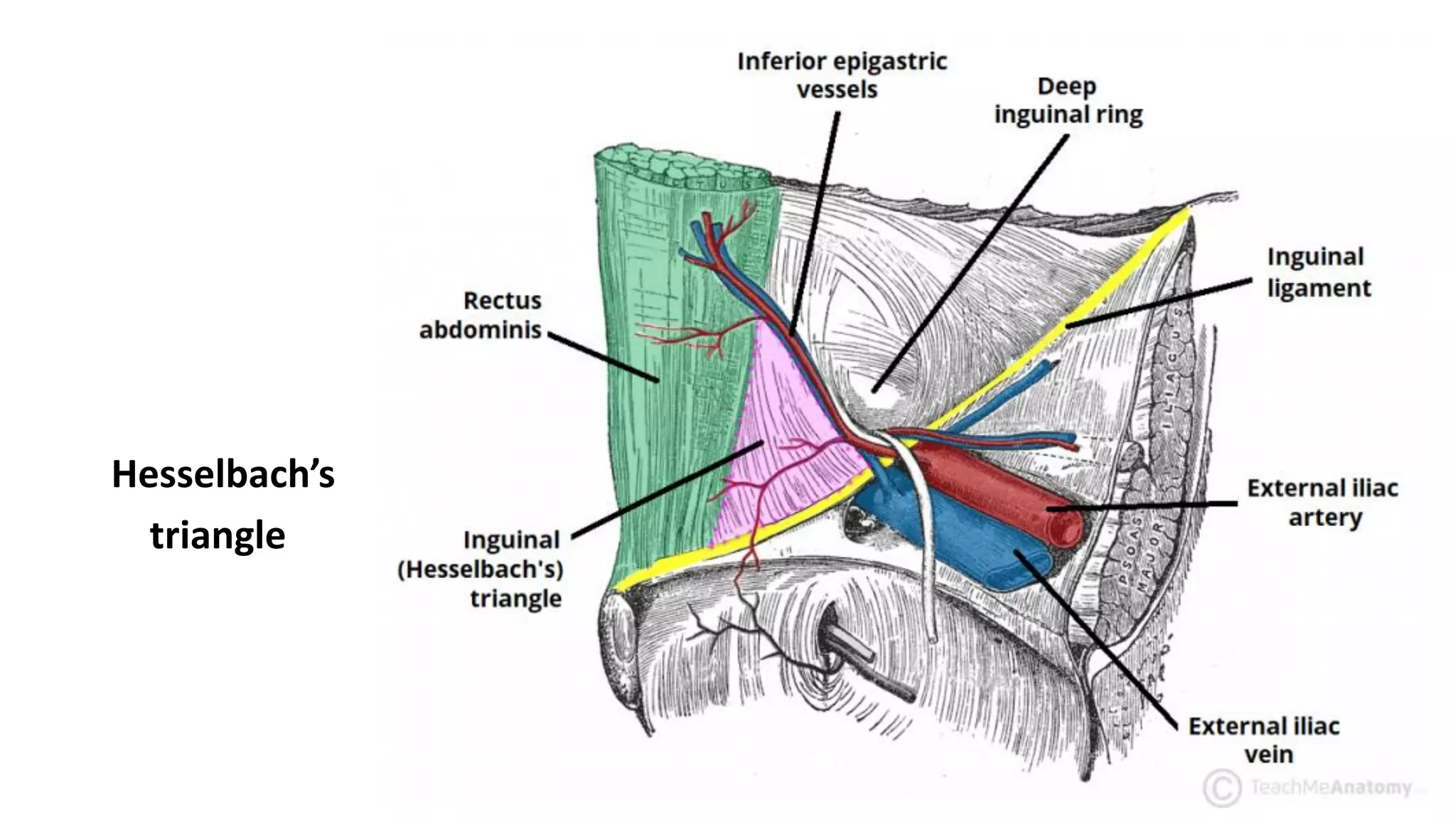
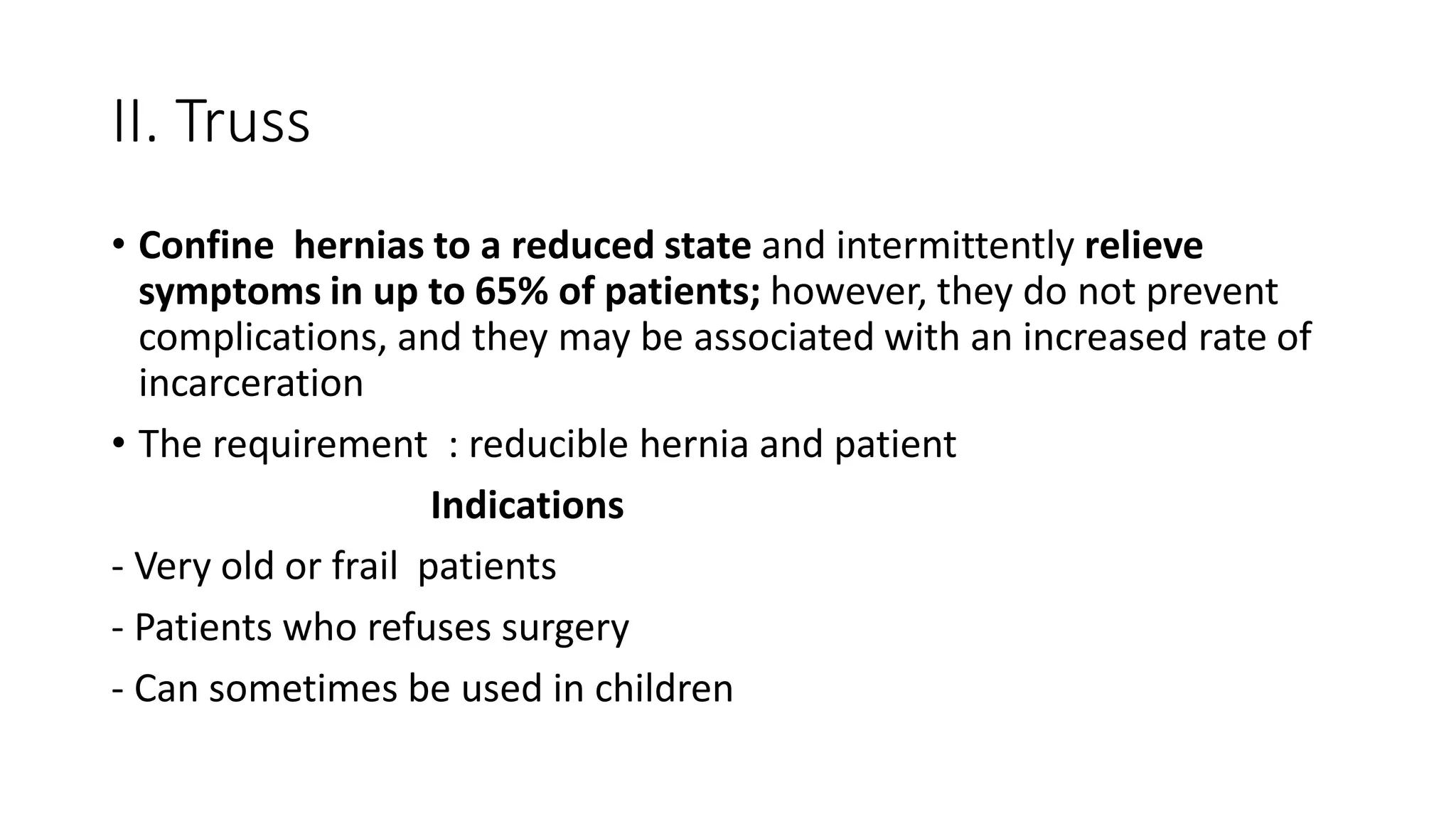
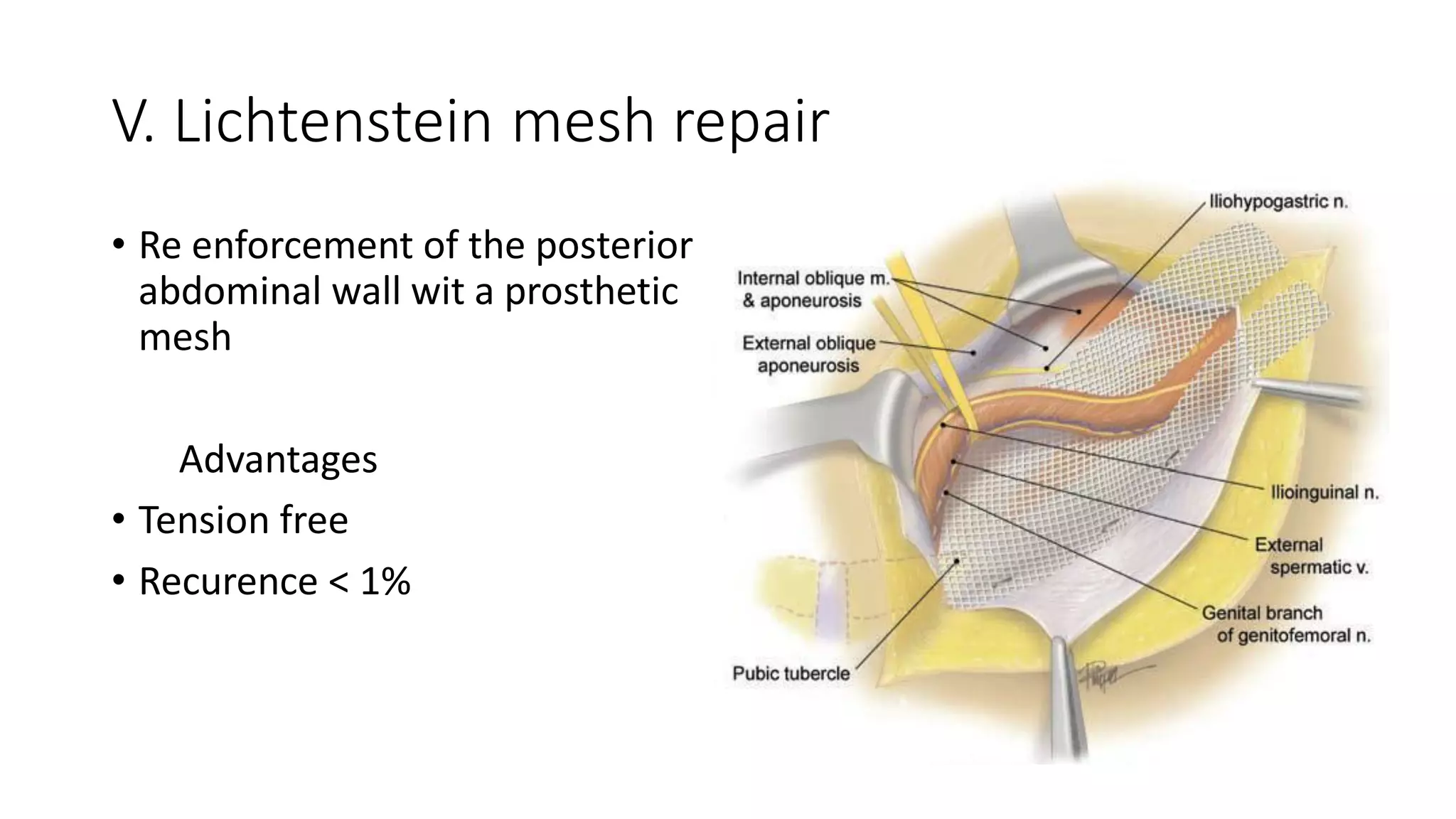
The document provides a comprehensive overview of inguinal hernias, including their anatomy, prevalence, causes, classifications, diagnosis, and treatment options. It highlights that inguinal hernias are more common in men, with various types classified by etiology and anatomy, and discusses both non-surgical and surgical management strategies. The document also addresses diagnostic imaging techniques and specific surgical approaches to hernia repair.