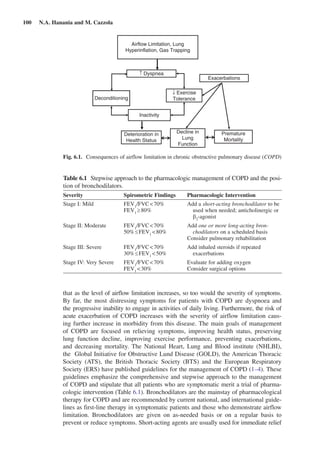
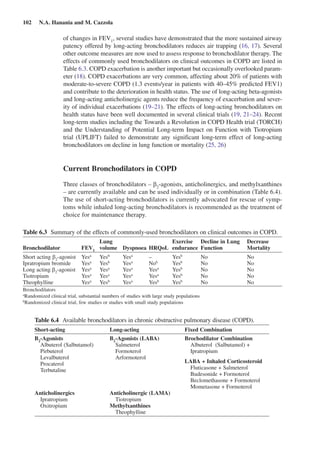
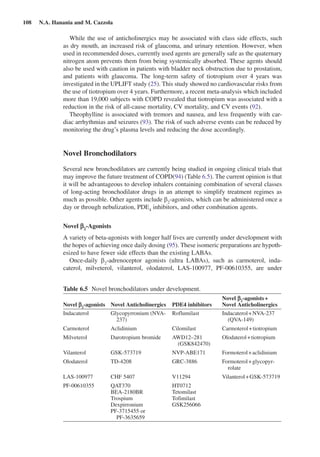
This document discusses bronchodilators and their role in treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It notes that bronchodilators are the mainstay of pharmacological COPD therapy and can improve symptoms, exercise tolerance, and reduce exacerbations. Both short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators are used, with short-acting for rescue of symptoms and long-acting as maintenance therapy. Common classes of bronchodilators include beta-agonists, anticholinergics, and methylxanthines. Combining different classes of bronchodilators can provide better efficacy than increasing the dose of a single agent.