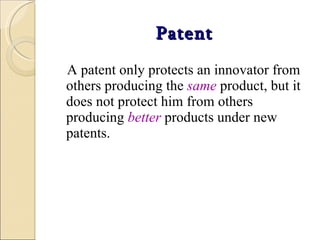
Intellectual property refers to creative works and inventions. It is divided into industrial property like patents, trademarks, and designs, and copyright for original creative works. While copyright makes it difficult to control sharing on the internet, patents give owners rights to prevent others from making or selling an invention without permission. Domain names can function as trademarks when they meet certain criteria, and "cybersquatting" aims to profit from a brand's goodwill. Protecting intellectual property creates competitive advantages and value through marketing, branding, sales, and licensing, but some argue it can also harm public interests.