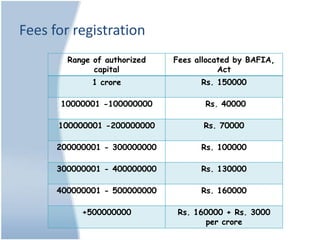
The document discusses the process of registering banks and financial institutions in Nepal according to the Bank and Financial Institutions Act (BAFIA) 2063. It involves getting approval from the Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB), incorporating and registering the company with the Company Registrar's Office, and obtaining an operating license from NRB. Fees for registration depend on the company's registered capital and range from Rs. 150000 to Rs. 160000 + Rs. 3000 per crore. Challenges include excessive bureaucracy, lack of proper documents, and a time-consuming process. The document also summarizes the registration process for insurance companies according to the Insurance Act 2049 and discusses some major insurance companies in Nepal like Prime