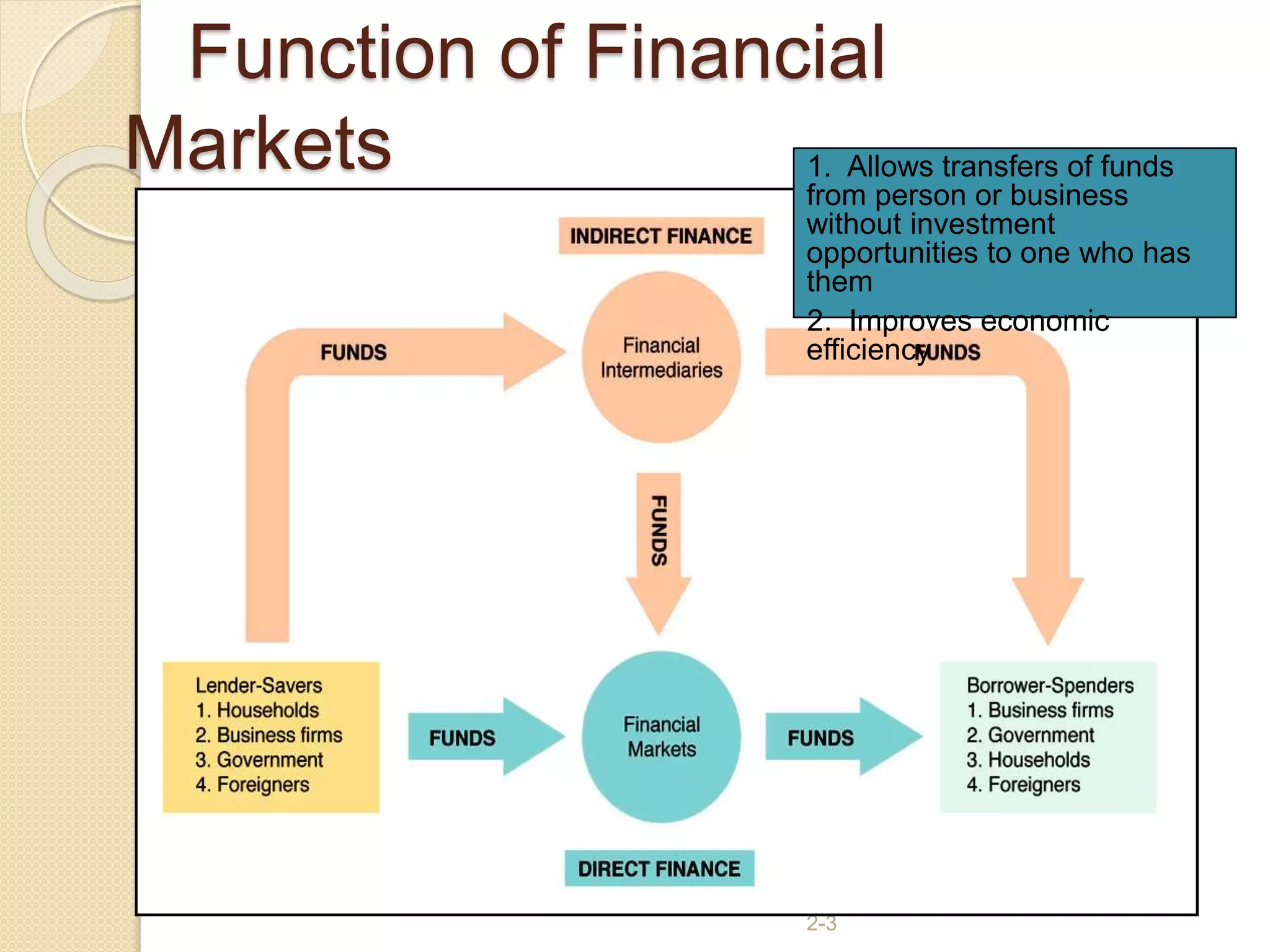
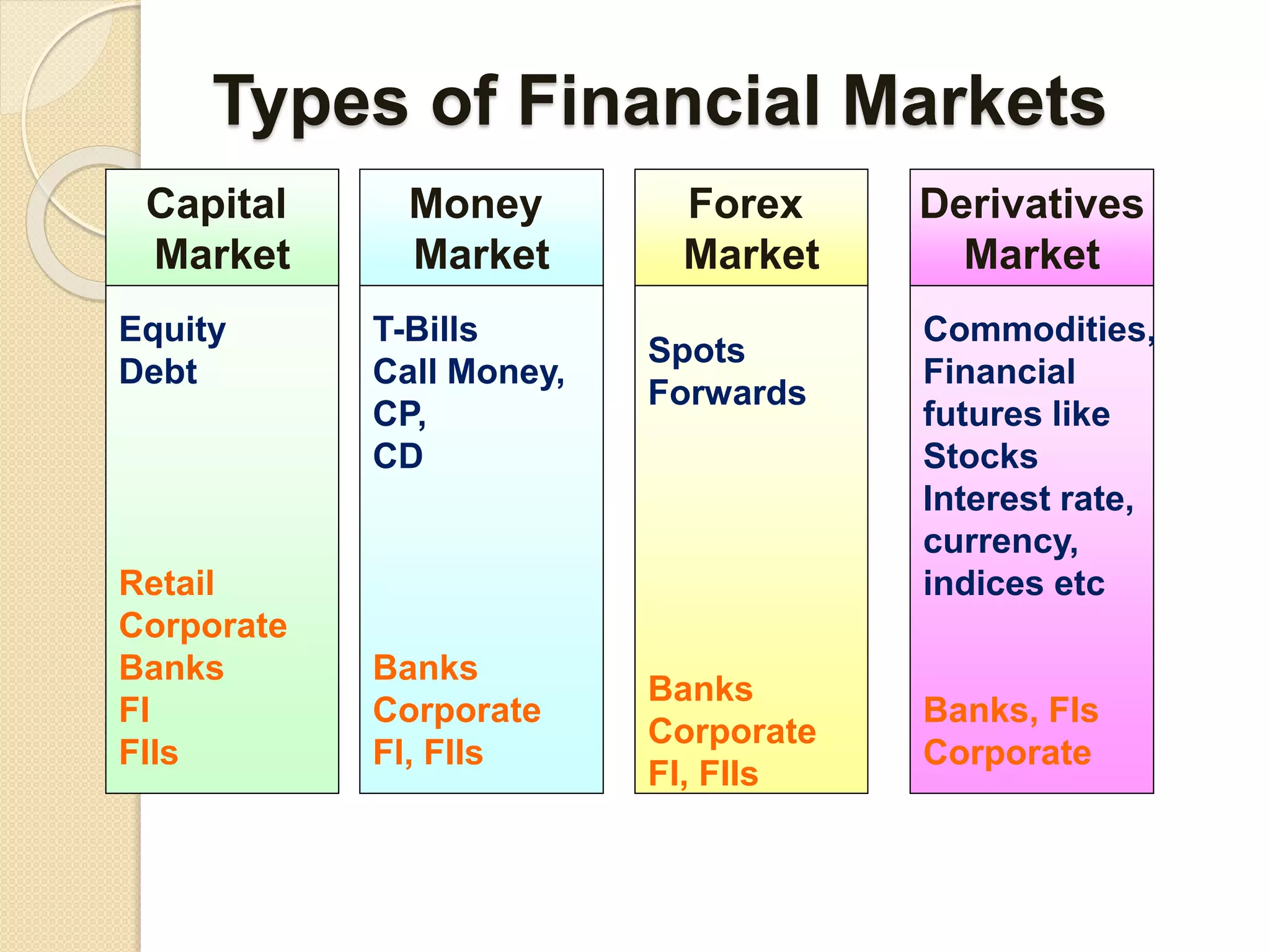
Financial markets allow funds to flow between those with a surplus and those with a deficit. They improve economic efficiency by connecting individuals and organizations wanting to borrow funds with those having funds available. There are several types of financial markets including capital markets, money markets, foreign exchange markets, and derivatives markets. These markets are regulated by different entities like RBI, SEBI, IRDA, and FMC. The capital market consists of the primary market for new share/bond issues and the secondary market for subsequent trading of existing securities.