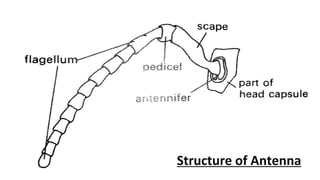
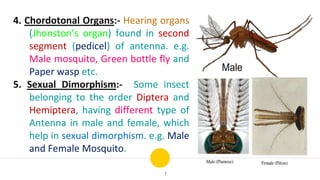
Antennae are paired appendages on the head of insects that serve sensory functions. They are segmented and consist of three parts: the scape, pedicel, and flagellum. Antennae detect smells, tastes, sounds, and help with tasks like finding food and mates. Their structure varies between insect orders and species, with different types including setaceous, filiform, moniliform, and clavate antennae. Antennae have adaptations for their specific habitats and behaviors.