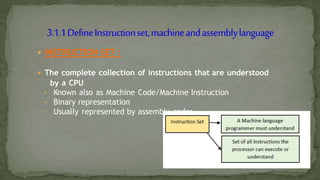
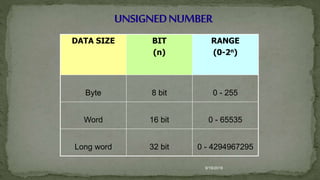
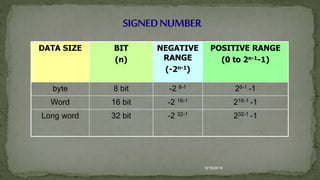
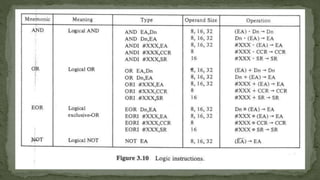
This document defines machine language, assembly language, and instruction sets. It discusses that machine language is binary code understood by the CPU and consists of instructions and operands. Assembly language uses mnemonics to represent machine code instructions. It is translated into machine language by an assembler. The document also categorizes instruction types into data transfer, arithmetic, and logical groups and provides examples of instructions from each group like MOVE, ADD, AND.

























![MNEMONIC AND.B #$3E, D3
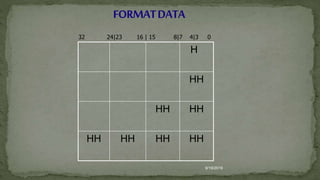
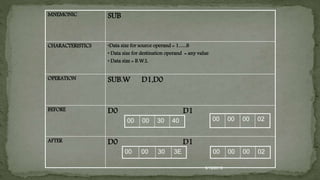
CHARACTERISTICS
[D3(B) AND $3E D3 (B) ]
(8 bit data in D3 ‘AND’ with 8 bit data and the output in
D3)
OPERATION
BEFORE D3
AFTER D3
9/19/2019
74 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0
AND 3E 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0
34 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0
12345674
12343634](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-190919120554/85/Instruction-Set-and-Assembly-Language-Programming-33-320.jpg)
![MNEMONIC OR.B D0, D1
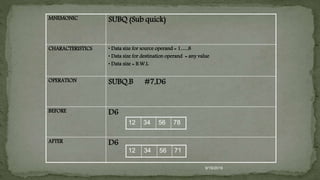
CHARACTERISTICS [D1 (B) or D0 (B) D1(B) ]
(8 bit data in D1 ‘OR’ with 8 bit data in D0, and the output in D1)
OPERATION
BEFORE D0 D1
AFTER D0 D1
9/19/2019
3E 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0
OR 74 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0
7E 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
1234563E98765474
1234367E98765474](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-190919120554/85/Instruction-Set-and-Assembly-Language-Programming-34-320.jpg)
![MNEMONIC NOT.B D1
CHARACTERISTICS
[D1(B) NOT D1 ]
(The content of D1 is NOT, and the
output in D1)
OPERATION AA 1010 1010
55 0101 0101
BEFORE
AFTER
9/19/2019
12345655
123436AA
D1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3-190919120554/85/Instruction-Set-and-Assembly-Language-Programming-35-320.jpg)