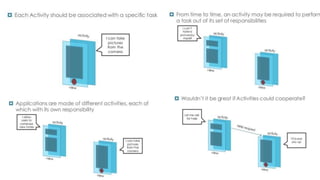
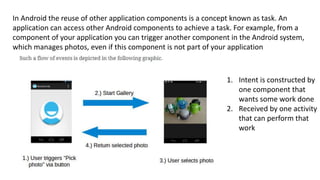
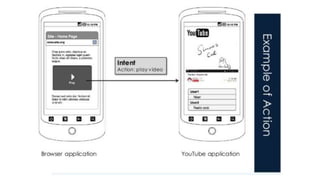
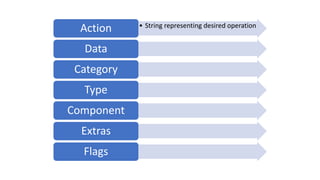
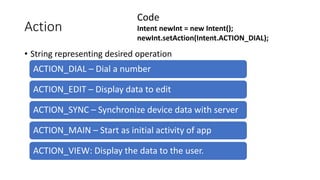
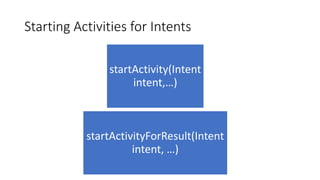
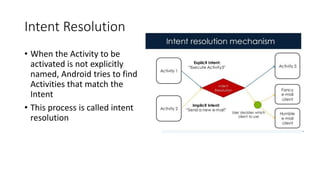
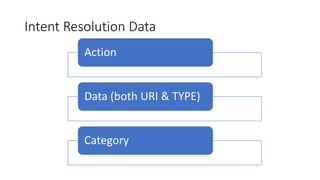
The document discusses intents in Android and how they allow communication between application components. Intents are objects that specify operations or events and contain action, data, category and other metadata. They allow activities to start other activities both within and between apps to perform tasks like taking a photo, making a call, or opening maps. When an activity starts another activity via an intent without specifying the component, Android performs intent resolution to match the intent to a capable activity based on intent filters.