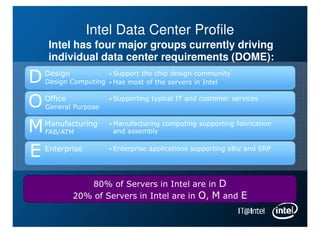
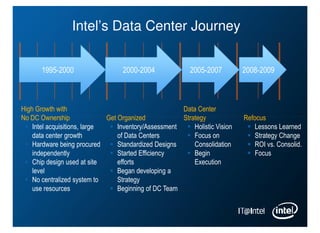
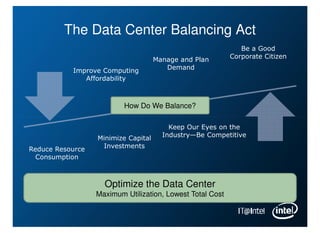
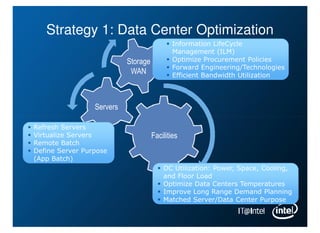
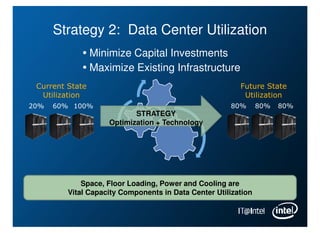
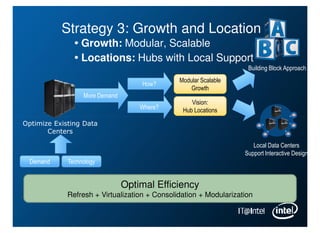
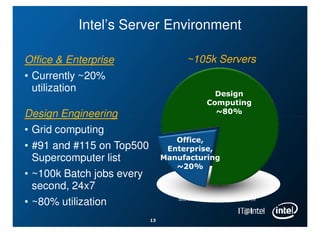
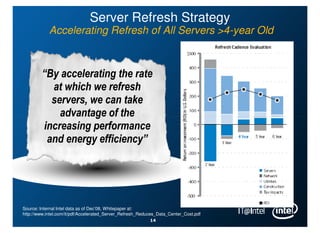
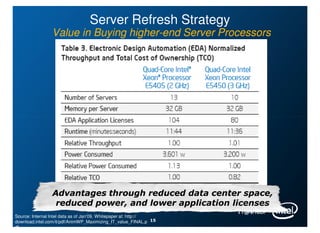
Intel is managing its large information technology infrastructure through the economic downturn by focusing on data center optimization and efficiencies. Key strategies include standardizing server designs, improving utilization through virtualization and server refresh, and optimizing data center locations. This allows Intel to reduce costs while continuing to support business operations and productivity.