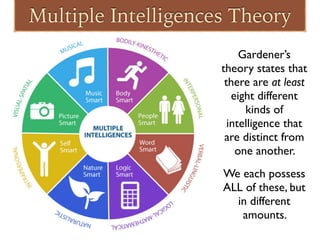
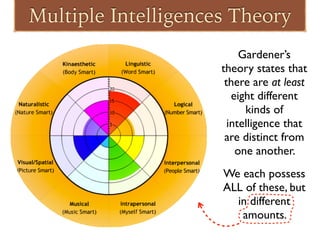
The document discusses different theories of intelligence, beginning with defining intelligence as the capacity to understand the world, think rationally, and effectively problem solve when faced with challenges. It describes crystallized intelligence involving acquired knowledge and fluid intelligence involving reasoning without prior knowledge. Gardner's Theory of Multiple Intelligences proposes there are at least eight types of intelligence: logical/mathematical, linguistic, musical, visual-spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, naturalist, interpersonal, and intrapersonal. The document provides examples of skills and abilities associated with each type of intelligence.