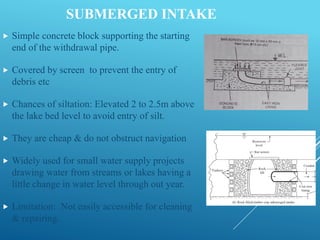
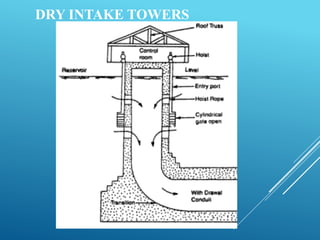
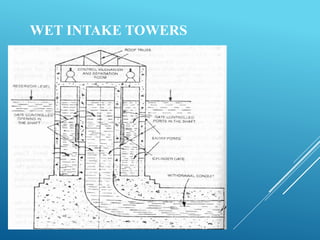
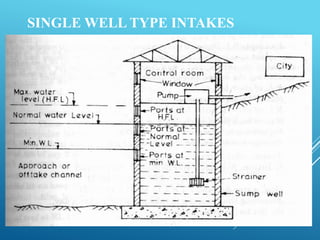
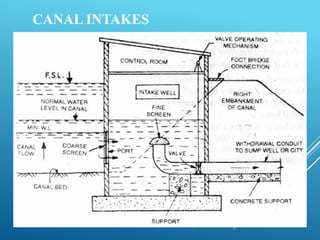
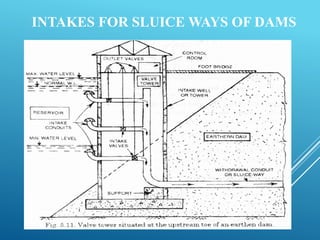
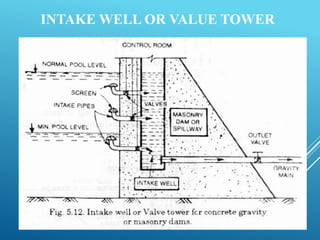
An intake structure withdraws water from its source and discharges it into a withdrawal conduit to transport it to a water treatment plant. It is constructed at the entrance of the withdrawal pipe to protect it from debris. Intake structures can directly transmit water via gravity flow from reservoirs or use pumps to lift water if gravity flow is not possible. The location of an intake structure is important and must consider factors like proximity to the treatment plant and source water quality. Common intake structures include submerged intakes, intake towers for large sources, and various designs for rivers and canals.