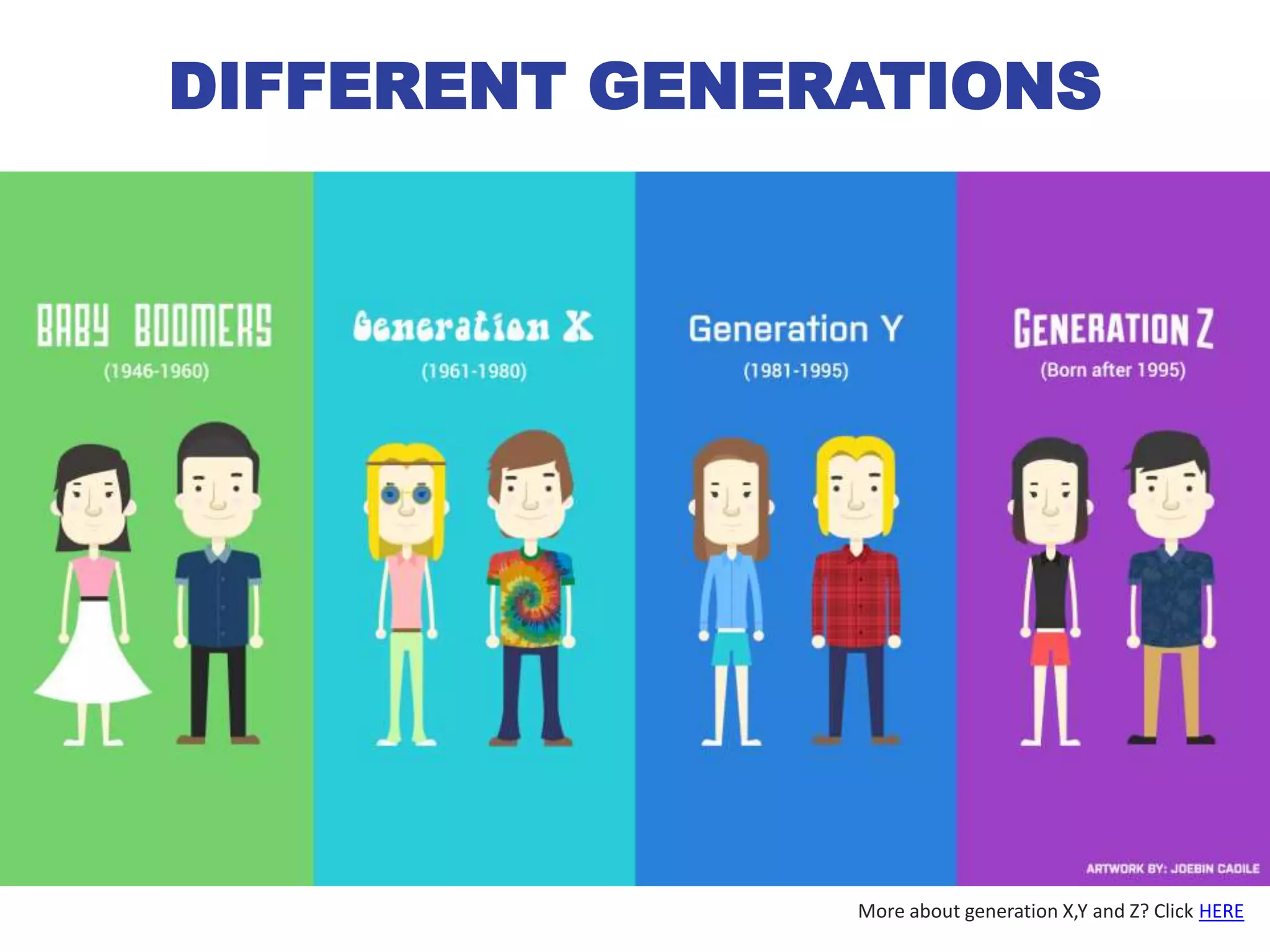
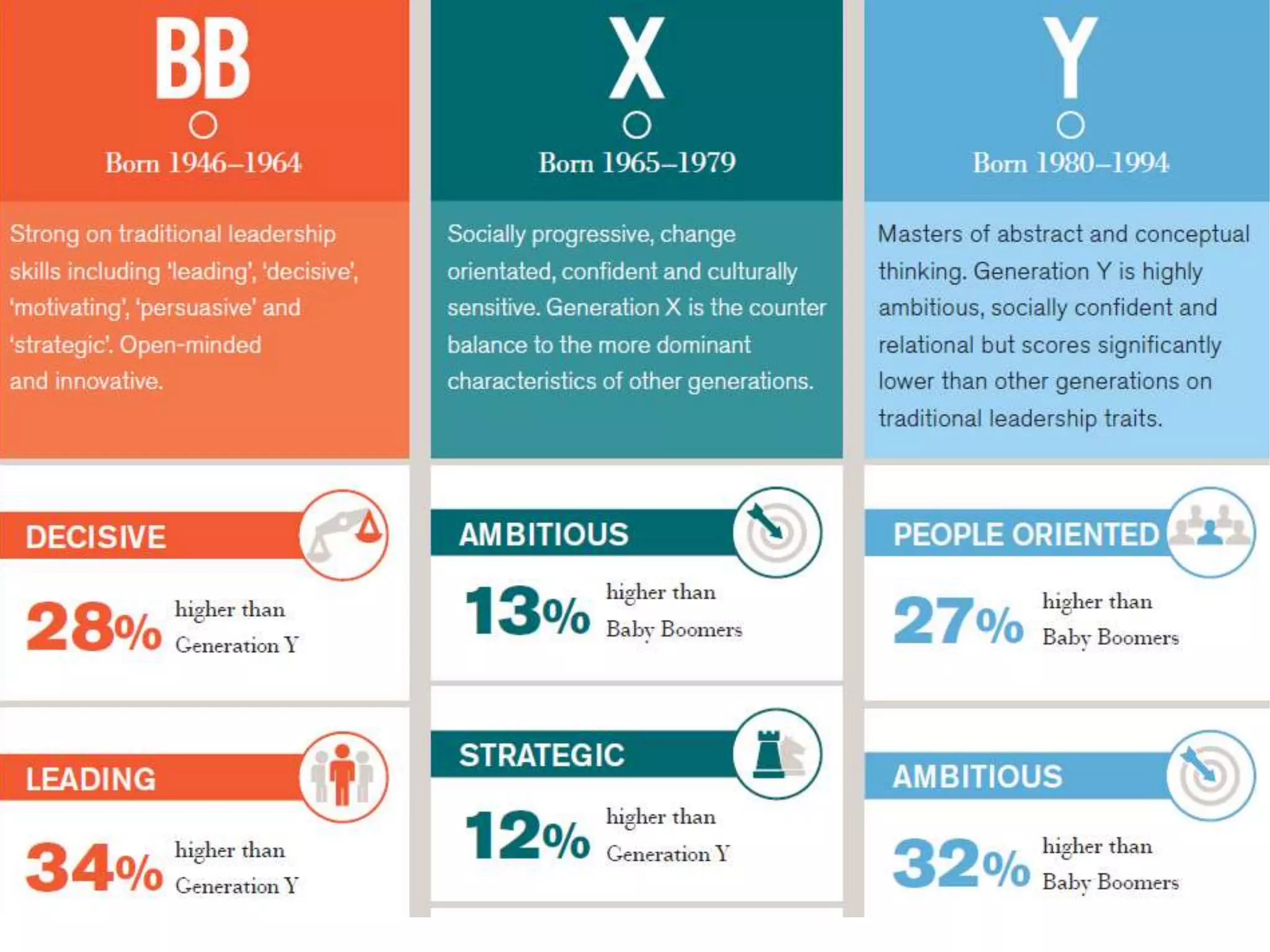
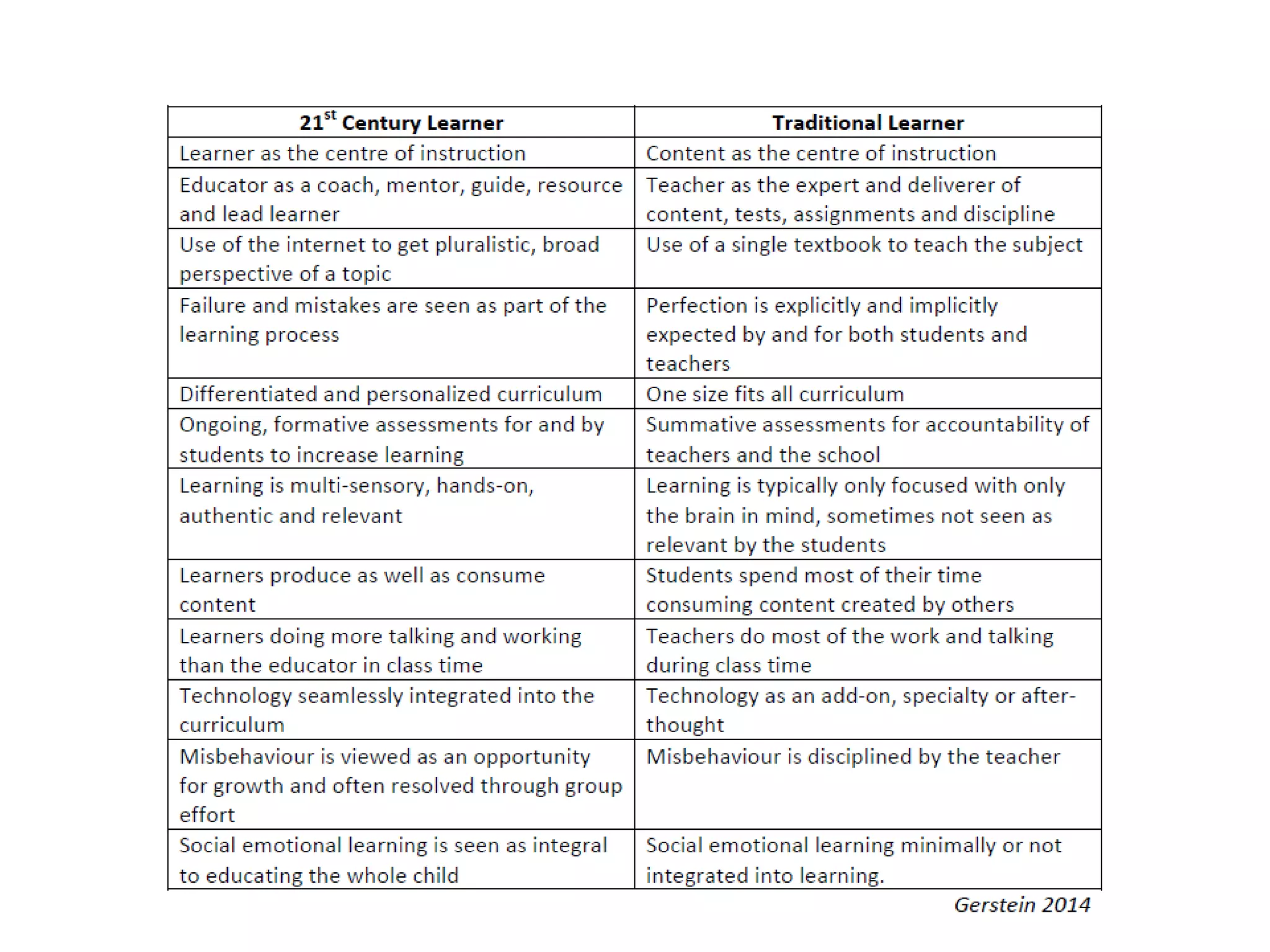
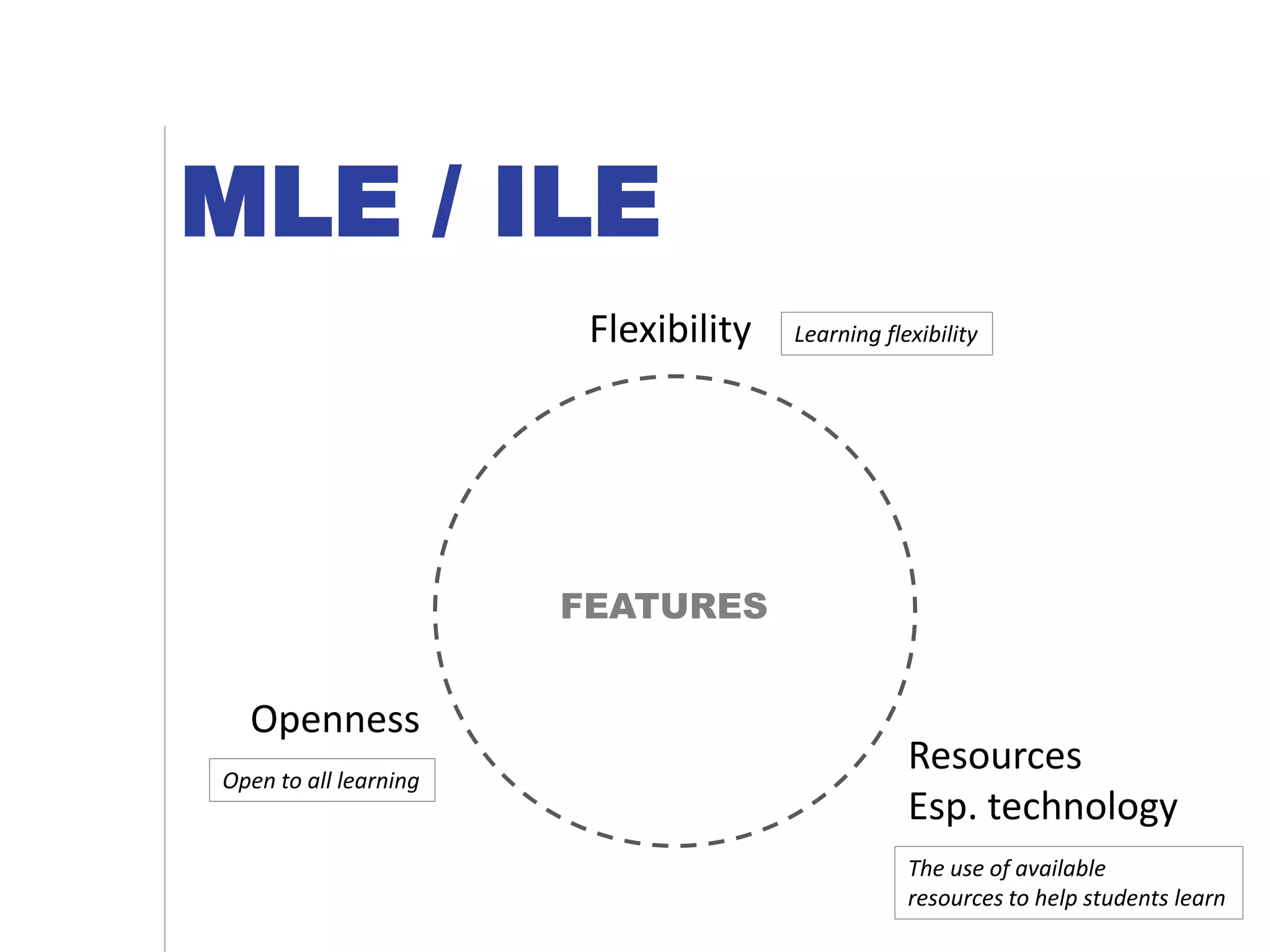
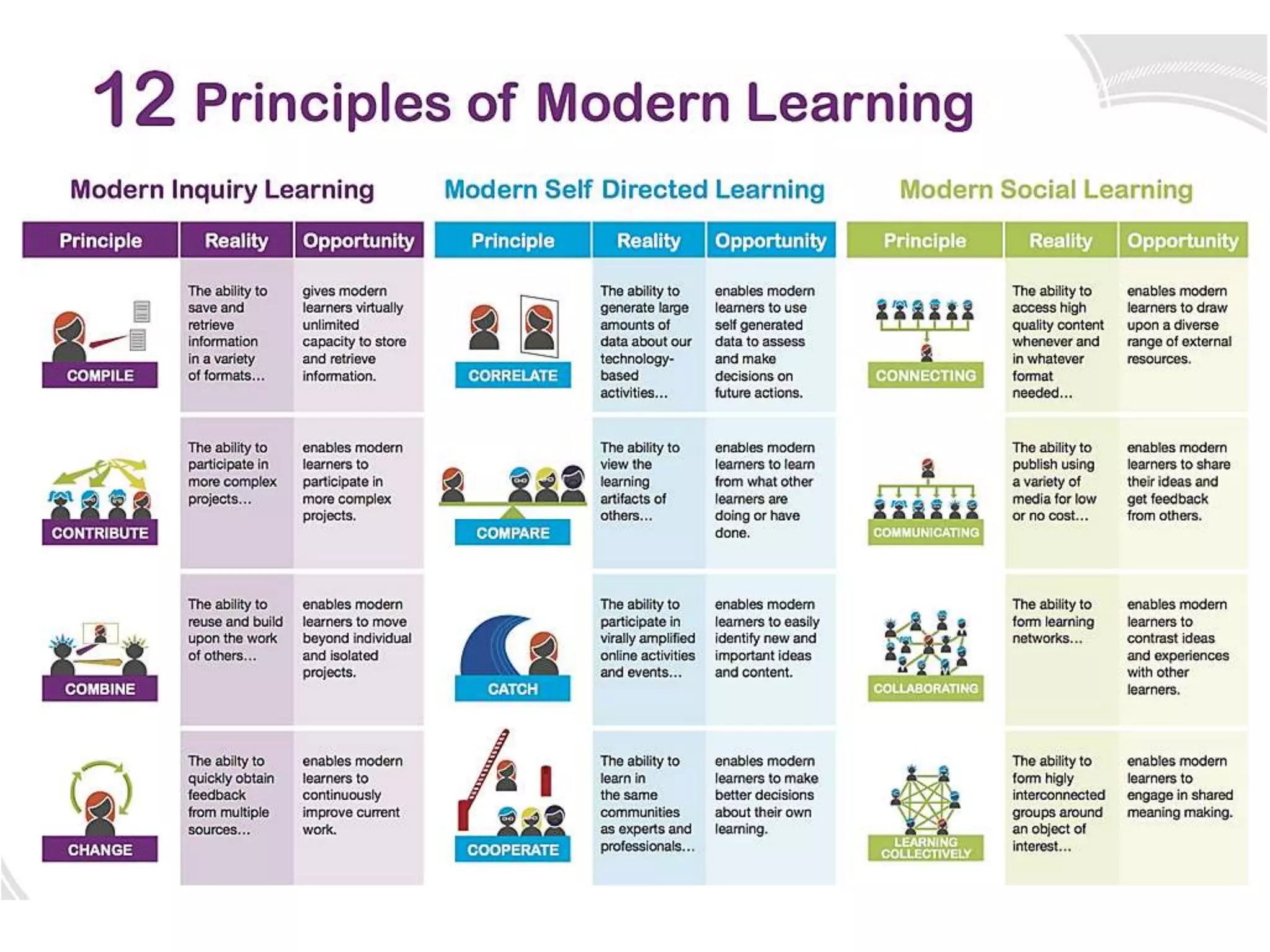
This document discusses innovative learning environments (ILEs) and their impact on teachers' professional identities. It describes how ILEs utilize flexibility, open resources like technology, and focus on learning rather than teaching. This represents a shift for teachers from dispensers of information to orchestrators of learning and helping students develop knowledge and wisdom. For teachers to be relevant in ILEs, the document emphasizes developing digital literacy and personal knowledge management skills. It questions whether teachers need to become more relevant guides or risk being replaced by technology like Google and YouTube.