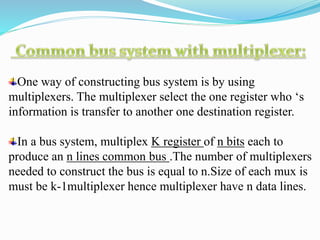
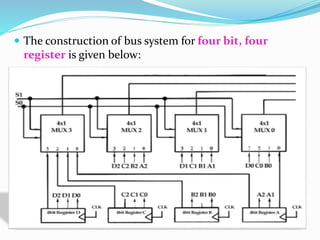
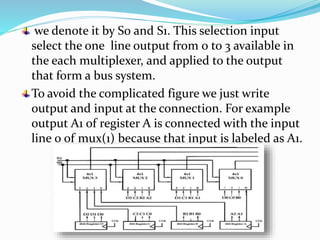
A bus system is an efficient way to transfer data between registers in a computer. It uses a set of common lines that can selectively connect one register at a time to allow its information to be transferred. One way to construct a bus system is by using multiplexers. For example, a 4-bit system with 4 registers would use 4 multiplexers, each with 3 inputs to selectively connect the bits of one register to the common 4-line bus. Control signals on the multiplexer selection lines determine which register is connected to the bus at any given time.