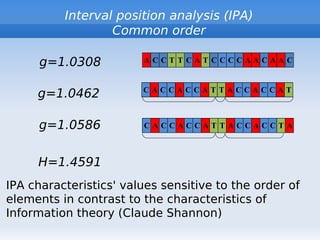
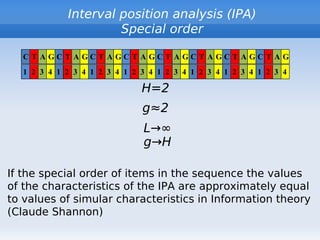
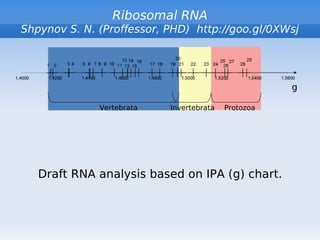
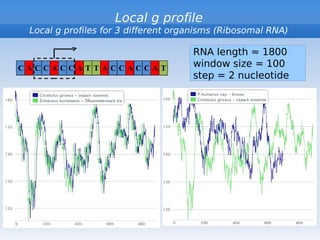
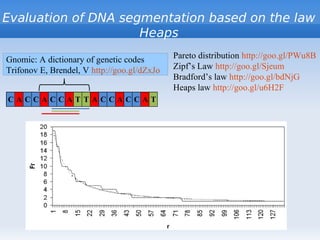
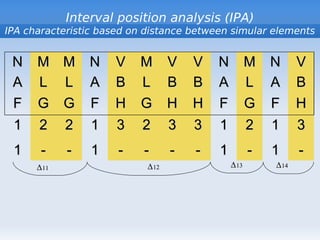
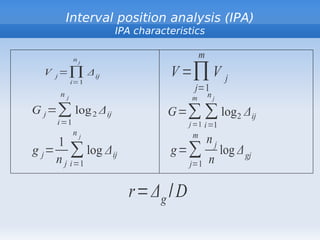
The document discusses interval position analysis (IPA), a method for analyzing DNA and RNA sequences. IPA calculates characteristics such as V, G, and g values based on the distances between similar elements in a sequence. The values of IPA characteristics are sensitive to the order of elements in a sequence. IPA can be used to construct phylogenetic trees and analyze local profiles of RNA sequences. Heap's law and rank distribution models are also discussed in relation to evaluating DNA segmentation.