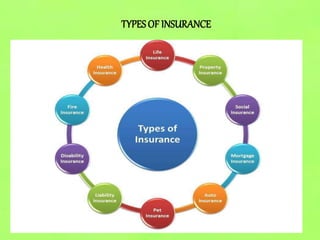
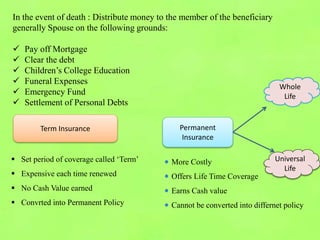
The document outlines the history and evolution of insurance, detailing its origins from ancient societies to modern regulations in India. It covers various types of insurance, including life, fire, and rural insurance, and explains essential concepts such as risk, premium, and the claims process. Additionally, it highlights eligibility criteria and benefits associated with rural insurance, aiming to financially protect rural communities engaged in agriculture and related activities.