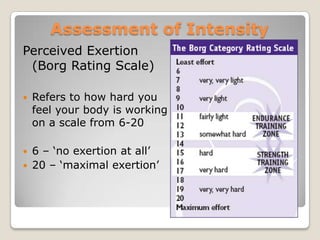
This document discusses various methods for assessing physical activity intensity and monitoring physical activity. It describes tools for measuring intensity levels like the talk test, target heart rate zones, and perceived exertion scales. It also outlines subjective self-report methods and objective tools like heart rate monitors, pedometers, accelerometers, and direct observation systems to quantitatively measure physical activity.