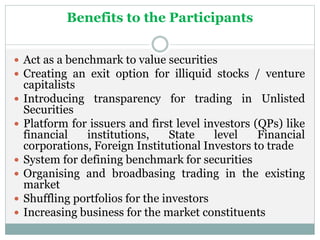
Inter-connected Stock Exchange (ISE) is a national stock exchange established in 1998 that provides trading, clearing, settlement and other services to over 800 members located across 18 cities. Its objectives include creating a single integrated market, providing access to multiple markets at low cost nationwide, and facilitating trading for small members. ISE has regional offices across major cities and provides depository services through partnerships with CDSL and NSDL.