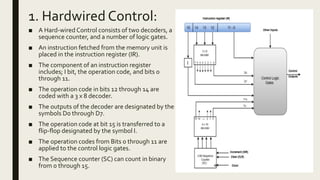
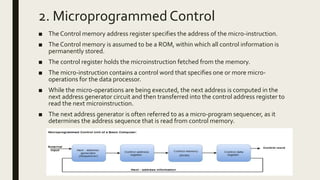
An instruction contains fields that specify the operation to be performed, the location of operands, and how operands will be located. There are three basic instruction formats: memory reference, register reference, and input-output. An instruction set is complete if it includes arithmetic, logical, shift, memory/register movement, program control, status checking, and input/output instructions. The control unit is classified as hardwired or microprogrammed. Hardwired control uses decoders, a sequence counter, and logic gates. Microprogrammed control uses a control memory, control register, and next address generator to sequence through microinstructions that specify operations.