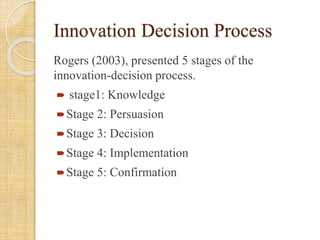
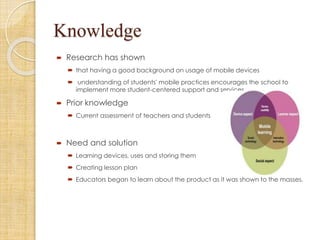
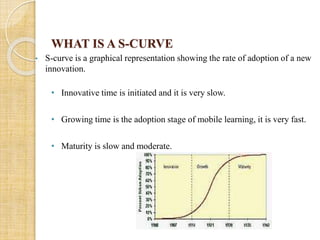
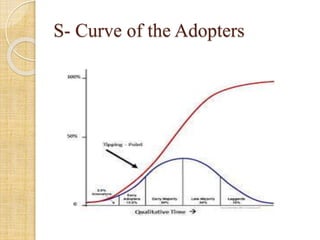
This document discusses mobile learning and its implementation in education. It defines mobile learning as using interactive technology to support teaching and learning. It lists different mobile technologies that can be used, such as tablets, smartphones, laptops, and interactive whiteboards. It also discusses some educational applications that can be used on mobile devices. The document then discusses the need for mobile learning to improve students' academic performance and engagement. It reviews several research studies on effective uses of mobile technology in education. Finally, it discusses some challenges in developing mobile learning and ensuring its adoption through teacher training and support.