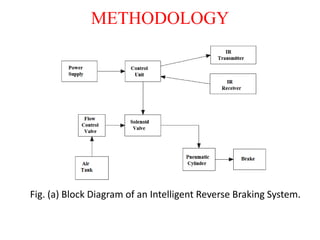
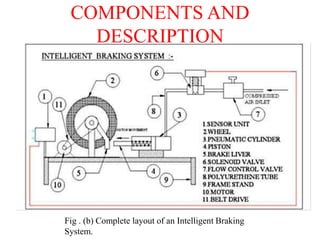
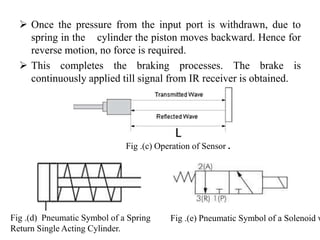
The document outlines a technical paper presentation on an intelligent reverse braking system designed for vehicles, highlighting its automated function triggered by ultrasonic sensors to prevent accidents. It includes a literature survey, methodology, and components involved, while discussing advantages such as improved safety and limitations including the need for maintenance. The conclusion emphasizes the future scope of enhancing vehicle safety through intelligent braking technologies.